Using Auth authorization technology in ThinkPHP6
With the continuous development of Internet applications, the security of Web applications has become an increasingly important issue. How to ensure the security of programs has become a problem faced by all developers. Auth authorization technology is a popular solution that provides role-based access control.
In this article, we will explore how to use Auth authorization technology in ThinkPHP6. First, we need to clarify the working principle and core concepts of Auth authorization.
- How Auth authorization works
The core of Auth authorization is role-based access control, which is mainly divided into the following three steps:
1.1 Create a role
Before using Auth authorization, you first need to create a role. A role is a set of permissions that defines the access a user has.
1.2 Assign permissions to roles
After creating a role, you need to assign the corresponding permissions to the role. Permissions refer to the authorization of which functional modules or data can be accessed.
1.3 Assign roles to users
Finally, you need to assign roles to users. A user can be assigned multiple roles, which determine the access rights the user has.
In the Auth authorization workflow, use the Access controller to implement access control. The Access controller is used to check whether the user has access rights to the current URL. If the user has access rights, he or she can continue to access the relevant content.
- Using Auth authorization technology in ThinkPHP6
Now that we have understood how Auth authorization works, below we will explain in detail how to use Auth authorization technology in ThinkPHP6. Suppose we have two kinds of users in the background: administrators and ordinary users. Administrators can access all content modules, while ordinary users can only access some content.
2.1 Install and configure the Auth plug-in
Before using Auth technology, we need to install and configure the Auth plug-in first. In ThinkPHP6, the Auth plug-in has been integrated into the framework and can be used with simple configuration.
First, create the auth.php configuration file in the config directory. The configuration information is as follows:
return [
// 用户认证的类名,不设置则使用核心集成认证方法
'auth' => AppAuth::class,
// 不需要认证的路由,可允许所有用户访问的路由
'no_auth' => ['index/index'],
// 需要认证且验证失败时跳转的地址
'fail_url' => 'index/login',
];2.2 Create a User model
Create a User model. The relevant code is as follows:
<?php
namespace appmodel;
use thinkModel;
class User extends Model {
// 定义角色关联
public function roles() {
return $this->belongsToMany(Role::class, 'user_role');
}
// 判断用户是否有权限访问当前操作
public function hasPermission($permission) {
foreach ($this->roles as $role) {
if ($role->checkPermission($permission)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}2.3 Create a Role model
Create a Role model, the relevant code is as follows:
<?php
namespace appmodel;
use thinkModel;
class Role extends Model {
// 定义权限关联
public function permissions() {
return $this->belongsToMany(Permission::class, 'role_permission');
}
// 检查角色是否有权限访问当前操作
public function checkPermission($permission) {
foreach ($this->permissions as $item) {
if ($item->name == $permission) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}2.4 Create a Permission model
Create a Permission model, the relevant code is as follows:
<?php
namespace appmodel;
use thinkModel;
class Permission extends Model {
}2.5 Create database tables
Create database tables, including user table, role table, permission table and two relational tables user_role and role_permission.
User table related structure:
| Field | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | |
| username | varchar(20) | |
| password | varchar(255) | |
| created_at | datetime | |
| updated_at | datetime |
role table Related structures:
| Field | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | |
| name | varchar(20) | |
| created_at | datetime | |
| updated_at | datetime |
Permission table related structure:
| Field | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | |
| name | varchar(20 ) |
user_role table related structure:
| Field | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | |
| user_id | int | |
| role_id | int |
role_permission table related structure:
| Field | Type | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| id | int | |
| role_id | int | |
| permission_id | int |
2.6 Controller code implementation
The following uses a sample controller to illustrate how to implement Auth authorization. The sample controller code is as follows:
<?php
namespace appdmincontroller;
use appmodelUser;
use thinkController;
class Index extends Controller {
// 后台首页
public function index() {
// 获取当前登录用户
$user_id = session('user_id');
$user = User::find($user_id);
// 判断用户是否有权限访问当前操作
if (!$user->hasPermission($this->request->path())) {
$this->error('无权访问');
}
return view();
}
// 登录页面
public function login() {
return view();
}
// 处理登录请求
public function do_login() {
$username = $this->request->param('username');
$password = $this->request->param('password');
// 根据用户名查询用户
$user = User::where('username', $username)->find();
// 验证用户密码
if ($user && password_verify($password, $user->password)) {
// 记录登录状态
session('user_id', $user->id);
// 跳转到后台首页
$this->redirect('index/index');
} else {
$this->error('登录失败');
}
}
// 退出登录
public function logout() {
session('user_id', null);
$this->redirect('index/login');
}
}- Summary
In this article, we introduced the working principle, core concepts and application implementation of Auth authorization in ThinkPHP6. Using Auth authorization technology can effectively improve the security of web applications and provide users with more secure and reliable services. In the subsequent web application development process, we should also pay attention to security guarantees and make best use of existing security technologies as much as possible.
