有时,任务是分析数据集并使用图表或绘图进行数据可视化。 plotly 是一个很好的开源图形库,可以与 python 一起使用,用于快速轻松地制作各种绘图和图表。在本文中,使用两个不同的示例,将名为 plotly 的 python 库与 python 代码结合使用来绘制散点图。在第一个示例中,计算机系统中安装的python用于运行为制作散点图而编写的python程序。另一个例子,使用google colab展示了在计算机中没有安装python的情况下,仍然可以使用python和plotly并可以制作散点图的方法。在这两个示例中,都使用 kaggle 的开源数据集进行数据分析和可视化。
sepal_length,sepal_width,petal_length,petal_width,species 5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.9,3,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.7,3.2,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.6,3.1,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa 5,3.6,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa 5.4,3.9,1.7,0.4,Iris-setosa 4.6,3.4,1.4,0.3,Iris-setosa 5,3.4,1.5,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.4,2.9,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa …….., ….., ……, ……., ……..
此 CSV 文件包含名为 sepal_length、sepal_width、petal_length、petal_width 和species 的五列。其中,我们将在示例 1 中使用 sepal_width 和 petal_width 作为散点图,在示例 2 中使用 sepal_length 和 petal_length 作为散点图。
第 1 步 - 首先导入 pandas 并绘制。 Plotly 是 Python 的开源图形库,将用于制作散点图。
步骤 2 - 现在读取 IRIS.csv 文件,因为此处给出的数据集将用于制作散点图。
第 3 步 - 制作一个数据框 dff 并显示该数据框的列和内容。
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
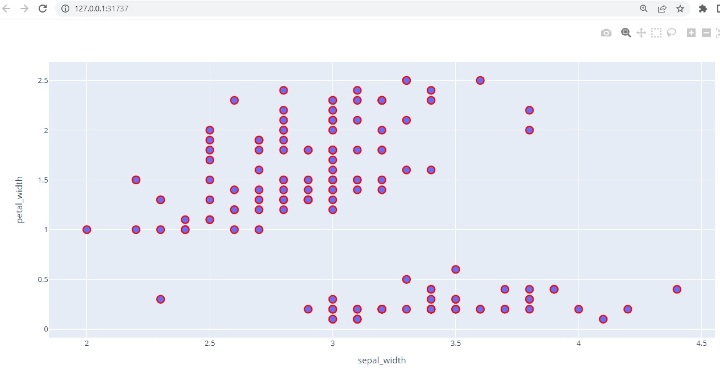
第 4 步 - 使用 scatter() 函数绘制散点图,并指定 x 轴的 sepal_width 和 y 轴的 petal_width。
第 5 步 - 设置标记的样式,例如大小和颜色。
第 6 步 - 编写函数来显示散点图。使用 cmd 窗口运行程序。该图将在浏览器的新选项卡中打开。
第 1 步 - 使用 Google 帐户登录。前往谷歌 Colab。打开一个新的 Colab Notebook 并在其中编写 Python 代码。
第 2 步 - 使用示例 1 中给出的链接上传从 Kaggle 下载并保存的 IRIS.csv 文件,因为此处给出的数据集将用于制作散点图。
第 3 步 - 现在导入 pandas 并绘制。 Plotly 是 Python 的开源图形库,将用于制作散点图。
第 4 步 - 制作一个数据框 dff 并显示该数据框的列和内容。
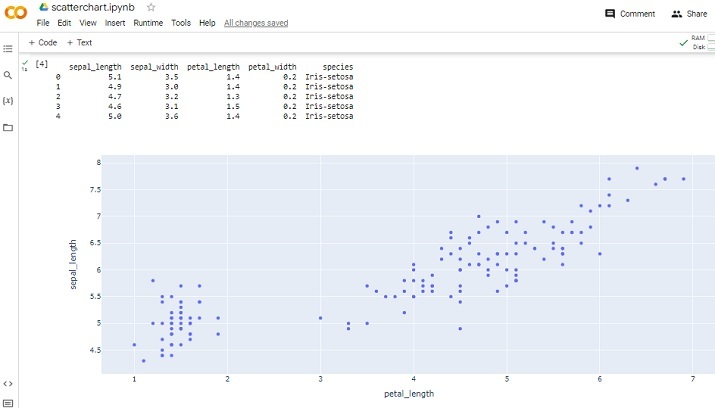
第 5 步 - 使用 scatter() 函数绘制散点图,并指定 x 轴的 petal_length 和 y 轴的 sepal_length。
第 6 步 - 编写函数来显示散点图。通过单击给定代码单元上的播放按钮来运行程序。检查结果,因为它将显示在 Colab 笔记本中。
为了制作散点图,我们将使用 Kaggle 上的可用数据。登录 Kaggle 并从此链接下载 CSV 文件 -
创建一个名为 Scatter.py 的文件。在该文件中写入以下代码
#include the required libraries
import pandas as pd
#This library is needed to make the scatter plot
import plotly.express as pxx
#read the CSV file and make a dataframe
dff = pd.read_csv("IRIS.csv")
#print the columns and data
print(dff.head())
#make the scatter plot
figg = pxx.scatter(dff, x="sepal_width", y="petal_width")
#set the properties of the scatter plot
figg.update_traces(marker=dict(size=12, line=dict(width=2, color="red")), selector=dict(mode='markers'))
#display the chart
figg.show()
#Uploading the csv from google.colab import dfiles data_to_load = dfiles.upload()
import pandas as pdd
import plotly.express as pxx
dff = pdd.read_csv("IRIS.csv")
print(dff.head()) figg = pxx.scatter(dff, x="petal_length", y="sepal_length") figg.show()
在这篇 Python 和 Plotly 文章中,通过两个不同的示例,给出了如何使用名为 Plotly 的 Python 库制作散点图的方法。首先,给出了从 Kaggle 下载并保存数据集进行分析的方法。然后编写一个 Python 程序来使用 Plotly 中的函数绘制散点图。在第二个示例中,使用 Google Colab 编写 Python 程序并使用相同的库和相同的数据集制作散点图。
以上就是如何使用Python-Plotly制作基本的散点图?的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

python怎么学习?python怎么入门?python在哪学?python怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了python速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号