 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 What algorithms does the React framework have? Detailed explanation of the algorithm of react framework
What algorithms does the React framework have? Detailed explanation of the algorithm of react framework
What algorithms does the React framework have? Detailed explanation of the algorithm of react framework
This article mainly tells a detailed explanation of the principles of the react framework. There is also a lot of in-depth understanding of react below. Let us take a look at this article now
I have been working on React for more than 2 years. I love and hate this framework. Everyone is familiar with its advantages, but its shortcomings are gradually exposed. In a large-scale project , when combined with third-party frameworks such as
ReduxandReactRouter, the amount of complex business code will become very large (the front-end code is often 1.5 times the previous size). If the underlying design is not good in the early stage, you will often face the problem of low development efficiency. The following summarizes some core concepts of the React framework, I hope it will be helpful to everyone:
React diff algorithm
React’s diff algorithm It is the biggest reliance of Virtual DOM. We all know that the performance of a page is generally determined by the rendering speed and number of renderings. How to maximize the use of the diff algorithm for development? Let's first look at how it works.
Traditional diff algorithm
Calculate the minimum operation required to convert one tree structure into another tree structure. The traditional diff algorithm compares nodes sequentially through loop recursion, which is inefficient and complex. The degree reaches O(n^3), where n is the total number of nodes in the tree. In other words, if you want to display 1,000 nodes, you will have to perform billions of comparisons in sequence. This performance consumption is unacceptable for front-end projects.
Core Algorithm
As seen above, the complexity of the traditional diff algorithm is O(n^3), which obviously cannot meet the performance requirements. And React transforms O(n^3) complexity problems into O(n) complexity problems by formulating bold strategies. How did he do that?
tree diff
There are very few cross-level movement operations of DOM nodes in Web UI and can be ignored. React has made a concise and clear optimization of the tree algorithm, that is, hierarchical comparison of trees. Two trees will only compare nodes at the same level. As shown in the figure below:
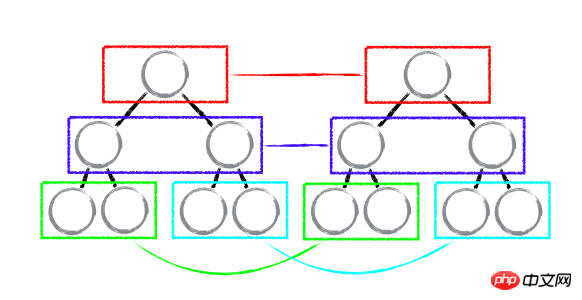
React uses updateDepth to control the level of the Virtual DOM tree. Only DOM nodes in the same color box will be compared, that is, the same color will be compared. All child nodes under a parent node. When it is found that a node no longer exists, the node and its sub-nodes will be completely deleted and will not be used for further comparisons. In this way, only one traversal of the tree is needed to complete the comparison of the entire DOM tree.
// tree diff算法实现updateChildren: function(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context) {
updateDepth++; var errorThrown = true; try { this._updateChildren(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context);
errorThrown = false;
} finally {
updateDepth--; if (!updateDepth) { if (errorThrown) {
clearQueue();
} else {
processQueue();
}
}
}
}Why should we reduce the cross-level operations of DOM nodes?
As shown below, the A node (including its sub-nodes) is moved entirely to the D node. Since React will only simply consider the position transformation of nodes at the same level, and for nodes at different levels, only creation and deletion are required. operate. When the root node finds that A has disappeared in the child node, it will destroy A directly; when D finds that there is an additional child node A, it will create a new A (including child nodes) as its child node. At this time, the execution of React diff is: create A -> create B -> create C -> delete A.
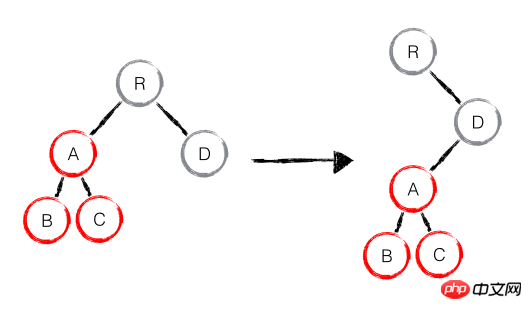
It can be found that when a node moves across levels, the imaginary move operation will not occur, but the tree with A as the root node will be completely re- Create, which is an operation that affects React performance.
component diff
Two components with the same class will generate similar tree structures, and two components with different classes will generate different tree structures.
