shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
Detailed explanation of React component life cycle
In the process of creating a component using React, a render method will be called, as well as triggering several life cycle methods. This article mainly talks about when these life cycle methods are executed.
Understand the life cycle of components. When a component is created or destroyed, certain operations can be performed. In addition, you can use these lifecycle hooks to change your components when props and state change.
Life cycle
In order to clearly understand the life cycle, we need to understand Component initialization, state change, props Change , Component uninstallation, and which hook functions will be executed when forceUpdate() is called.
Component initialization
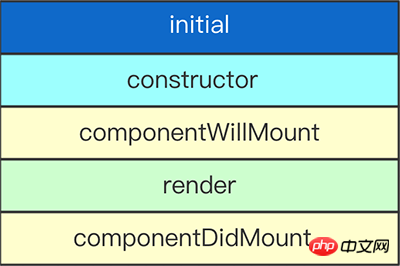
constructor()
ReactThe component's constructor will be called before assembly. When defining a constructor for a React.Component subclass, you should call super(props) before any other expressions. Otherwise, this.props will be undefined in the constructor.
The constructor is the appropriate place to initialize state. If you don't initialize state and don't bind methods, then you don't need to define a constructor for your React component.
State can be initialized based on attributes. This effectively "forks" the property and sets the state based on the initial property. Here's an example of a valid React.Component subclass constructor:
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
color: props.initialColor
};
}componentWillMount()
componentWillMount()
componentWillMount() Called immediately before assembly occurs. It is called before render(), so setting the state synchronously in this method will not trigger a rerender. Avoid introducing any side effects or subscriptions in this method.
This is the only life cycle hook function that will be called when rendered on the server side. Generally, we recommend using constructor() instead.
render()
render() method is required.
When called, it should check this.props and this.state and return one of the following types:
-
React elements. Typically created with JSX. This element may be a representation of a native DOM component, such as
, or a synthetic component you define. Strings and numbers. These will be rendered as text nodes in the DOM.
Portals. Created by ReactDOM.createPortal.
null. Nothing is rendered.
Boolean value. Nothing is rendered. (Usually found in the return test &&
writing method, where test is a Boolean value.)
When returning null or false, ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this) will return null. render()The function should be pure, which means it should not change the state of the component, return the same result every time it is called, and not interact directly with the browser. If you need to interact with the browser, place the task in the componentDidMount() stage or other life cycle methods. Keeping the render() method pure makes components easier to think about.
Note
IfshouldComponentUpdate()returnsfalse, therender()function will not be called.
componentDidMount()
componentDidMount()
componentDidMount() Called immediately after the component is assembled. Initialization makes the DOM node should proceed here. If you need to load data from the remote end, this is a suitable place to implement network requests. Setting the state in this method will trigger rerendering.
State Changes
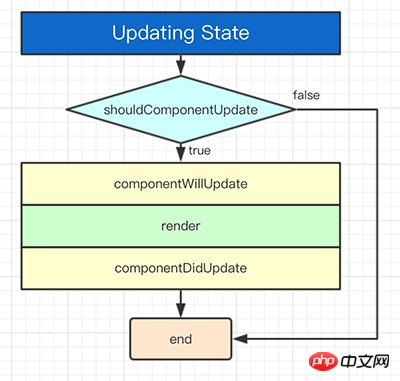
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
Copy after login
Use shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
shouldComponentUpdate() to Let React know whether changes to the current state or properties do not affect the component's output. The default behavior is to rerender on every state change, and in most cases you should rely on the default behavior.
shouldComponentUpdate() is called before rendering. Default is true. This method is not called during initial rendering or when forceUpdate() is used.
false does not prevent child components from re-rendering.
shouldComponentUpdate(): Returned undefined instead of a boolean value.Note that even if the attribute is not React may also call this method on any changes, so if you want to handle changes, make sure to compare the current and next values. This can happen when a parent component causes your component to re-render.
