Java detailed analysis of Bean scope
This article brings you relevant knowledge about java. The Spring framework is an IoC container that manages Beans, so Beans are naturally important resources in Spring. The scope of Beans is What's the meaning? How many types are there? Let’s take a look at it together, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended study: "java Video Tutorial"
Spring framework is an IoC container that manages Beans, so Beans are naturally Spring An important resource in Bean, what does the scope of Bean mean? How many types are there? Let’s take a look next.
PS: Public classes in Java can be called Beans or Java Beans.
1. Scope
The scope of a Bean refers to a certain behavior mode of the Bean in the entire Spring framework. For example, the singleton scope means that there is only one copy of the Bean in the entire Spring, and it is shared globally. When someone modifies the value, what another person reads is the modified value.
For example, we define a singleton Bean object user in Spring (the default scope is singleton). The specific implementation code is as follows:
@Component
public class UserBean {
@Bean
public User user() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("Java"); // 此行为重点:用户名称为 Java
return user;
}
}Then, in class A The user object is used and modified in class B. The specific implementation code is as follows:
@Controller
public class AController {
@Autowired
private User user;
public User getUser() {
User user = user;
user.setName("MySQL"); // 此行为重点:将 user 名称修改了
return user;
}
}Finally, the user object is also used in class B. The specific implementation code is as follows:
@Controller
public class BController {
@Autowired
private User user;
public User getUser() {
User user = user;
return user;
}
}At this time we access the B object In the getUser method, you will find that the user name at this time is "MySQL" modified in class A instead of the original "Java". This means that the Bean object user defaults to the singleton scope. If this singleton object is modified anywhere, other classes will get a modified value when called again.
2. Scope classification
In Spring, there are five common scopes of Bean:
- singleton: singleton scope;
- prototype: prototype scope (multiple instance scope);
- request: request scope;
- session: session scope;
- application: global scope .
Note: The last three scopes are only applicable to the Spring MVC framework.
2.1 singleton
Official description: (Default) Scopes a single bean definition to a single object instance for each Spring IoC container.
Description: This scope There is only one instance of the Bean below in the IoC container: the obtained Bean (that is, obtained through applicationContext.getBean and other methods) and the assembled Bean (that is, injected through @Autowired) are both the same object.
Scenario: Usually stateless beans use this scope. Stateless means that the property state of the Bean object does not need to be updated.
Note: Spring selects this scope by default.
2.2 prototype
Official description: Scopes a single bean definition to any number of object instances.
Description: Each time the Bean under this scope is New instances will be created for every request: obtaining beans (ie, obtaining them through applicationContext.getBean and other methods) and assembling beans (ie, injecting them through @Autowired) are both new object instances.
Scenario: Usually stateful beans use this scope.
2.3 request
Official description: Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a single HTTP request. That is, each HTTP request has its own instance of a bean created off the back of a single bean definition. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Description: Each Http request creates a new Bean instance, similar to prototype.
Scenario: An Http request and response shared bean.
Note: Limited to use in Spring MVC framework.
2.4 session
Official description: Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of an HTTP Session. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Description : In an Http Session, define a Bean instance.
Scenario: Shared Bean of user session, for example: recording a user’s login information.
Note: Limited to use in Spring MVC framework.
2.5 application
Official description: Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a ServletContext. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext.
Description: In an Http Servlet Context, define a Bean instance.
Scenario: Context information of Web applications, such as recording shared information of an application.
Note: Limited to use in Spring MVC framework.
3. Scope setting
We can set the scope of the Bean through the @Scope annotation. There are two ways to set it:
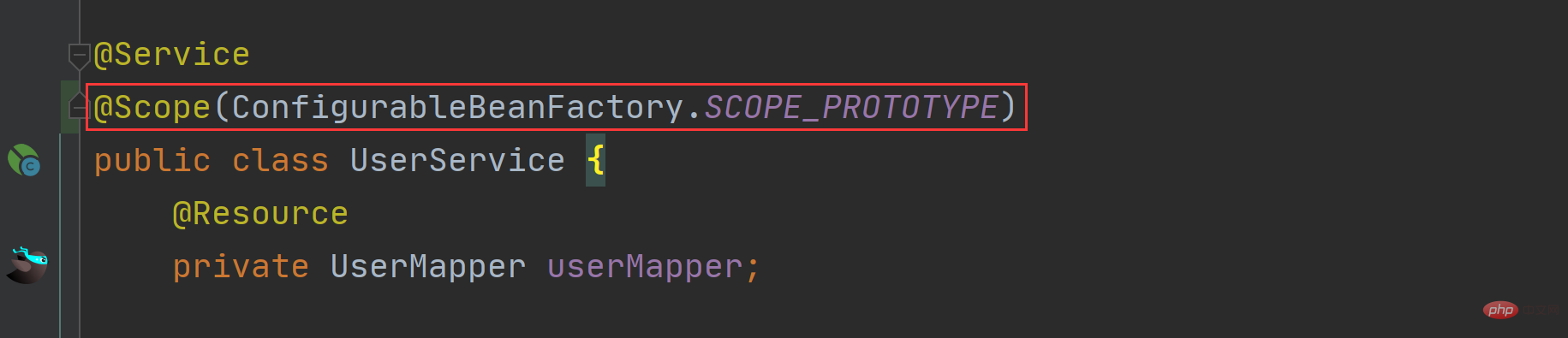
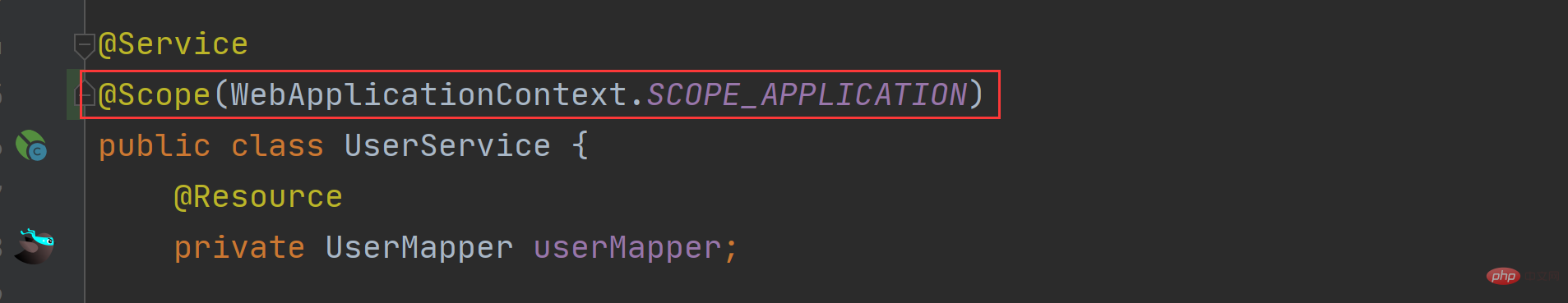
Set the scope directly Specific values, such as: @Scope("prototype");
Set the SCOPE_XXX variables provided by ConfigurableBeanFactory and WebApplicationContext, such as @Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE).
The specific setting code is as follows:

