python mathematical modeling example analysis
SciPy learning
''' SciPy 包含的模块有最优化、线性代数、积分、插值、特殊函数、快速傅里叶变换、 信号处理和图像处理、常微分方程求解和其他科学与工程中常用的计算。 ''' # 安装scipy库: # SciPy终端安装命令:pip install SciPy # https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/python-pip-install-usage.html Python pip 安装与使用 # 查看scipy版本: import scipy print(scipy.__version__) # SciPy模块功能表 ''' 模块 功能 scipy.cluster 聚类分析等 scipy.constants 物理和数学函数 scipy.fftpack 傅里叶变换 scipy.integrate 积分 scipy.interpolate 插值 scipy.io 数据输入和输出 scipy.linalg 线性代数 scipy.ndimage n维图像 scipy.odr 正交距离回归 scipy.optimize 优化 scipy.signal 信号处理 scipy.sparse 稀疏矩阵 scipy.spatial 空间数据结构和算法 scipy.special 特殊函数 scipy.stats 统计 ''' # 使用 dir() 函数来查看 constants 模块包含的常量: from scipy import constants print(dir(constants)) ''' 单位类型 常量模块包含以下几种单位: 公制单位 二进制,以字节为单位 质量单位 角度换算 时间单位 长度单位 压强单位 体积单位 速度单位 温度单位 能量单位 功率单位 力学单位 ''' print() # SciPy 常量模块: # constants 是 scipy 的常量模块 from scipy import constants # 查看一英亩等于多少平方米: print(constants.acre) # 输出 4046.8564223999992 # SciPy 常量模块 constants 提供了许多内置的数学常数 # 圆周率: pi # 黄金比例: golden from scipy import constants print(constants.pi) # 输出 3.141592653589793 【圆周率】 print(constants.golden) # 输出 1.618033988749895 【黄金比例】
SciPy basic operations
1-Solving nonlinear equations (group)
1-1
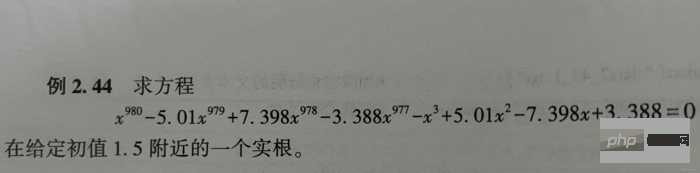
The solution code is as follows:
# scipy.optimize模块的fsolve和root可求非线性方程(组)的解
# 格式:
from scipy.optimize import fsolve
from scipy.optimize import root
# fsolve或root求解非线性方程组时,先把非线性方程组写成 F(x)=0 这样的形式【x:向量;F(x):向量函数】
fx = lambda x: x**980-5.01*x**979-3.388*x**977\
+7.398*x**978-x**3+5.01*x**2-7.398*x+3.388
x1 = fsolve(fx, 1.5, maxfev=420) # 函数调用420次【调用小了,会报警告】
x2 = root(fx, 1.5)
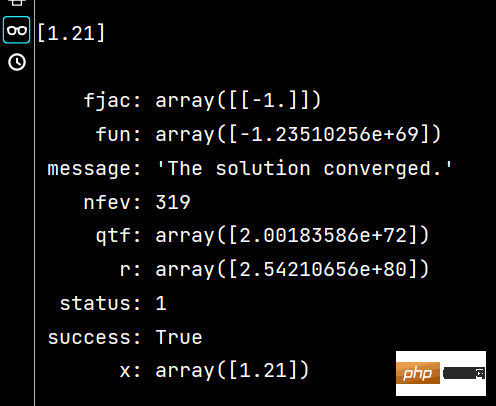
print(x1) # 相当于答案
print()
print(x2) # 相当于解题过程The results of running x1 and x2 are as follows:
1-2
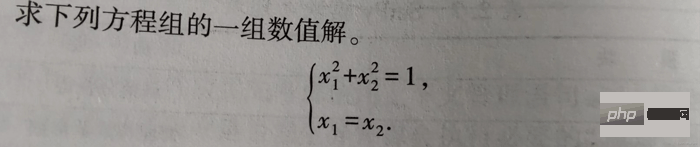
The solution code is as follows:
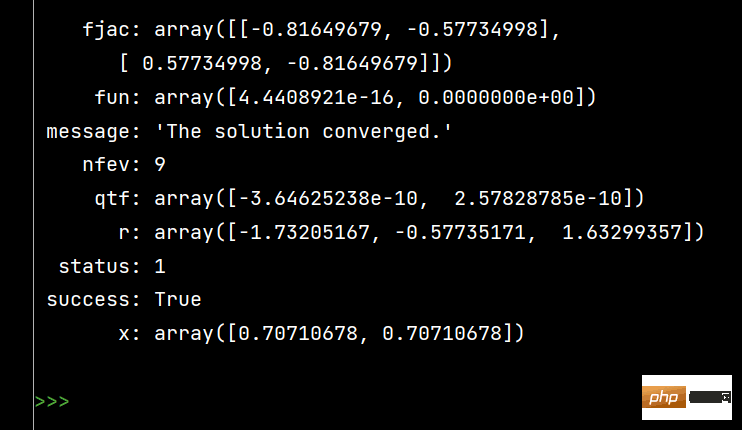
from scipy.optimize import fsolve, root fs2 = lambda s: [s[0]**2+s[1]**2-1, s[0]-s[1]] s1 = fsolve(fs2, [1, 1]) print() s2 = root(fs2, [1, 1]) print(s1) # 输出 [0.70710678 0.70710678] print() print(s2)
The effect of running s2 is as follows:
2-Integral
The scipy.integrate module provides a variety of integration modes.
