Python web server related knowledge points
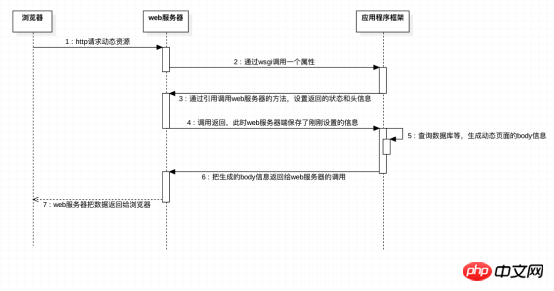
1. The process of browser requesting dynamic pages
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])return 'Hello World!'- environ: a dict object containing all HTTP request information;
- start_response: a function that sends an HTTP response.
import time,multiprocessing,socket,os,reclass MyHttpServer(object):def __init__(self):
serveSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.serveSocket = serveSocket
self.HTMLPATH = './html'def bind(self,port=8000):
self.serveSocket.bind(('',port))def start(self):
self.serveSocket.listen()while True:
clientSocket, clientAddr = self.serveSocket.accept()
print(clientSocket)
multiprocessing.Process(target=self.serveHandler, args=(clientSocket, clientAddr)).start()
clientSocket.close()def serveHandler(self,clientSocket,clientAddr):try:
recvData = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode('gbk')
fileName = re.split(r' +', recvData.splitlines()[0])[1]
filePath = self.HTMLPATHif fileName.endswith('.py'):try:
pyname=fileName[1:-3]# 导入
pyModule = __import__(pyname)
env={}
responseBody = pyModule.application(env,self.startResponse)
responseLine = self.responseLine
responseHeader = self.responseHeaderexcept ImportError:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date: %s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '<h1>很抱歉,服务器中找不到你想要的内容<h1>'else:if '/'== fileName:
filePath += '/index.html'else:
filePath += fileNametry:
file = None
file =open(filePath,'r',encoding='gbk')
responseBody = file.read()
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date:%s' % time.ctime()except FileNotFoundError:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date:%s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '很抱歉,服务器中找不到你想要的内容'finally:if (file!=None) and (not file.closed):
file.close()except Exception as ex:
responseLine = 'HTTP/1.1 500 ERROR'
responseHeader = 'Server: ererbai' + os.linesep
responseHeader += 'Date: %s' % time.ctime()
responseBody = '服务器正在维护中,请稍后再试。%s'%exfinally:
senData = responseLine + os.linesep + responseHeader + os.linesep + os.linesep + responseBody
print(senData)
senData = senData.encode('gbk')
clientSocket.send(senData)if (clientSocket!=None) and ( not clientSocket._closed):
clientSocket.close()def startResponse(self,status,responseHeaders):
self.responseLine = status
self.responseHeader = ''for k,v in responseHeaders:
kv = k + ':' + v + os.linesep
self.responseHeader += kvif __name__ == '__main__':
server = MyHttpServer()
server.bind(8000)
server.start()- index.html
<html><head><title>首页-毕业季</title><meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=gbk"></head><body>我们仍需共生命的慷慨与繁华相爱,即使岁月以刻薄和荒芜相欺。</body></html>
- biye.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="gbk"><title>毕业季</title></head><body><br>当年以为六月不过也很平常<br>当自己真正经历了毕业<br>才知道偶尔看到六月毕业季等字里所流露的种种想要重温却不敢提及的回忆<br>毕业了<br>那个夏天,我的毕业季,我的青春年少<br>六月<br>有人笑着说解脱,有人哭着说不舍<br>那年,<br>你对我说的你好<br>在不知不觉中<br>变成了<br>再见。</body></html>

biyeji.png
import timedef application(env,startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server','bfe/1.0.8.18'),('Date','%s'%time.ctime()),('Content-Type','text/plain')]
startResponse(status,responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBodyCopy after login
Access results:import timedef application(env,startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server','bfe/1.0.8.18'),('Date','%s'%time.ctime()),('Content-Type','text/plain')]
startResponse(status,responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBody
Home page

biye.html
 ##mytime.py
##mytime.py'''
自定义的符合wsgi的框架
'''import timeclass Application(object):def __init__(self, urls):'''框架初始化的时候需要获取路由列表'''
self.urls = urlsdef __call__(self, env, startResponse):'''
判断是静态资源还是动态资源。
设置状态码和响应头和响应体
:param env:
:param startResponse:
:return:
'''# 从请求头中获取文件名
fileName = env.get('PATH_INFO')# 判断静态还是动态if fileName.startwith('/static'):
fileName = fileName[7:]if '/' == fileName:
filePath += '/index.html'else:
filePath += fileNametry:
file = None
file = open(filePath, 'r', encoding='gbk')
responseBody = file.read()
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]except FileNotFoundError:
status = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]
responseBody = '<h1>找不到<h1>'finally:
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)if (file != None) and (not file.closed):
file.close()else:
isHas = False # 表示请求的名字是否在urls中,True:存在,False:不存在for url, func in self.urls:if url == fileName:
responseBody = func(env, startResponse)
isHas = Truebreakif isHas == False:
status = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'ererbai')]
responseBody = '<h1>找不到<h1>'
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)return responseBodydef mytime(env, startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'time')]
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)
responseBody = str(time.ctime())return responseBodydef mynews(env, startResponse):
status = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK'
responseHeaders = [('Server', 'news')]
startResponse(status, responseHeaders)
responseBody = str('xx新闻')return responseBody'''路由列表'''
urls = [
('/mytime', mytime),
('/mynews', mynews)
]
application = Application(urls)The above is the detailed content of Python web server related knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.






