 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Firefox event processing automatically finds the event function (for onclick=foo())_javascript skills
Firefox event processing automatically finds the event function (for onclick=foo())_javascript skills
Firefox event processing automatically finds the event function (for onclick=foo())_javascript skills
IE and firefox event processing
In IE, the event object is saved and maintained as a global variable. All browser events, whether triggered by the user
or other events, will update the window.event object. So in the code, you can easily get the event object by simply calling window.event
, and then use event.srcElement to get the element that triggered the event for further processing
In ff, the event object is not a global object, generally In this case, if it happens on-site and is used on-site, ff will automatically pass the event object
to the corresponding event processing function. In the code, the first parameter of the function is the event object under ff.
The above is my personal understanding of the event processing methods under the two browsers. It may not be very clear. I wrote some code to
explain it in detail
<script> <br>window.onload=function(){ <br>document.getElementById("btn1").onclick=foo1 <br>document.getElementById("btn2").onclick=foo2 <br>document.getElementById("btn3").onclick=foo3 <br>} <br>function foo1(){ <br>//In ie, window.event makes the global object <br>alert(window.event) // Under ie, "[object]" is displayed, and under ff, "undefined" is displayed <br> //In ff, the first parameter automatically changes from the event object <br>alert(arguments[0]) // Under ie, it displays "undefined", under ff, it displays "[object]" <br>} <br>function foo2(e){ <br>alert(window.event) // Under ie, "[object]" is displayed, and under ff, "undefined" is displayed <br>//Note, I have never passed parameters to foo2. Now ff automatically passes parameters to foo2, and the passed parameter e is the event object <br>alert(e) // Under ie, it displays "undefined", under ff, it displays "[object]" <br>} <br>function foo3 (){ //Compatible with both ie and ff writing methods, take the event object <br>alert(arguments[0] || window.event) // Under both ie and ff, "[object]" is displayed <br>var evt =arguments[0] || window.event <br>var element=evt.srcElement || evt.target //Get btn3 object under ie and ff <br>alert(element.id) // btn3 <br>} <br></script>
Seeing this, we seem to have understood the event handling methods of ie and ff, and have found a solution.
But. . . . It's not over yet.
Look at the code
<script> <br>function foo(){ <br>alert(arguments[0] || window.event) <br>} <br></script>
Unfortunately, the result foo gives us is undefined, not the expected object
The reason is the way the event is bound
onclick=" foo()" is executed directly. The foo() function does not have any parameters.
In this case, firefox has no chance to pass any parameters to foo
In this case, btn.onclick=foo, because it is not directly Only after executing the function does firefox have the opportunity to pass parameters to foo
Solution:
Method 1: A stupid method. Since firefox has no chance to pass parameters, be diligent and pass them yourself
Method 2: Automatic Find
<script> <br>function foo4(){ <br>var evt=getEvent() <br>var element=evt.srcElement || evt.target <br>alert(element.id) <br>} <br>function getEvent(){ //compatible with both ie and ff writing <br>if(document.all) return window.event; <br>func=getEvent .caller; <br>while(func!=null){ <br>var arg0=func.arguments[0]; <br>if(arg0){ <br>if((arg0.constructor==Event || arg0 .constructor ==MouseEvent) <br>|| (typeof(arg0)=="object" && arg0.preventDefault && arg0.stopPropagation)){ <br>return arg0; <br>} <br>} <br>func =func.caller; <br>} <br>return null; <br>} <br></script>
Method 2 was originally created by lostinet, and I have improved on it. The original function is as follows:
var arg0=func.arguments[0];
if(arg0)
{
if(arg0.constructor==Event)
return arg0;
}
func=func.caller;
}
return null;
}
Simple summary:
Both of the above In the solution, event processing under ff and ie is correctly handled (whether it is onclick="foo()" or onclick=foo)
But I personally recommend using the getEvent() method to handle event issues uniformly.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to remove Firefox Snap in Ubuntu Linux?
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
How to remove Firefox Snap in Ubuntu Linux?
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:00 PM
To remove FirefoxSnap in Ubuntu Linux, you can follow these steps: Open a terminal and log in to your Ubuntu system as administrator. Run the following command to uninstall FirefoxSnap: sudosnapremovefirefox You will be prompted for your administrator password. Enter your password and press Enter to confirm. Wait for command execution to complete. Once completed, FirefoxSnap will be completely removed. Note that this will remove versions of Firefox installed via the Snap package manager. If you installed another version of Firefox through other means (such as the APT package manager), you will not be affected. Go through the above steps
 Python GUI programming: Get started quickly and easily create interactive interfaces
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Python GUI programming: Get started quickly and easily create interactive interfaces
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
A brief introduction to python GUI programming GUI (Graphical User Interface, graphical user interface) is a way that allows users to interact with computers graphically. GUI programming refers to the use of programming languages to create graphical user interfaces. Python is a popular programming language that provides a rich GUI library, making Python GUI programming very simple. Introduction to Python GUI library There are many GUI libraries in Python, the most commonly used of which are: Tkinter: Tkinter is the GUI library that comes with the Python standard library. It is simple and easy to use, but has limited functions. PyQt: PyQt is a cross-platform GUI library with powerful functions.