Integrals are mainly divided into the following two categories:
Numerical integration of a given function
For numerical integration of given discrete points, the function has trapz
Title:
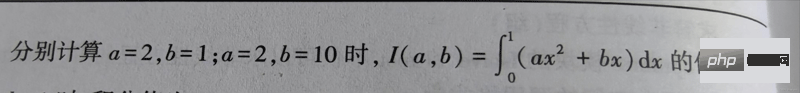
'''
函数 说明
quad(func, a, b, args) 计算一重数值积分
dblquad(func, a, b, gfun, hfun, args) 计算二重数值积分
tplquad(func, a, b, gfun, hfun, qfun, rfun) 计算三重数值积分
nquad(func, ranges, args) 计算多变量积分
'''
from scipy.integrate import quad
def func(x, a, b):
return a*x**2+b*x
z1 = quad(func, 0, 1, args=(2, 1))
z2 = quad(func, 0, 1, args=(2, 10))
print(z1) # 输出 (1.1666666666666665, 1.2952601953960159e-14)
print(z2) # 输出 (5.666666666666667, 6.291263806209221e-14)
# 注:输出的后一个值为积分值的绝对误差3-Least squares solution
# 最小二乘解 # scipy.optimize 模块求非线性方程组最小二乘解格式: ''' from scipy.optimize import least_squares least_squares(fun, x0) 注:用到loadtxt需自行准备好文件【准备文件】 ''' from scipy.optimize import least_squares import numpy as np s = np.loadtxt('data.txt') x0 = s[0] y0 = s[1] d = s[2] fs = lambda x: np.sqrt((x0-s[0])**2+(y0-s[1])**2-d) xc = least_squares(fs, np.random.rand(2)) print(xc) print() print(xc.s)
4-Maximum modular eigenvalue and corresponding eigenvector
Question:

# 4-最大模特征值及对应的特征向量
# 题目描述:求下列矩阵的最大模特征值及对应的特征向量:
from scipy.sparse.linalg import eigs
import numpy as np
m = np.array([
[1, 2, 3],
[2, 1, 3],
[3, 3, 6]
], dtype=float)
a, b = np.linalg.eig(m)
c, d = eigs(m, 1)
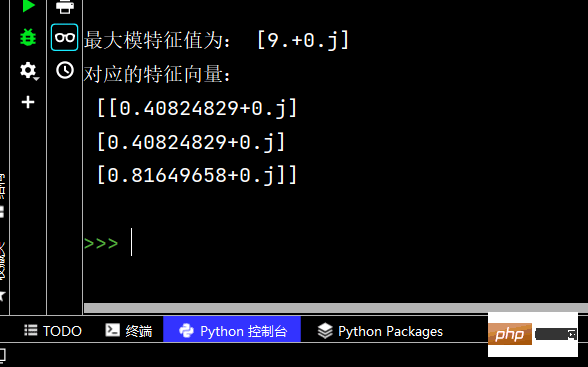
print('最大模特征值为:', c) # 输出 最大模特征值为: [9.+0.j]
print('对应的特征向量:\n', d)The running results are as follows:
Numpy Learning (continued)
# NumPy 广播(Broadcast)
# 广播是 numpy 对不同形状的数组进行数值计算的方式, 对数组的算术运算通常在相应的元素上进行。
# 如果两个数组 a 和 b 形状相同,即满足 a.shape == b.shape,那么 a*b 的结果就是 a 与 b 数组对应位相乘。
# 这要求维数相同,且各维度的长度相同。
'''
对两个数组,分别比较他们的每一个维度(若其中一个数组没有当前维度则忽略),满足:
数组拥有相同形状。
当前维度的值相等。