If they are components of the same type, continue to compare
virtual DOM treeaccording to the original strategy.If not, the component will be judged as
dirty component, thereby replacing all child nodes under the entire component.For the same type of component, there may be no change in its
Virtual DOM. If you can know this for sure, you can save a lot of diff operation time, soReactAllows users to determine whether the component needs to be diffed throughshouldComponentUpdate().
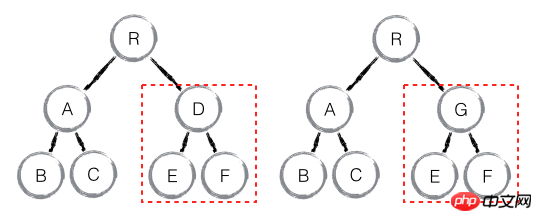
As shown above, when component D changes to component G, even if the two component have similar structures, once React determines D and G is a different type of component, so the structures of the two will not be compared, but component D will be deleted directly and component G and its sub-nodes will be re-created. Although React diff will affect performance when two component are different types but have similar structures, as the React official blog says: Different types of component There are very few opportunities for similar DOM tree, so it is difficult for such extreme factors to have a significant impact on the implementation and development process.
element diff
For a group of child nodes at the same level, they can be distinguished by a unique id. React proposes an optimization strategy: developers are allowed to add unique keys to distinguish the same group of child nodes at the same level. Although it is only a small change, the performance has undergone earth-shaking changes!
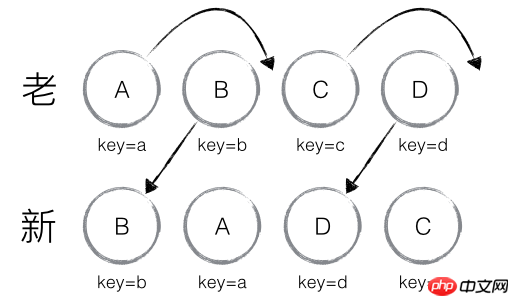
The nodes contained in the new and old sets are as shown in the figure below. The new and old sets are compared by diff. Through the key, it is found that the nodes in the new and old sets are the same nodes, so there is no need to delete and create nodes. , you only need to move the positions of the nodes in the old set and update them to the positions of the nodes in the new set. At this time, the diff result given by React is: B and D do not perform any operations, and A and C perform moving operations.
Development Suggestions
(1)[Based on tree diff] When developing components, maintaining a stable DOM structure helps maintain overall performance. In other words, do as little dynamic manipulation of the DOM structure as possible, especially movement operations. When the number of nodes is too large or the number of page updates is too large, the page freeze phenomenon is more obvious. You can hide or show nodes via CSS without actually removing or adding DOM nodes.
(2)[Based on component diff] When developing components, pay attention to using shouldComponentUpdate() to reduce unnecessary updates of components. In addition, similar structures should be encapsulated into components as much as possible, which not only reduces the amount of code, but also reduces the performance consumption of component diff.
(3)[Based on element diff] For list structures, try to reduce operations like moving the last node to the head of the list. When the number of nodes is too large or update operations are too frequent, It will affect the rendering performance of React to a certain extent.
React Lifecycle
The life cycle of React can be divided into four situations:
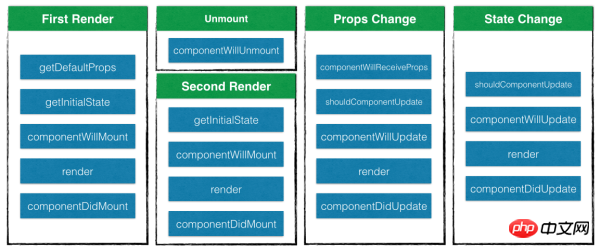
When it is loaded for the first time component, execute
getDefaultProps,getInitialState,componentWillMount,renderandcomponentDidMountin order;When unloading a component, execute
componentWillUnmount;When reloading a component, execute
getInitialState# in order. ##,componentWillMount,renderandcomponentDidMount, but does not executegetDefaultProps;- When the component is rendered again, the component receives the updated status. At this time,
componentWillReceiveProps
,shouldComponentUpdate,componentWillUpdate,renderandcomponentDidUpdate.
mountComponent Responsible for managing in the life cycle getInitialState, componentWillMount, render, and componentDidMount.