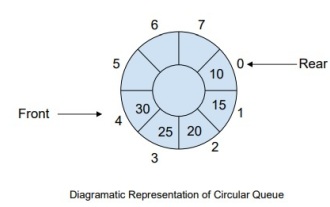 How to manage a complete circular queue of events in C++?
Sep 04, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
How to manage a complete circular queue of events in C++?
Sep 04, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
Introduction CircularQueue is an improvement on linear queues, which was introduced to solve the problem of memory waste in linear queues. Circular queues use the FIFO principle to insert and delete elements from it. In this tutorial, we will discuss the operation of a circular queue and how to manage it. What is a circular queue? Circular queue is another type of queue in data structure where the front end and back end are connected to each other. It is also known as circular buffer. It operates similarly to a linear queue, so why do we need to introduce a new queue in the data structure? When using a linear queue, when the queue reaches its maximum limit, there may be some memory space before the tail pointer. This results in memory loss, and a good algorithm should be able to make full use of resources. In order to solve the waste of memory
 Can mozilla firefox be uninstalled?
Mar 15, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
Can mozilla firefox be uninstalled?
Mar 15, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
Mozilla Firefox can be uninstalled; Firefox is a third-party browser and can be uninstalled if it is not needed. Uninstallation method: 1. In the Start menu, click "Windwos System" - "Control Panel"; 2. In the "Control Panel" interface, click "Programs and Features"; 3. In the new interface, find and double-click Firefox Browser icon; 4. In the uninstall pop-up window, click "Next"; 5. Click "Uninstall".
 Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event
May 14, 2023 pm 05:40 PM
Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event
May 14, 2023 pm 05:40 PM
Event processing library in PHP8.0: Event With the continuous development of the Internet, PHP, as a popular back-end programming language, is widely used in the development of various Web applications. In this process, the event-driven mechanism has become a very important part. The event processing library Event in PHP8.0 will provide us with a more efficient and flexible event processing method. What is event handling? Event handling is a very important concept in the development of web applications. Events can be any kind of user row
 Firefox 113 new features: support for AV1 animations, enhanced password generator and picture-in-picture features
Mar 05, 2024 pm 05:20 PM
Firefox 113 new features: support for AV1 animations, enhanced password generator and picture-in-picture features
Mar 05, 2024 pm 05:20 PM
According to recent news, while Mozilla released the stable version of Firefox 112, it also announced that the next major version, Firefox 113, has entered the Beta channel and supports AV1 animations, enhanced password generator and picture-in-picture features. The main new functions/features of Firefox 113 are as follows: Support for AV1 format animated images (AVIS); Enhance the security of the password generator by introducing special characters; Enhance the picture-in-picture function, support rewind, display video time, and enable full screen more easily Mode provides official DEB installation files for Debian and Ubuntu distributions. Updated bookmark import feature, icons for imported bookmarks are supported by default. Hardware accelerated AV1 video decoding is enabled by default on supported hardware using w
 How to use Mozilla Firefox in Scrapy to solve the problem of scanning QR code to log in?
Jun 22, 2023 pm 09:50 PM
How to use Mozilla Firefox in Scrapy to solve the problem of scanning QR code to log in?
Jun 22, 2023 pm 09:50 PM
For crawlers to crawl websites that require login, verification code or scan code login is a very troublesome problem. Scrapy is a very easy-to-use crawler framework in Python, but when processing verification codes or scanning QR codes to log in, some special measures need to be taken. As a common browser, Mozilla Firefox provides a solution that can help us solve this problem. The core module of Scrapy is twisted, which only supports asynchronous requests, but some websites require the use of cookies and
 What is the meaning of bubbling events
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:53 AM
What is the meaning of bubbling events
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:53 AM
Bubbling events mean that in web development, when an event is triggered on an element, the event will propagate to upper elements until it reaches the document root element. This propagation method is like a bubble gradually rising from the bottom, so it is called a bubbling event. In actual development, knowing and understanding how bubbling events work is very important to handle events correctly. The following will introduce the concept and usage of bubbling events in detail through specific code examples. First, we create a simple HTML page with a parent element and three children