当前维度的值有一个是 1。
若条件不满足,抛出 "ValueError: frames are not aligned" 异常
'''
import numpy as np
a = np.array([3, 6, 9])
b = np.array([2, 4, 6])
c = a * b
print(c) # 输出 [ 6 24 54]
# 若形状不同时,numpy 将自动触发广播机制
import numpy as np
x = np.array([
[4, 2, 5],
[5, 2, 0],
[2, 6, 1],
[1, 4, 5]
])
y = np.array([3, 1, 2])
print(x+y)
yy = np.tile(y, (4, 1)) # 重复b的各个维度
print(x+yy)1 Numpy mathematical function
1-1 Trigonometric function
# NumPy 数学函数 # NumPy 包含大量的各种数学运算的函数,包括三角函数,算术运算的函数,复数处理函数等。 # 1-三角函数 # NumPy 提供了标准的三角函数:sin()、cos()、tan()。 import numpy as np lxw = np.array([0, 30, 45, 60, 90]) # sin() zx = np.sin(lxw*np.pi/180) print(zx) # 计算角度的反正弦【单位:弧度】 fzx = np.arcsin(zx) print(fzx) # 检查结果【通过转化为角度制】 jg = np.degrees(fzx) print(jg) # 输出 [ 0. 30. 45. 60. 90.] # cos() yx = np.cos(lxw*np.pi/180) print(yx) # 反余弦 fyx = np.arccos(yx) print(fyx) # 检查结果: jg2 = np.degrees(fyx) print(jg2) # 输出 [ 0. 30. 45. 60. 90.] # tan() zq = np.tan(lxw*np.pi/180) print(zq) # 反正切 fzq = np.arctan(zq) print(fzq) # 检查结果: jg3 = np.degrees(fzq) print(jg3) # 输出 [ 0. 30. 45. 60. 90.]
2-Rounding function
2-1 numpy.around()
# 2-舍入函数 # 2-1 numpy.around() ''' numpy.around() 函数返回指定数字的四舍五入值。 格式: numpy.around(a,decimals) 参数说明: a: 数组 decimals: 舍入的小数位数。 默认值为0。 如果为负,整数将四舍五入到小数点左侧的位置 ''' import numpy as np bl = np.array([15.222, 22.6555, 13.71111]) print(np.around(bl)) # 输出 [15. 23. 14.] print(np.around(bl, 2)) # 输出 [15.22 22.66 13.71] print(np.around(bl, -1)) # 输出 [20. 20. 10.]
2-2 numpy.floor()
# 2-2 numpy.floor() # numpy.floor() 返回小于或者等于指定表达式的最大整数,即向下取整 import numpy as np xx = np.array([23.3, 13.43, 2.9]) print(np.floor(xx)) # 输出 [23. 13. 2.]
2-3 numpy.ceil()
# 2-3 numpy.ceil() # numpy.ceil() 返回大于或者等于指定表达式的最小整数,即向上取整 import numpy as np xs = np.array([23.1, 23.5, 54.9]) print(np.ceil(xs)) # 输出 [24. 24. 55.]