在装配期间,React并不会调用带有初始属性的componentWillReceiveProps方法。其仅会调用该方法如果某些组件的属性可能更新。调用this.setState通常不会触发componentWillReceiveProps。
componentWillUpdate()
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
当接收到新属性或状态时,componentWillUpdate()为在渲染前被立即调用。在更新发生前,使用该方法是一次准备机会。该方法不会在初始化渲染时调用。
注意你不能在这调用this.setState(),若你需要更新状态响应属性的调整,使用componentWillReceiveProps()代替。
注意:若shouldComponentUpdate()返回false,componentWillUpdate()将不会被调用。
componentDidUpdate()
componentDidUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
当接收到新属性或状态时,componentWillUpdate()为在渲染前被立即调用。在更新发生前,使用该方法是一次准备机会。该方法不会在初始化渲染时调用。
注意:你不能在这调用this.setState(),若你需要更新状态响应属性的调整,使用componentWillReceiveProps()代替。注意:若
shouldComponentUpdate()返回false,componentWillUpdate()将不会被调用。
Props Changes
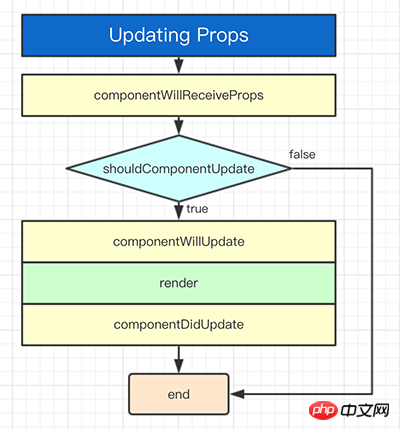
componentWillReceiveProps()
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps)
componentWillReceiveProps()在装配了的组件接收到新属性前调用。若你需要更新状态响应属性改变(例如,重置它),你可能需对比this.props和nextProps并在该方法中使用this.setState()处理状态改变。
注意:即使属性未有任何改变,React可能也会调用该方法,因此若你想要处理改变,请确保比较当前和之后的值。这可能会发生在当父组件引起你的组件重渲。
在装配期间,React并不会调用带有初始属性的componentWillReceiveProps方法。其仅会调用该方法如果某些组件的属性可能更新。调用this.setState通常不会触发componentWillReceiveProps。
Unmounting

componentWillUnmount()
componentWillUnmount()
componentWillUnmount() 在组件被卸载和销毁之前立刻调用。可以在该方法里处理任何必要的清理工作,例如解绑定时器,取消网络请求,清理任何在componentDidMount环节创建的DOM元素。
forceUpdate
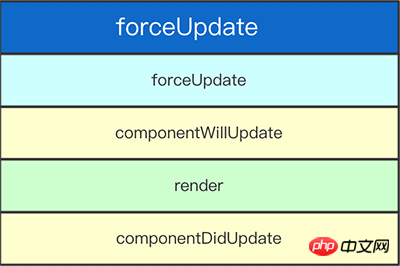
默认情况,当你的组件或状态发生改变,你的组件将会重渲。若你的render()方法依赖其他数据,你可以通过调用forceUpdate()来告诉React组件需要重渲。
调用forceUpdate()将会导致组件的 render()方法被调用,并忽略shouldComponentUpdate()。这将会触发每一个子组件的生命周期方法,涵盖,每个子组件的shouldComponentUpdate() 方法。若当标签改变,React仅会更新DOM。
通常你应该尝试避免所有forceUpdate() 的用法并仅在render()函数里从this.props和this.state读取数据。
forceUpdate() Example
// forceUpdate() Example
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(){
super();
this.forceUpdateHandler = this.forceUpdateHandler.bind(this);
};
componentWillUpdate() {
console.info('componentWillUpdate called');
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.info('componentDidUpdate called');
}
forceUpdateHandler(){
this.forceUpdate();
};
render(){
return(
<p>
<button onClick= {this.forceUpdateHandler} >FORCE UPDATE</button>
<h4>Random Number : { Math.random() }</h4>
</p>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'));相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of React component life cycle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework? With the continuous development of Internet technology, front-end frameworks play a vital role in Web development. PHP, Vue and React are three representative front-end frameworks, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. When choosing which front-end framework to use, developers need to make an informed decision based on project needs, team skills, and personal preferences. This article will compare the characteristics and uses of the three front-end frameworks PHP, Vue and React.
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and React framework: Steps: Set up the back-end Java framework. Create project structure. Configure build tools. Create React applications. Write REST API endpoints. Configure the communication mechanism. Practical case (SpringBoot+React): Java code: Define RESTfulAPI controller. React code: Get and display the data returned by the API.
 Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Linux system call system() function System call is a very important part of the Linux operating system. It provides a way to interact with the system kernel. Among them, the system() function is one of the commonly used system call functions. This article will introduce the use of the system() function in detail and provide corresponding code examples. Basic Concepts of System Calls System calls are a way for user programs to interact with the operating system kernel. User programs request the operating system by calling system call functions
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React combines JSX and HTML to improve user experience. 1) JSX embeds HTML to make development more intuitive. 2) The virtual DOM mechanism optimizes performance and reduces DOM operations. 3) Component-based management UI to improve maintainability. 4) State management and event processing enhance interactivity.