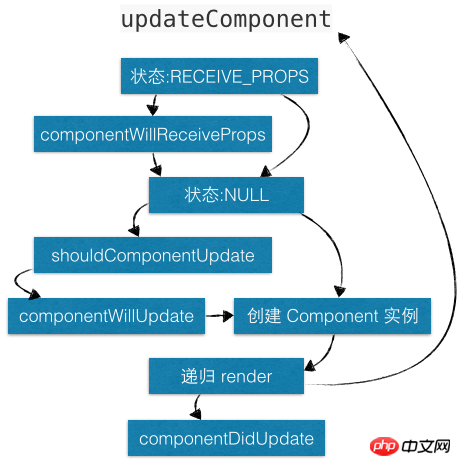
updateComponent Responsible for managing componentWillReceiveProps, shouldComponentUpdate in the life cycle , componentWillUpdate, render and componentDidUpdate.

unmountComponent is responsible for managing componentWillUnmount in the life cycle. (If you want to see more, go to the PHP Chinese website React Reference Manual column to learn)
UNMOUNTING, if componentWillUnmount## exists #, then execute; if setState is called in componentWillUnmount at this time, reRender will not be triggered. The update status is NULL, and the component uninstallation operation is completed. The implementation code is as follows: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>// 卸载组件unmountComponent: function() {
// 设置状态为 UNMOUNTING
this._compositeLifeCycleState = CompositeLifeCycle.UNMOUNTING; // 如果存在 componentWillUnmount,则触发
if (this.componentWillUnmount) { this.componentWillUnmount();
} // 更新状态为 null
this._compositeLifeCycleState = null; this._renderedComponent.unmountComponent(); this._renderedComponent = null;
ReactComponent.Mixin.unmountComponent.call(this);
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><h2 id="React生命周期总结">React生命周期总结</h2><p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn//upload/image/939/139/606/1536648897123010.png" class="lazy" title="1536648897123010.png" alt="What algorithms does the React framework have? Detailed explanation of the algorithm of react framework"/></p><table><thead><tr class="firstRow"><th>生命周期</th><th>调用次数</th><th>能否使用setState()</th></tr></thead><tbody><tr><td>getDefaultProps</td><td>1</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>getInitialState</td><td>1</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentWillMount</td><td>1</td><td>是</td></tr><tr><td>render</td><td>>=1</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentDidMount</td><td>1</td><td>是</td></tr><tr><td>componentWillReceiveProps</td><td>>=0</td><td>是</td></tr><tr><td>shouldComponentUpdate</td><td>>=0</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentWillUpdate</td><td>>=0</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentDidUpdate</td><td>>=0</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentWillUnmount</td><td>1</td><td>否</td></tr><tr><td>componentDidUnmount</td><td>1</td><td>否</td></tr></tbody></table><h1 id="setState实现机制">setState实现机制</h1><p><code>setState是React框架的核心方法之一,下面介绍一下它的原理:
// 更新 statesetState: function(partialState, callback) {
// 合并 _pendingState
this.replaceState(
assign({}, this._pendingState || this.state, partialState),
callback
);
},当调用 setState 时,会对 state 以及 _pendingState 更新队列进行合并操作,但其实真正更新 state 的幕后黑手是replaceState。
// 更新 statereplaceState: function(completeState, callback) {
validateLifeCycleOnReplaceState(this); // 更新队列
this._pendingState = completeState; // 判断状态是否为 MOUNTING,如果不是,即可执行更新
if (this._compositeLifeCycleState !== CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING) {
ReactUpdates.enqueueUpdate(this, callback);
}
},replaceState 会先判断当前状态是否为 MOUNTING,如果不是即会调用 ReactUpdates.enqueueUpdate 执行更新。
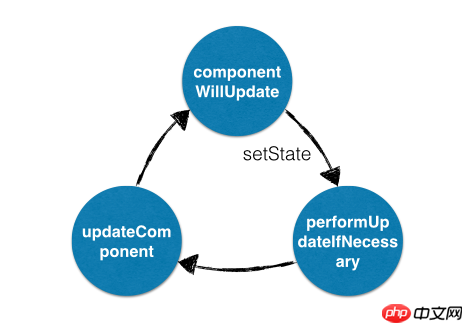
当状态不为 MOUNTING 或 RECEIVING_PROPS 时,performUpdateIfNecessary 会获取 _pendingElement、_pendingState、_pendingForceUpdate,并调用 updateComponent 进行组件更新。
// 如果存在 _pendingElement、_pendingState、_pendingForceUpdate,则更新组件performUpdateIfNecessary: function(transaction) {
var compositeLifeCycleState = this._compositeLifeCycleState; // 当状态为 MOUNTING 或 RECEIVING_PROPS时,则不更新
if (compositeLifeCycleState === CompositeLifeCycle.MOUNTING ||
compositeLifeCycleState === CompositeLifeCycle.RECEIVING_PROPS) { return;
} var prevElement = this._currentElement; var nextElement = prevElement; if (this._pendingElement != null) {
nextElement = this._pendingElement; this._pendingElement = null;
} // 调用 updateComponent
