A brief introduction to the use of react redux middleware
This article mainly introduces the use of redux middleware. Now I will share it with you and give you a reference.
Students who have used react all know the existence of redux. Redux is a front-end warehouse used to store data and a framework for adding, deleting, modifying and checking the warehouse. It is not only applicable to react , also used in other front-end frameworks. Anyone who has studied the redux source code thinks that the source code is very sophisticated, and this blog post will introduce the processing of middleware in redux.
Before talking about redux middleware, let’s use two pictures to briefly introduce the basic principles of redux:
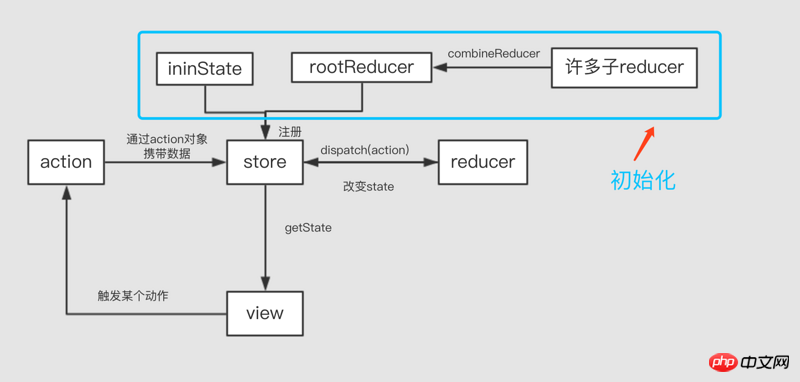
The picture shows the basic process of redux. I won’t go into details here.
Generally, not only redux is used in react, but also react-redux:
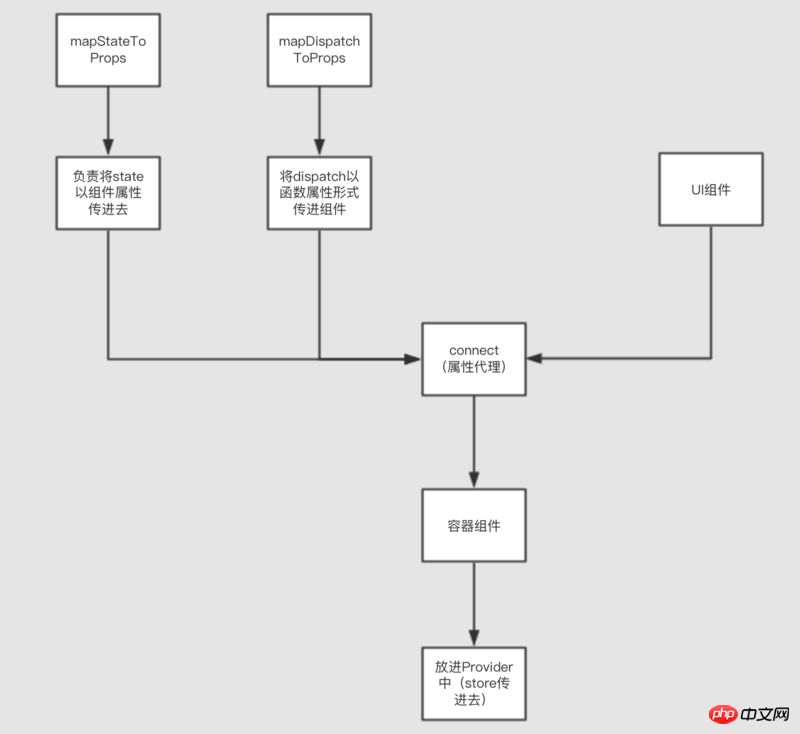
react-redux will not be detailed here.
redux middleware
Under normal circumstances, redux does not have the ability to handle asynchronous requests. Young communication is enhanced through indirection or adding middleware. In addition to the ability to dispatch, yes redux has asynchronous capabilities;
Generally speaking, there are two ways for redux to handle asynchronous processing: indirect method and middleware method;
Indirect method:
The indirect method is to customize the asynchronous behavior and retain the dispatch synchronization function.
Idea: The asynchronously returned result is stuffed into the action, and then synchronized to the reduce through dispatch, and then the state is changed;
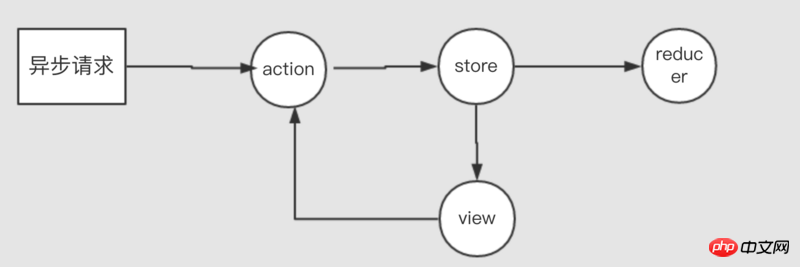
demo:
request.get(API)
.then(d => {
store.dispatch(type: xxx, playload: d)
})This method does not destroy the synchronization mechanism of dispatch. It uses dispatch to synchronize the data to the state in the original way. However, the disadvantage is that each call will write a lot of data. A long paragraph.