3 Numpy arithmetic functions
NumPy arithmetic functions include simple addition Subtraction, multiplication and division: add(), subtract(), multiply() and divide()
- ##Reciprocal: reciprocal()
- Power: power()
- Remainder: mod() | remainder()
Note: The arrays must have the same The shape or conforms to the array broadcasting rules
The relevant code is as follows:
import numpy as np sz = np.arange(9, dtype=np.float_).reshape(3, 3) sz2 = np.array([5, 2, 1]) # 注:如果相除,这里是被除数的话,里面不能有0 # 数组相加 xj = np.add(sz, sz2) print(xj) # 数组相减 xj2 = np.subtract(sz, sz2) print(xj2) # 数组相乘 xc = np.multiply(sz, sz2) print(xc) # 数组相除 xc2 = np.divide(sz, sz2) print(xc2) print() # numpy.power() # numpy.power() 函数将第一个输入数组中的元素作为底数,计算它与第二个输入数组中相应元素的幂 import numpy as np m = np.array([1, 4, 8]) # 数组1 mc = np.power(m, 3) # 数组1所有元素对应的3次方 print(mc) # 输出 [ 1 64 512] m2 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) # 数组2 mc2 = np.power(m, m2) # 数组1作为底数,数组2作为幂 print(mc2) # 输出 [ 1 16 512] print() # numpy.mod() # numpy.mod() 