How to use diff algorithm
This time I will show you how to use the diff algorithm, what are the precautions when using the diff algorithm, the following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Virtual dom
The diff algorithm must first clarify the concept that the object of diff is the virtual dom, and updating the real dom is the result of the diff algorithm
Vnode base class
constructor (
。。。
) {
this.tag = tag
this.data = data
this.children = children
this.text = text
this.elm = elm
this.ns = undefined
this.context = context
this.fnContext = undefined
this.fnOptions = undefined
this.fnScopeId = undefined
this.key = data && data.key
this.componentOptions = componentOptions
this.componentInstance = undefined
this.parent = undefined
this.raw = false
this.isStatic = false
this.isRootInsert = true
this.isComment = false
this.isCloned = false
this.isOnce = false
this.asyncFactory = asyncFactory
this.asyncMeta = undefined
this.isAsyncPlaceholder = false
}This part of the code is mainly to better understand the meaning of the attribute of the specific diff in the diff algorithm. Of course, it can also be better understood Understand the vnode instance
The overall process
The core function is the patch function
isUndef judgment (whether it is undefined or null)
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root elementcreateElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) Here you can find that creating nodes is not inserted one by one, but put into a queue for unified batch processing
Core function sameVnode
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && (
(
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
) || (
isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) &&
a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory &&
isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error)
)
)
)
}Here is an outer comparison function that directly compares the keys and tags of the two nodes. ), compare data (note that data here refers to VNodeData), and directly compare types for input.
export interface VNodeData {
key?: string | number;
slot?: string;
scopedSlots?: { [key: string]: ScopedSlot };
ref?: string;
tag?: string;
staticClass?: string;
class?: any;
staticStyle?: { [key: string]: any };
style?: object[] | object;
props?: { [key: string]: any };
attrs?: { [key: string]: any };
domProps?: { [key: string]: any };
hook?: { [key: string]: Function };
on?: { [key: string]: Function | Function[] };
nativeOn?: { [key: string]: Function | Function[] };
transition?: object;
show?: boolean;
inlineTemplate?: {
render: Function;
staticRenderFns: Function[];
};
directives?: VNodeDirective[];
keepAlive?: boolean;
}This will confirm whether the two nodes have further comparison value, otherwise they will be replaced directly
The replacement process is mainly a createElm function and the other is to destroy the oldVNode
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, [oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}Insert To simplify the process, it is to determine the type of the node and call
createComponent respectively (it will determine whether there are children and then call it recursively)
createComment
createTextNode
After creation After using the insert function
, you need to use the hydrate function to map the virtual dom and the real dom
function insert (parent, elm, ref) {
if (isDef(parent)) {
if (isDef(ref)) {
if (ref.parentNode === parent) {
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref)
}
} else {
nodeOps.appendChild(parent, elm)
}
}
}Core function
function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode)
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}const el = vnode.el = oldVnode.el This is a very important step. Let vnode.el refer to the current real dom. When el is modified, vnode.el will change synchronously.
Compare whether the two references are consistent
I don’t know what asyncFactory does after that, so I can’t understand this comparison
Static node comparison key, no re-rendering will be done after the same, directly copy componentInstance (once command takes effect here)
If vnode is a text node Or Comment node, but when vnode.text != oldVnode.text, you only need to update the text content of vnode.elm
Comparison of children
If only oldVnode has child nodes, then delete these nodes
If only vnode has child nodes, then delete them Create these child nodes. If oldVnode is a text node, set the text of vnode.elm to empty String
If both are present, updateChildren will be updated. This will be detailed later.
If neither oldVnode nor vnode has child nodes, but oldVnode is a text node or comment node, set the text of vnode.elm to an empty string
updateChildren
This part focuses on the entire algorithm
First four pointers, oldStart, oldEnd, newStart, newEnd, two arrays, oldVnode, Vnode .
