How Webpack builds Electron apps
This time I will show you how Webpack builds Electron applications. What are the precautions for Webpack to build Electron applications. The following is a practical case, let's take a look.
Electron allows you to use Web development technology to develop cross-platform desktop applications, led by Github and open source. The familiar Atom and VSCode Editor are developed using Electron.
Electron is a combination of Node.js and the Chromium browser. It uses the web page displayed by the Chromium browser as the application GUI, through Node.js to interact with the operating system. When you are in Electron When you operate a window in an application, you are actually operating a web page. When your operation needs to be completed through the operating system, the web page will interact with the operating system through Node.js.
The advantages of developing desktop applications in this way are:
To lower the development threshold, you only need to master web development technology and Node.js. A large number of web development technologies and ready-made libraries can be reused in Electron;
- Since both Chromium browser and Node.js are Cross-platform, Electron can write a code to run on different operating systems.
When running an Electron application, it starts by launching a main process. The main process is started by executing an entry JavaScript file through Node.js. The content of this entry file main.js is as follows:
const { app, BrowserWindow } = require('electron')
// 保持一个对于 window 对象的全局引用,如果你不这样做,
// 当 JavaScript 对象被垃圾回收, window 会被自动地关闭
let win
// 打开主窗口
function createWindow() {
// 创建浏览器窗口
win = new BrowserWindow({ width: 800, height: 600 })
// 加载应用的 index.html
const indexPageURL = `file://${dirname}/dist/index.html`;
win.loadURL(indexPageURL);
// 当 window 被关闭,这个事件会被触发
win.on('closed', () => {
// 取消引用 window 对象
win = null
})
}
// Electron 会在创建浏览器窗口时调用这个函数。
app.on('ready', createWindow)
// 当全部窗口关闭时退出
app.on('window-all-closed', () => {
// 在 macOS 上,除非用户用 Cmd + Q 确定地退出
// 否则绝大部分应用会保持激活
if (process.platform !== 'darwin') {
app.quit()
}
})After the main process is started, it will always run in the background. The window you see and operate is not the main process, but the window sub-process newly started by the main process.
The application has a series of life cycle events from startup to exit. Use the electron.app.on() function to monitor life cycle events and react at specific moments. For example, use BrowserWindow to display the main window of the application in the app.on('ready') event.
The window that is started is actually a web page, and it will load the web page address passed in loadURL when it is started. Each window is a separate web page process, and communication between windows requires the use of the main process to pass messages.
Generally speaking, developing Electron applications is very similar to developing Web applications. The difference is that Electron's running environment has built-in browser and Node.js APIs. When developing web pages, in addition to using the APIs provided by the browser, you can also use Node. API provided by js.
Connect to Webpack
Next, make a simple Electron application, which requires a main window to be displayed after the application is started. There is a button in the main window. After clicking this button, a new window will be displayed, and React will be used to develop the web page.
Since each window in the Electron application corresponds to a web page, two web pages need to be developed, namely the index.html of the main window and the newly opened window. login.html. In other words, the project consists of 2 single-page applications. This is very similar to the project in 3-10 Managing Multiple Single-page Applications. Let us transform it into a Electron applications.
The places that need to be changed are as follows:
Create a new entry file main.js for the main process in the project root directory. The content is consistent with the above mentioned;
The code of the main window web page is as follows:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { remote } from 'electron';
import path from 'path';
import './index.css';
class App extends Component {
// 在按钮被点击时
handleBtnClick() {
// 新窗口对应的页面的 URI 地址
const modalPath = path.join('file://', remote.app.getAppPath(), 'dist/login.html');
// 新窗口的大小
let win = new remote.BrowserWindow({ width: 400, height: 320 })
win.on('close', function () {
// 窗口被关闭时清空资源
win = null
})
// 加载网页
win.loadURL(modalPath)
// 显示窗口
win.show()
}
render() {
return (
<p>
<h1>Page Index</h1>
<button onClick={this.handleBtnClick}>Open Page Login</button>
</p>
)
}
}
render(<App/>, window.document.getElementById('app'));The most critical part is to use the API provided by the electron library to open a new window in the button click event and load the address of the web page file.
The code in the page part has been modified. Next, the construction code will be modified. Here you need to do the following to build:
Construct two web pages that can be run in the browser, corresponding to the interfaces of the two windows;
Because the JavaScript code of the web page may call the Node.js native module or electron module, that is, the output code depends on these modules. However, since these modules have built-in support, the built code cannot package these modules.