计算输入数组中相应元素的相除后的余数 # 函数 numpy.remainder() 也产生相同的结果 import numpy as np sz1 = np.array([23, 45, 67]) sz2 = np.array([2, 3, 5]) print(np.mod(sz1, sz2)) # 输出 [1 0 2] print(np.remainder(sz1, sz2)) # 输出 [1 0 2]
#SettingWithCopyWarning of pandas
# pandas的SettingWithCopyWarning报警复现、原因、解决方案 # 读取数据 import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('nba.csv') print(df.head()) # 核心解决问题:pandas的dataframe的修改写操作,只允许在源dataframe上进行,一步到位 # 解决方法(两种): ''' 1-将get+set的两步操作,改成set的一步操作 2-若须处理筛选数据做后续的处理分析,使用copy复制dataframe ''' # pandas不允许先筛选子dataframe,在进行修改写入
Please prepare the csv file first】
Series sorting:
# Pandas 数据排序
'''
Series的排序:
Series.sort_values(ascending=True, inplace=False)
参数说明:
· ascending: 默认为True升序排序,False为False
· inplace: 是否修改原始Series
DataFrame的排序:
DataFrame.sort_values(by, ascending=True, inplace=False)
参数说明:
· by:字符串或者List<字符串>,单列排序或者多列排序
· ascending: bool或者List,升序还是降序
· inplace: 是否修改原始DataFrame
'''
# Series的排序:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('nba.csv')
print(df.head()) # 输出前五行