this.updateComponent(
transaction,
prevElement,
nextElement
);
}如果在
shouldComponentUpdate或componentWillUpdate中调用setState,此时的状态已经从RECEIVING_PROPS -> NULL,则performUpdateIfNecessary就会调用updateComponent进行组件更新,但updateComponent又会调用shouldComponentUpdate和componentWillUpdate,因此造成循环调用,使得浏览器内存占满后崩溃。
开发建议
不建议在 getDefaultProps、getInitialState、shouldComponentUpdate、componentWillUpdate、render 和 componentWillUnmount 中调用 setState,特别注意:不能在 shouldComponentUpdate 和 componentWillUpdate中调用 setState,会导致循环调用。
本篇文章到这就结束了(想看更多就到PHP中文网React使用手册栏目中学习),有问题的可以在下方留言提问。
The above is the detailed content of What algorithms does the React framework have? Detailed explanation of the algorithm of react framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 Groundbreaking CVM algorithm solves more than 40 years of counting problems! Computer scientist flips coin to figure out unique word for 'Hamlet'
Jun 07, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Groundbreaking CVM algorithm solves more than 40 years of counting problems! Computer scientist flips coin to figure out unique word for 'Hamlet'
Jun 07, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Counting sounds simple, but in practice it is very difficult. Imagine you are transported to a pristine rainforest to conduct a wildlife census. Whenever you see an animal, take a photo. Digital cameras only record the total number of animals tracked, but you are interested in the number of unique animals, but there is no statistics. So what's the best way to access this unique animal population? At this point, you must be saying, start counting now and finally compare each new species from the photo to the list. However, this common counting method is sometimes not suitable for information amounts up to billions of entries. Computer scientists from the Indian Statistical Institute, UNL, and the National University of Singapore have proposed a new algorithm - CVM. It can approximate the calculation of different items in a long list.
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React combines JSX and HTML to improve user experience. 1) JSX embeds HTML to make development more intuitive. 2) The virtual DOM mechanism optimizes performance and reduces DOM operations. 3) Component-based management UI to improve maintainability. 4) State management and event processing enhance interactivity.
 Java Framework Learning Roadmap: Best Practices in Different Domains
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:53 PM
Java Framework Learning Roadmap: Best Practices in Different Domains
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:53 PM
Java framework learning roadmap for different fields: Web development: SpringBoot and PlayFramework. Persistence layer: Hibernate and JPA. Server-side reactive programming: ReactorCore and SpringWebFlux. Real-time computing: ApacheStorm and ApacheSpark. Cloud Computing: AWS SDK for Java and Google Cloud Java.
 React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React is the preferred tool for building interactive front-end experiences. 1) React simplifies UI development through componentization and virtual DOM. 2) Components are divided into function components and class components. Function components are simpler and class components provide more life cycle methods. 3) The working principle of React relies on virtual DOM and reconciliation algorithm to improve performance. 4) State management uses useState or this.state, and life cycle methods such as componentDidMount are used for specific logic. 5) Basic usage includes creating components and managing state, and advanced usage involves custom hooks and performance optimization. 6) Common errors include improper status updates and performance issues, debugging skills include using ReactDevTools and Excellent