The above is the detailed content of Using Auth authorization technology in ThinkPHP6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
To run the ThinkPHP project, you need to: install Composer; use Composer to create the project; enter the project directory and execute php bin/console serve; visit http://localhost:8000 to view the welcome page.
 There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
ThinkPHP has multiple versions designed for different PHP versions. Major versions include 3.2, 5.0, 5.1, and 6.0, while minor versions are used to fix bugs and provide new features. The latest stable version is ThinkPHP 6.0.16. When choosing a version, consider the PHP version, feature requirements, and community support. It is recommended to use the latest stable version for best performance and support.
 The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
StableDiffusion3’s paper is finally here! This model was released two weeks ago and uses the same DiT (DiffusionTransformer) architecture as Sora. It caused quite a stir once it was released. Compared with the previous version, the quality of the images generated by StableDiffusion3 has been significantly improved. It now supports multi-theme prompts, and the text writing effect has also been improved, and garbled characters no longer appear. StabilityAI pointed out that StableDiffusion3 is a series of models with parameter sizes ranging from 800M to 8B. This parameter range means that the model can be run directly on many portable devices, significantly reducing the use of AI
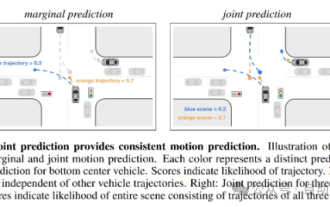 This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
Trajectory prediction plays an important role in autonomous driving. Autonomous driving trajectory prediction refers to predicting the future driving trajectory of the vehicle by analyzing various data during the vehicle's driving process. As the core module of autonomous driving, the quality of trajectory prediction is crucial to downstream planning control. The trajectory prediction task has a rich technology stack and requires familiarity with autonomous driving dynamic/static perception, high-precision maps, lane lines, neural network architecture (CNN&GNN&Transformer) skills, etc. It is very difficult to get started! Many fans hope to get started with trajectory prediction as soon as possible and avoid pitfalls. Today I will take stock of some common problems and introductory learning methods for trajectory prediction! Introductory related knowledge 1. Are the preview papers in order? A: Look at the survey first, p
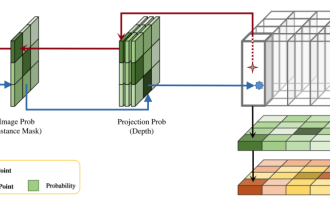 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.
 How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Steps to run ThinkPHP Framework locally: Download and unzip ThinkPHP Framework to a local directory. Create a virtual host (optional) pointing to the ThinkPHP root directory. Configure database connection parameters. Start the web server. Initialize the ThinkPHP application. Access the ThinkPHP application URL and run it.
 Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Performance comparison of Laravel and ThinkPHP frameworks: ThinkPHP generally performs better than Laravel, focusing on optimization and caching. Laravel performs well, but for complex applications, ThinkPHP may be a better fit.
 How to install thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
How to install thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
ThinkPHP installation steps: Prepare PHP, Composer, and MySQL environments. Create projects using Composer. Install the ThinkPHP framework and dependencies. Configure database connection. Generate application code. Launch the application and visit http://localhost:8000.