- It is very simple to complete the above requirements because Webpack has built-in support for Electron. Just add a line of code to the Webpack configuration file, as follows:
target: 'electron-renderer',
这句配置曾在2-7其它配置项-Target中提到,意思是指让 Webpack 构建出用于 Electron 渲染进程用的 JavaScript 代码,也就是这2个窗口需要的网页代码。
以上修改都完成后重新执行 Webpack 构建,对应的网页需要的代码都输出到了项目根目录下的 dist 目录里。
为了以 Electron 应用的形式运行,还需要安装新依赖:
# 安装 Electron 执行环境到项目中 npm i -D electron
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How Webpack builds Electron apps. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
VUE3 Getting Started Tutorial: Packaging and Building with Webpack
Jun 15, 2023 pm 06:17 PM
Vue is an excellent JavaScript framework that can help us quickly build interactive and efficient web applications. Vue3 is the latest version of Vue, which introduces many new features and functionality. Webpack is currently one of the most popular JavaScript module packagers and build tools, which can help us manage various resources in our projects. This article will introduce how to use Webpack to package and build Vue3 applications. 1. Install Webpack
 How to use Nginx web server caddy
May 30, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
How to use Nginx web server caddy
May 30, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
Introduction to Caddy Caddy is a powerful and highly scalable web server that currently has 38K+ stars on Github. Caddy is written in Go language and can be used for static resource hosting and reverse proxy. Caddy has the following main features: Compared with the complex configuration of Nginx, its original Caddyfile configuration is very simple; it can dynamically modify the configuration through the AdminAPI it provides; it supports automated HTTPS configuration by default, and can automatically apply for HTTPS certificates and configure it; it can be expanded to data Tens of thousands of sites; can be executed anywhere with no additional dependencies; written in Go language, memory safety is more guaranteed. First of all, we install it directly in CentO
 How to implement form validation for web applications using Golang
Jun 24, 2023 am 09:08 AM
How to implement form validation for web applications using Golang
Jun 24, 2023 am 09:08 AM
Form validation is a very important link in web application development. It can check the validity of the data before submitting the form data to avoid security vulnerabilities and data errors in the application. Form validation for web applications can be easily implemented using Golang. This article will introduce how to use Golang to implement form validation for web applications. 1. Basic elements of form validation Before introducing how to implement form validation, we need to know what the basic elements of form validation are. Form elements: form elements are
 Using Jetty7 for Web server processing in Java API development
Jun 18, 2023 am 10:42 AM
Using Jetty7 for Web server processing in Java API development
Jun 18, 2023 am 10:42 AM
Using Jetty7 for Web Server Processing in JavaAPI Development With the development of the Internet, the Web server has become the core part of application development and is also the focus of many enterprises. In order to meet the growing business needs, many developers choose to use Jetty for web server development, and its flexibility and scalability are widely recognized. This article will introduce how to use Jetty7 in JavaAPI development for We
 Real-time protection against face-blocking barrages on the web (based on machine learning)
Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM
Real-time protection against face-blocking barrages on the web (based on machine learning)
Jun 10, 2023 pm 01:03 PM
Face-blocking barrage means that a large number of barrages float by without blocking the person in the video, making it look like they are floating from behind the person. Machine learning has been popular for several years, but many people don’t know that these capabilities can also be run in browsers. This article introduces the practical optimization process in video barrages. At the end of the article, it lists some applicable scenarios for this solution, hoping to open it up. Some ideas. mediapipeDemo (https://google.github.io/mediapipe/) demonstrates the mainstream implementation principle of face-blocking barrage on-demand up upload. The server background calculation extracts the portrait area in the video screen, and converts it into svg storage while the client plays the video. Download svg from the server and combine it with barrage, portrait
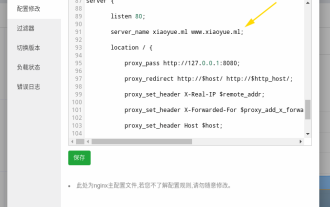 How to configure nginx to ensure that the frps server and web share port 80
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to configure nginx to ensure that the frps server and web share port 80
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:19 AM
First of all, you will have a doubt, what is frp? Simply put, frp is an intranet penetration tool. After configuring the client, you can access the intranet through the server. Now my server has used nginx as the website, and there is only one port 80. So what should I do if the FRP server also wants to use port 80? After querying, this can be achieved by using nginx's reverse proxy. To add: frps is the server, frpc is the client. Step 1: Modify the nginx.conf configuration file in the server and add the following parameters to http{} in nginx.conf, server{listen80
 What are web standards?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
What are web standards?
Oct 18, 2023 pm 05:24 PM
Web standards are a set of specifications and guidelines developed by W3C and other related organizations. It includes standardization of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, DOM, Web accessibility and performance optimization. By following these standards, the compatibility of pages can be improved. , accessibility, maintainability and performance. The goal of web standards is to enable web content to be displayed and interacted consistently on different platforms, browsers and devices, providing better user experience and development efficiency.
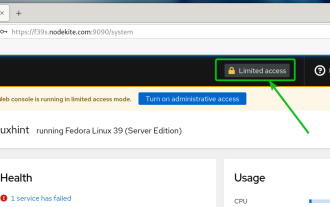 How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Cockpit is a web-based graphical interface for Linux servers. It is mainly intended to make managing Linux servers easier for new/expert users. In this article, we will discuss Cockpit access modes and how to switch administrative access to Cockpit from CockpitWebUI. Content Topics: Cockpit Entry Modes Finding the Current Cockpit Access Mode Enable Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Disabling Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Conclusion Cockpit Entry Modes The cockpit has two access modes: Restricted Access: This is the default for the cockpit access mode. In this access mode you cannot access the web user from the cockpit