Middleware method
The core part of the middleware method is the high-order function applyMiddleWare provided by redux, which returns a brand new store object through multiple layers of calls. The only difference between the new store object and the original object is that dispatch has the asynchronous function;
Source code:
const applyMiddleWare = (...middlewares) => createStore => (reducer, initState) =>{
const store = createStore(reducer, initState);
const _dispatch = store.dispatch;
const MiddleWareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: action => _dispatch(action) 1)
};
const chain = [];
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => {middleware(MiddleWareAPI)}); 2)
let dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch); 3)
return {
dispatch,
...store
}
} Just a dozen lines of code, but it contains a lot of subtleties. The blogger chose three of them to analyze the subtleties:
1) MiddleWareAPI is mainly inserted into the middle The file is finally inserted into the action so that the action can have the dispatch capability. The main reason why an anonymous function is used here is because the store in MiddleWareAPI.dispatch must be consistent with the store returned by applyMiddleWare. It should be noted that MiddleWareAPI.dispatch does not really change the state. It can be understood as a bridge between action and middleware.
2) The change is to insert MiddleWareAPI into all middleware, and then return a function, and the form of middleware will be mentioned later.
3) This is the most subtle point. Compose will inject the chain array from right to left into the previous middleware, while store.dispatch will inject into the rightmost middleware. In fact, compose can be understood as a reduce function here.
eg:
M = [M1,M2,M3] ----> M1(M2(M3(store.dispatch)));
From here you can actually know what middleware looks like:
Basic form of middleware:
const MiddleWare = store => next => action => {
...
}Parameter explanation:
store: In fact, it is MiddleWareAPI;
next: There are two situations here. If the middleware is changed to the rightmost position in the middlewares array, then next is store.dispatch; otherwise it is the return value of a middleware on the adjacent left ( Closure function is the function action => {});
action: It can be a function or an object containing a promise;
You may be a little confused here. The confusion may be that you can’t tell the difference between next and store.dispatch;
Difference:
next (far right middleware): In fact, it is the dispatch that actually triggers the reducer and changes the state. The dispatch and state here are synchronously related; the action here must be an object and cannot contain asynchronous information;
next (not the rightmost middleware): In fact, it is the function returned by the adjacent previous middleware (action => {...}); the action here is the action in the upper-level middleware next (action), the first middleware The action is the action in store.dispatch(action) in the project.
store.dispatch in middleware: It is actually used to plug in actions. It is understood here as the communication channel between actions and middleware.
Flowchart:
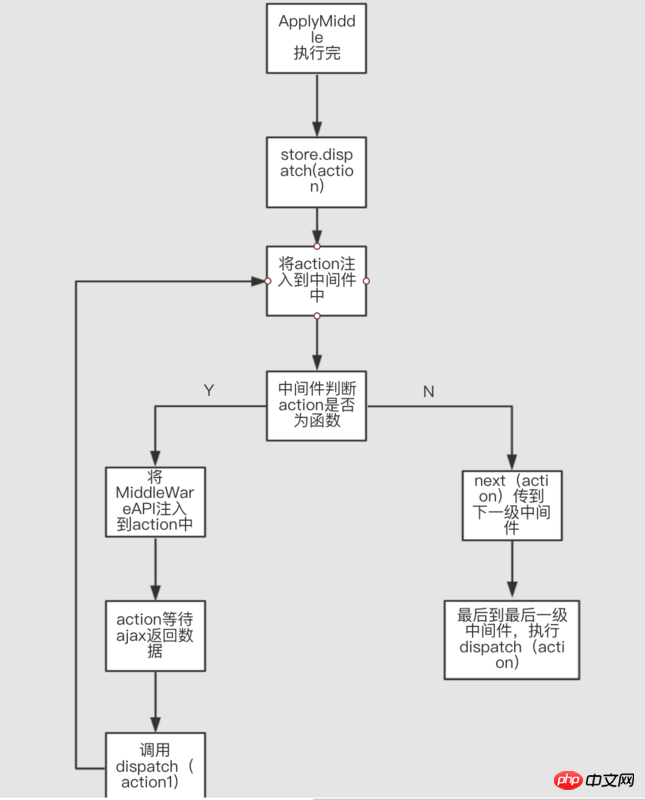
demo:
export const MiddleForTest = store => next => action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
action(store);
} else {
next(action);
}
};
export const MiddleForTestTwo = store => next => action => {
next(action);
};
export function AjaxAction(store) {
setTimeout(function () {
store.dispatch({
type: 'up',
playload: '异步信息'
})
}, 1000)
}
store.dispatch(AjaxAction);said here should be correct We have a general understanding of middleware. Next, we will introduce commonly used middleware and write one yourself.