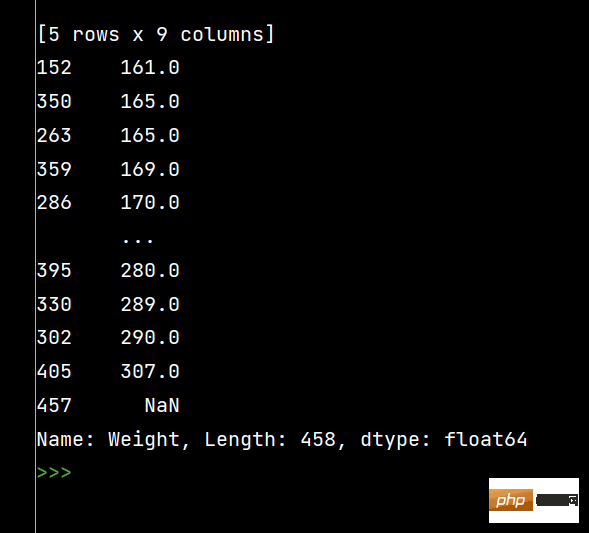
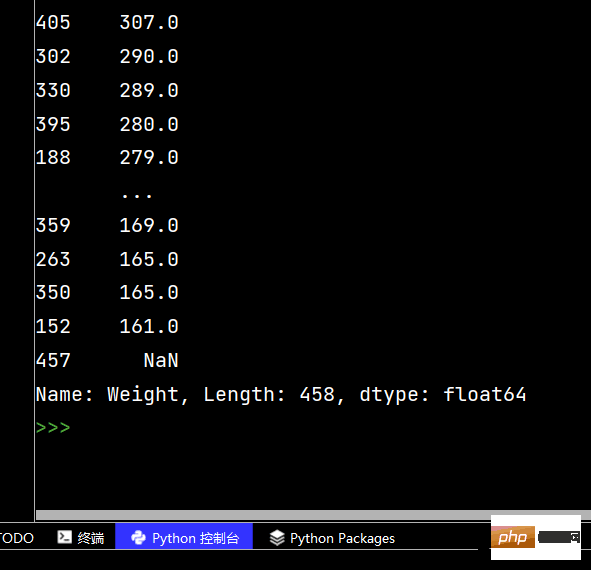
print(df['Weight'].sort_values()) # 升序排序
print(df['Weight'].sort_values(ascending=False)) # 降序排序The running results are as follows:
 ##DataFrame sorting
##DataFrame sorting
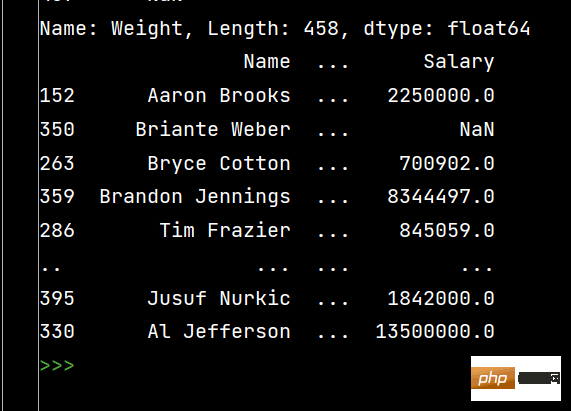
# DataFrame的排序 # 单列排序: print(df.sort_values(by='Weight'))
##
print(df.sort_values(by="Weight", ascending=False)) # 降序排序
# 多列排序: print(df.sort_values(by=['Age', 'Weight']))
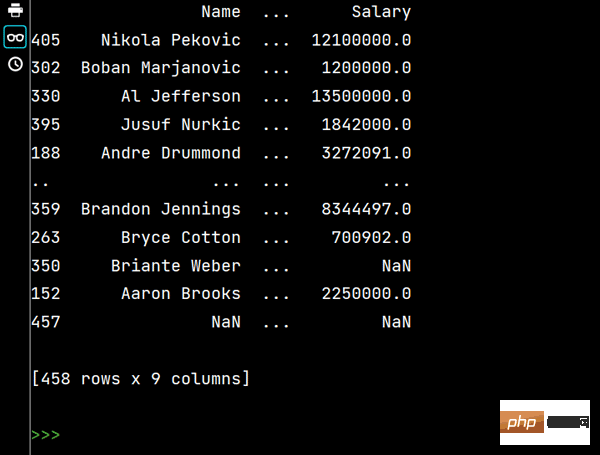
# 两个字段都是降序排序 print(df.sort_values(by=['Age', 'Weight'], ascending=False))
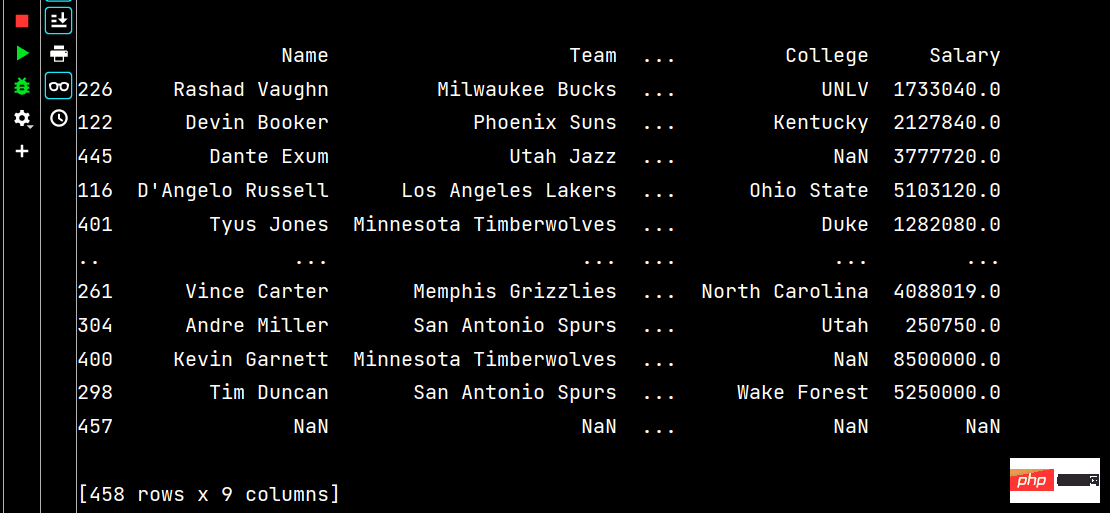
# 分别指定升序还是降序 print(df.sort_values(by=['Age', 'Weight'], ascending=[False, True]))
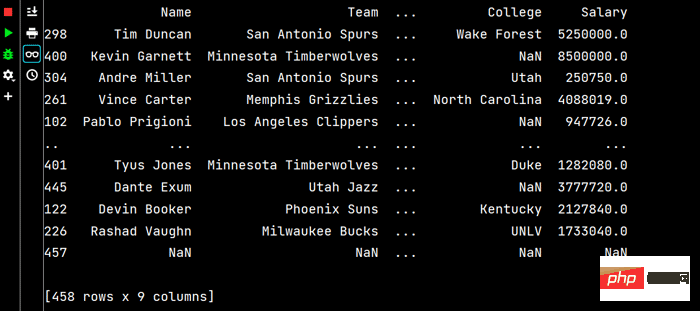
Pandas string processing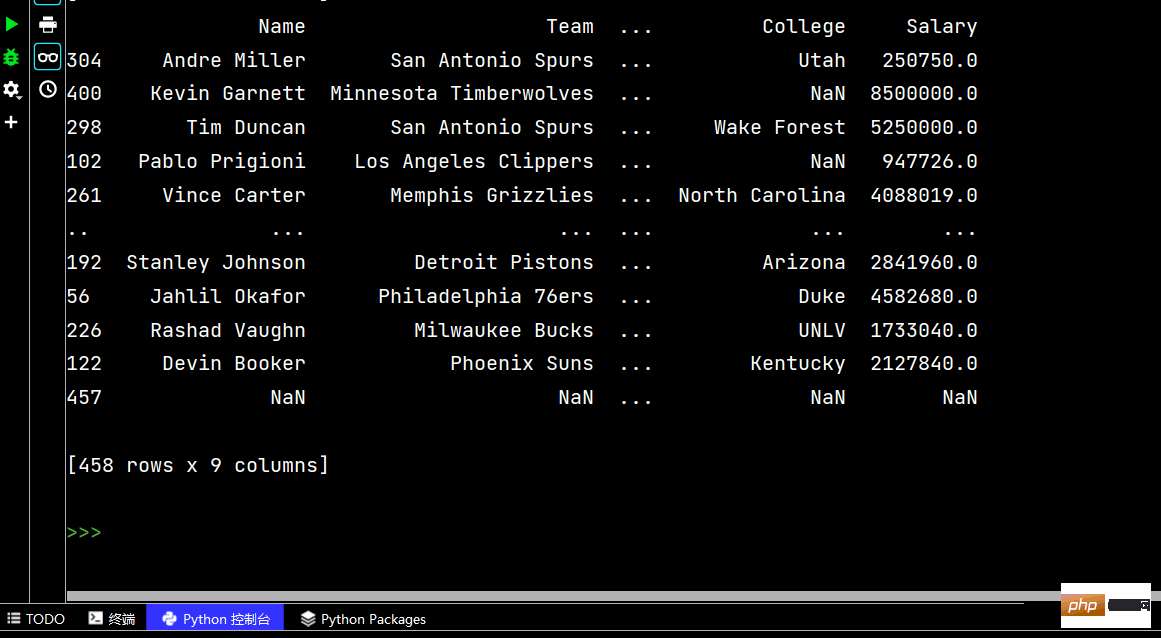
df['lrl'].str.replace("%", "").astype("int32")Copy after login# Pandas字符串处理:
'''
1-使用方法:先获取Series的属性,然后再属性上调用函数
2-只能在字符串列上使用,不能再数字列上使用
3-DataFrame没有str属性和使用
4-Series.str并不是原生Python字符串,它是封装的一套方法
'''