The scope of a Bean refers to a certain behavioral pattern of the Bean in the entire Spring framework. There are 5 common scopes of Bean: singleton (single case scope), prototype (prototype scope), request (request scope), session (request scope), and application (global scope). Pay attention to the last three functions. Domains are only available in the Spring MVC framework.
Recommended study: "java video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Java detailed analysis of Bean scope. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1279
1279
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Composer: Aiding PHP Development Through AI
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:27 AM
AI can help optimize the use of Composer. Specific methods include: 1. Dependency management optimization: AI analyzes dependencies, recommends the best version combination, and reduces conflicts. 2. Automated code generation: AI generates composer.json files that conform to best practices. 3. Improve code quality: AI detects potential problems, provides optimization suggestions, and improves code quality. These methods are implemented through machine learning and natural language processing technologies to help developers improve efficiency and code quality.
 What does 'platform independence' mean in the context of Java?
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What does 'platform independence' mean in the context of Java?
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Java's platform independence means that the code written can run on any platform with JVM installed without modification. 1) Java source code is compiled into bytecode, 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by the JVM, 3) The JVM provides memory management and garbage collection functions to ensure that the program runs on different operating systems.
 H5: Key Improvements in HTML5
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:26 AM
H5: Key Improvements in HTML5
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:26 AM
HTML5 brings five key improvements: 1. Semantic tags improve code clarity and SEO effects; 2. Multimedia support simplifies video and audio embedding; 3. Form enhancement simplifies verification; 4. Offline and local storage improves user experience; 5. Canvas and graphics functions enhance the visualization of web pages.
 How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
How to use MySQL functions for data processing and calculation
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
MySQL functions can be used for data processing and calculation. 1. Basic usage includes string processing, date calculation and mathematical operations. 2. Advanced usage involves combining multiple functions to implement complex operations. 3. Performance optimization requires avoiding the use of functions in the WHERE clause and using GROUPBY and temporary tables.
 Discuss situations where writing platform-specific code in Java might be necessary.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Discuss situations where writing platform-specific code in Java might be necessary.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Reasons for writing platform-specific code in Java include access to specific operating system features, interacting with specific hardware, and optimizing performance. 1) Use JNA or JNI to access the Windows registry; 2) Interact with Linux-specific hardware drivers through JNI; 3) Use Metal to optimize gaming performance on macOS through JNI. Nevertheless, writing platform-specific code can affect the portability of the code, increase complexity, and potentially pose performance overhead and security risks.
 How to use type traits in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to use type traits in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
typetraits are used in C for compile-time type checking and operation, improving code flexibility and type safety. 1) Type judgment is performed through std::is_integral and std::is_floating_point to achieve efficient type checking and output. 2) Use std::is_trivially_copyable to optimize vector copy and select different copy strategies according to the type. 3) Pay attention to compile-time decision-making, type safety, performance optimization and code complexity. Reasonable use of typetraits can greatly improve code quality.
 How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
How to configure the character set and collation rules of MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:06 PM
Methods for configuring character sets and collations in MySQL include: 1. Setting the character sets and collations at the server level: SETNAMES'utf8'; SETCHARACTERSETutf8; SETCOLLATION_CONNECTION='utf8_general_ci'; 2. Create a database that uses specific character sets and collations: CREATEDATABASEexample_dbCHARACTERSETutf8COLLATEutf8_general_ci; 3. Specify character sets and collations when creating a table: CREATETABLEexample_table(idINT
 How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
How to rename a database in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:00 PM
Renaming a database in MySQL requires indirect methods. The steps are as follows: 1. Create a new database; 2. Use mysqldump to export the old database; 3. Import the data into the new database; 4. Delete the old database.