redux-thunk:主要是适用于action是一个函数的情况,它是对原有的中间件模式再封装多一层,原则上是支持promise为主的action函数;
export function AjaxThunk (url, type) {
return dispatch => {
Ajax(url)
.then(d => {
dispatch({
type,
playload: d
})
})
}
}
store.dispatch(AjaxThunk(url1, 'add'));redux-promise:主要就是针对action对象,action对象是一个promise的异步请求函数:
它的大概实现思路是:
const promiseAction = store => next => action => {
const {type, playload} = action;
if (playload && typeof playload.then === 'function') {
playload.then(result => {
store.dispatch({type, playload: result});
}).catch(e => {})
} else {
next(action);
}
}
action = {
type: 'xxx',
playload: Ajax(url)
}自定义中间件:很多时候网上的redux中间件可能不太符合项目中的需要,所以这时候可以自己写一套适合项目的中间件,以下指示本博主的一个demo,形式不唯一:
export const PromiseWares = store => next => action => {
next({type: 'right', playload: 'loading'});
if (typeof action === 'function') {
const {dispatch} = store;
action(dispatch);
} else {
const {type, playload} = action;
if (playload && typeof playload.then === 'function') {
playload.then(result => {
store.dispatch({type, playload: result});
}).catch(e => {})
} else {
next(action);
next({type: 'right', playload: 'noLoading'});
}
}
};上面是我整理给大家的,希望今后会对大家有帮助。
相关文章:
Jquery具体实例介绍AJAX何时用,AJAX应该在什么地方用
The above is the detailed content of A brief introduction to the use of react redux middleware. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is the principle of tomcat middleware
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
What is the principle of tomcat middleware
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
The principle of tomcat middleware is implemented based on Java Servlet and Java EE specifications. As a Servlet container, Tomcat is responsible for processing HTTP requests and responses and providing the running environment for Web applications. The principles of Tomcat middleware mainly involve: 1. Container model; 2. Component architecture; 3. Servlet processing mechanism; 4. Event listening and filters; 5. Configuration management; 6. Security; 7. Clustering and load balancing; 8. Connector technology; 9. Embedded mode, etc.
 PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework? With the continuous development of Internet technology, front-end frameworks play a vital role in Web development. PHP, Vue and React are three representative front-end frameworks, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. When choosing which front-end framework to use, developers need to make an informed decision based on project needs, team skills, and personal preferences. This article will compare the characteristics and uses of the three front-end frameworks PHP, Vue and React.
 How to handle form validation using middleware in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
How to handle form validation using middleware in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
How to use middleware to handle form validation in Laravel, specific code examples are required Introduction: Form validation is a very common task in Laravel. In order to ensure the validity and security of the data entered by users, we usually verify the data submitted in the form. Laravel provides a convenient form validation function and also supports the use of middleware to handle form validation. This article will introduce in detail how to use middleware to handle form validation in Laravel and provide specific code examples.
 Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and React framework: Steps: Set up the back-end Java framework. Create project structure. Configure build tools. Create React applications. Write REST API endpoints. Configure the communication mechanism. Practical case (SpringBoot+React): Java code: Define RESTfulAPI controller. React code: Get and display the data returned by the API.
 How to use middleware for response transformation in Laravel
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:57 AM
How to use middleware for response transformation in Laravel
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:57 AM
How to use middleware for response conversion in Laravel Middleware is one of the very powerful and practical features in the Laravel framework. It allows us to process requests and responses before the request enters the controller or before the response is sent to the client. In this article, I will demonstrate how to use middleware for response transformation in Laravel. Before starting, make sure you have Laravel installed and a new project created. Now we will follow these steps: Create a new middleware Open
 How to use middleware for data recovery in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
How to use middleware for data recovery in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
Laravel is a popular PHP web application framework that provides many fast and easy ways to build efficient, secure and scalable web applications. When developing Laravel applications, we often need to consider the issue of data recovery, that is, how to recover data and ensure the normal operation of the application in the event of data loss or damage. In this article, we will introduce how to use Laravel middleware to implement data recovery functions and provide specific code examples. 1. What is Lara?
 How to use middleware for scheduled task scheduling in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
How to use middleware for scheduled task scheduling in Laravel
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
How to use middleware for scheduled task scheduling in Laravel Introduction: Laravel is a popular PHP open source framework that provides convenient and powerful tools to develop web applications. One of the important features is scheduled tasks, which allows developers to run specific tasks at specified intervals. In this article, we will introduce how to use middleware to implement Laravel's scheduled task scheduling, and provide specific code examples. Environment Preparation Before starting, we need to make sure
 How to use middleware for multi-language support in Laravel
Nov 03, 2023 pm 01:07 PM
How to use middleware for multi-language support in Laravel
Nov 03, 2023 pm 01:07 PM
Laravel is a widely used PHP framework that provides many convenient features and tools, including middleware that supports multiple languages. In this article, we will detail how to use middleware to implement Laravel's multi-language support and provide some specific code examples. Configuring the language pack First, we need to configure Laravel's language pack so that it can support multiple languages. In Laravel, language packages are usually placed in the resources/lang directory, where each language