# 获取Series的属性
# print(df['Salary'].str) # 报错【示范】
# AttributeError: Can only use .str accessor with string values!
# AttributeError:只能使用。带字符串值的str访问器!
# 一定得是字符串列
print(df['College'].str)
# 运行结果为: <pandas.core.strings.accessor.StringMethods object at 0x00000204444EBC48>
# 判断是不是数字列
print(df['College'].str.isnumeric())
# print(df['College'].len) # 报错【示范】
# AttributeError: 'Series' object has no attribute 'len'
# AttributeError:“Series”对象没有属性“len”
Copy after login
df['lrl'].str.replace("%", "").astype("int32")# Pandas字符串处理: ''' 1-使用方法:先获取Series的属性,然后再属性上调用函数 2-只能在字符串列上使用,不能再数字列上使用 3-DataFrame没有str属性和使用 4-Series.str并不是原生Python字符串,它是封装的一套方法 ''' # 获取Series的属性 # print(df['Salary'].str) # 报错【示范】 # AttributeError: Can only use .str accessor with string values! # AttributeError:只能使用。带字符串值的str访问器! # 一定得是字符串列 print(df['College'].str) # 运行结果为: <pandas.core.strings.accessor.StringMethods object at 0x00000204444EBC48> # 判断是不是数字列 print(df['College'].str.isnumeric()) # print(df['College'].len) # 报错【示范】 # AttributeError: 'Series' object has no attribute 'len' # AttributeError:“Series”对象没有属性“len”
# 使用str的startswith、contains等得到bool的Series可以做条件查询
tj = df['Height'].str.startswith("6-2")
print(tj)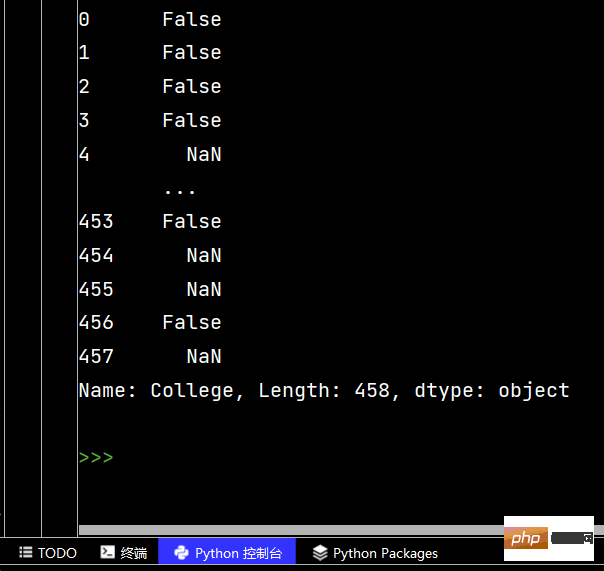
# 去掉Height中间的“-”
print(df['Height'].str.replace("-", ""))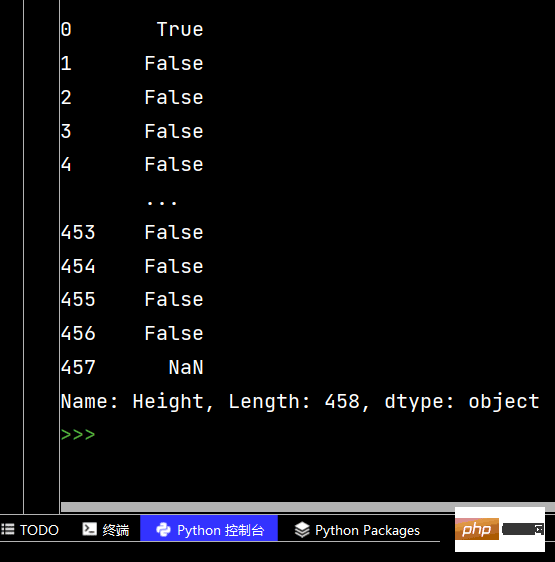
# 取第一位数
print(df['Height'].str.replace("-", "").str.slice(0, 1))
# 同上
print(df['Height'].str.replace("-", "").str[0:1])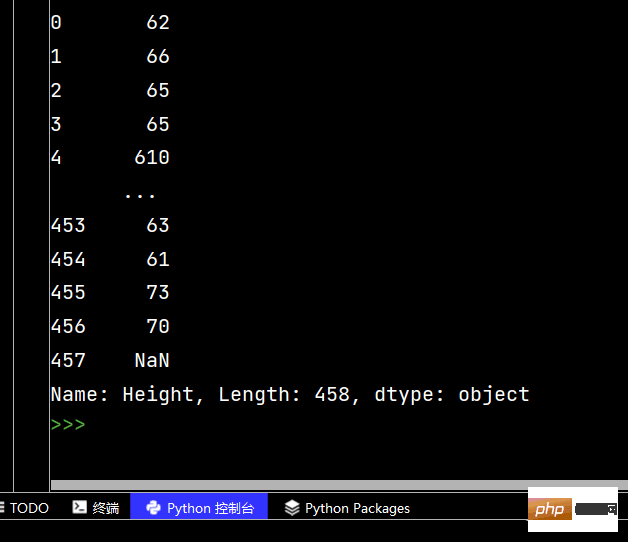
The above is the detailed content of python mathematical modeling example analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.