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
} else {
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// same key but different element. treat as new element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}Several situations and processing of a loop comparison (the following - all refer to index -) The comparison is the node node of the comparison. The abbreviation is not rigorous and the comparison uses the sameVnode function, which is not true. Congruent
Conditions for the entire loop not to end oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx
- ##oldStart === newStart, oldStart newStart
- oldEnd === newEnd, oldEnd-- newEnd--
- oldStart === newEnd, oldStart Insert to the end of the queue oldStart newEnd--
- oldEnd === newStart, oldEnd is inserted into the beginning of the queue oldEnd-- newStart
- This is the only way to handle all the remaining situations. kind of processing, after processing newStart
newStart在old中发现一样的那么将这个移动到oldStart前
没有发现一样的那么创建一个放到oldStart之前
循环结束后并没有完成
还有一段判断才算完
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to use diff algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
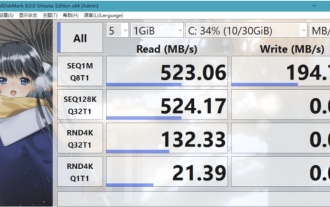 What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
What software is crystaldiskmark? -How to use crystaldiskmark?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:58 PM
CrystalDiskMark is a small HDD benchmark tool for hard drives that quickly measures sequential and random read/write speeds. Next, let the editor introduce CrystalDiskMark to you and how to use crystaldiskmark~ 1. Introduction to CrystalDiskMark CrystalDiskMark is a widely used disk performance testing tool used to evaluate the read and write speed and performance of mechanical hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD). Random I/O performance. It is a free Windows application and provides a user-friendly interface and various test modes to evaluate different aspects of hard drive performance and is widely used in hardware reviews
 How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
How to download foobar2000? -How to use foobar2000
Mar 18, 2024 am 10:58 AM
foobar2000 is a software that can listen to music resources at any time. It brings you all kinds of music with lossless sound quality. The enhanced version of the music player allows you to get a more comprehensive and comfortable music experience. Its design concept is to play the advanced audio on the computer The device is transplanted to mobile phones to provide a more convenient and efficient music playback experience. The interface design is simple, clear and easy to use. It adopts a minimalist design style without too many decorations and cumbersome operations to get started quickly. It also supports a variety of skins and Theme, personalize settings according to your own preferences, and create an exclusive music player that supports the playback of multiple audio formats. It also supports the audio gain function to adjust the volume according to your own hearing conditions to avoid hearing damage caused by excessive volume. Next, let me help you
 How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
How to use Baidu Netdisk app
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:46 PM
Cloud storage has become an indispensable part of our daily life and work nowadays. As one of the leading cloud storage services in China, Baidu Netdisk has won the favor of a large number of users with its powerful storage functions, efficient transmission speed and convenient operation experience. And whether you want to back up important files, share information, watch videos online, or listen to music, Baidu Cloud Disk can meet your needs. However, many users may not understand the specific use method of Baidu Netdisk app, so this tutorial will introduce in detail how to use Baidu Netdisk app. Users who are still confused can follow this article to learn more. ! How to use Baidu Cloud Network Disk: 1. Installation First, when downloading and installing Baidu Cloud software, please select the custom installation option.
 How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
How to use NetEase Mailbox Master
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:32 PM
NetEase Mailbox, as an email address widely used by Chinese netizens, has always won the trust of users with its stable and efficient services. NetEase Mailbox Master is an email software specially created for mobile phone users. It greatly simplifies the process of sending and receiving emails and makes our email processing more convenient. So how to use NetEase Mailbox Master, and what specific functions it has. Below, the editor of this site will give you a detailed introduction, hoping to help you! First, you can search and download the NetEase Mailbox Master app in the mobile app store. Search for "NetEase Mailbox Master" in App Store or Baidu Mobile Assistant, and then follow the prompts to install it. After the download and installation is completed, we open the NetEase email account and log in. The login interface is as shown below
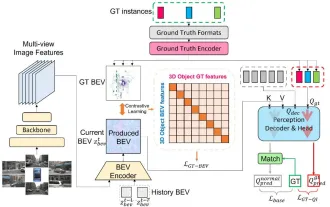 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
BTCC tutorial: How to bind and use MetaMask wallet on BTCC exchange?
Apr 26, 2024 am 09:40 AM
MetaMask (also called Little Fox Wallet in Chinese) is a free and well-received encryption wallet software. Currently, BTCC supports binding to the MetaMask wallet. After binding, you can use the MetaMask wallet to quickly log in, store value, buy coins, etc., and you can also get 20 USDT trial bonus for the first time binding. In the BTCCMetaMask wallet tutorial, we will introduce in detail how to register and use MetaMask, and how to bind and use the Little Fox wallet in BTCC. What is MetaMask wallet? With over 30 million users, MetaMask Little Fox Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets today. It is free to use and can be installed on the network as an extension
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Explore the underlying principles and algorithm selection of the C++sort function
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
The bottom layer of the C++sort function uses merge sort, its complexity is O(nlogn), and provides different sorting algorithm choices, including quick sort, heap sort and stable sort.






