 web3.0
web3.0
 What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis
What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis
What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis
The English name of cryptocurrency arbitrage is Crypto Arbitrage, which refers to a strategy of trading on two exchanges at the same time and making profits by locking the spread on both sides.
Cryptocurrency investment has large fluctuations and high risks. Investors want to find strategies that can reduce risks and make profits. Cryptocurrency arbitrage is one of the types of strategies, but is arbitrage strategies really necessarily low risk?

What is cryptocurrency arbitrage?
When there are different quotes for the same cryptocurrency pair, buy low and sell high at the same time, and use risk-free or extremely low risk to earn the profits of the spread, which is cryptocurrency arbitrage.
Arbitrage transactions in the cryptocurrency field generally refer to buying and selling cryptocurrencies on different exchanges. When the pricing of these cryptocurrencies varies, the transactions that use the price difference and buy low and sell high as at the same time as possible to make profits are called cryptocurrency arbitrage.
The execution method is to find 2 identical products, or very high-related products, but have different quotes from each other. If you buy a low price and sell a high price, the middle price difference will deduct the transaction cost. This is the profit of cryptocurrency arbitrage transactions.
Cryptocurrencies with the same or high correlation, different prices will occur between different exchanges and between different currency pairs, and thus different types of arbitrage strategies are derived, with different difficulties and competitiveness, and with different transaction costs.
The following will introduce these different types of cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies.
Supplement: What is arbitrage?
The English name of arbitrage is Arbitrage. Arbitrage trading strategy refers to a trading method in which the same assets are bought and sold in different markets and make profits by using price differences.
Arbitrage trading may occur in any financial instrument, and arbitrage opportunities most often occur in stocks, futures, foreign exchange and other commodities.
In the efficiency market hypothesis, the prices of the same commodity in different markets should be the same, and in theory there will be no arbitrage opportunities. But that's not the case.
In the real world, although the market is efficient in the long run, it may be inefficient in the short term. The reason may be due to factors such as market sentiment, regulations, liquidity, etc. Arbitrage trading exists due to short-term market inefficiency.
In the field of financial economics, arbitrage theory must be to ensure risk-free profit (Risk Free Profit).
But in the actual market, arbitrage will still be accompanied by risks, such as time difference, liquidity issues, handling fees, etc., which will be introduced in detail later.
The 4 most common cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies
Cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies are not just about trading between different exchanges to make a difference.
Here are the 4 most common cryptocurrency arbitrage types:
1. Exchange arbitrage
Exchange arbitrage, also commonly known as brick-moving arbitrage, is like moving bricks, moving assets between different exchanges back and forth.
Cryptocurrencies are not traded in a centralized market, and on different exchanges, the same cryptocurrency pairs, may have completely different quotes. The reason may be factors such as different participants and liquidity on different exchanges, or prices are updated asynchronously.
Therefore, when there is a price difference between different exchanges and the same cryptocurrency pair, investors between different exchanges can buy at low-priced exchanges and sell at high-priced exchanges to earn the price difference.
Examples of the principle of arbitrage operation on exchanges:
Suppose a certain moment:
Exchange A, the price of BTC/USDT is 87,000.
B Exchange, the price of BTC/USDT is 87,500.
At this time, the investor used 87,000 USDT to buy BTC on Exchange A, and at the same time, he sold BTC on Exchange B to get 87,500 USDT. He invested 87,000 USDT but obtained 87,500 USDT. After deducting the necessary costs, the exchange arbitrage.
The exchange brick-moving arbitrage can be divided into direct brick-moving and hedging brick-moving:
- Cross-Exchange Arbitrage: First buy low on Exchange A, then transfer to Exchange B and sell high, but transfer may cause a time difference and you have to bear the risk of intermediate price changes.
- Hedged Arbitrage / Market-Neutral Arbitrage: Trading is executed on two exchanges at the same time, one buys and one sells, the price difference is not affected by price fluctuations, and both exchanges require that they own cryptocurrency assets at the same time. Those who sell can borrow first and then sell it, and wait for the assets to be transferred from another exchange and then repaid, achieving the shorting effect. Shorting transactions may increase the interest cost.
"Simultaneous trading" is the core of exchange arbitrage
Real brick-moving transactions refer to buying and selling on two exchanges at the same time to make profits by locking the price difference, which is in line with the principle of " risk-free profit " of arbitrage.
Simply buying first and then selling, and there is a time difference between buying and selling, rather than trading at the same time, it is speculation rather than arbitrage, because the price is not locked and the risk is higher.
If you buy first and then sell (buy on Exchange A, transfer to Exchange B and then sell), there will be a risk of price fluctuation, and it will take time to complete the transfer. When the assets are transferred to Exchange B and sell for sale, the market price has changed.
In particular, cryptocurrency prices fluctuate greatly, which does not conform to the arbitrage spirit of "locking the price spread".
Physically, it is indeed not easy for us to achieve 100% simultaneous transactions, but we can achieve approximation or perform through procedural execution.
2. Triangle arbitrage
When trading three different trading pairs across currencies in the same exchange, when there is a pricing error, earn the spread to make a profit.
Triangle arbitrage trading opportunities are generally fewer, because this opportunity is relatively more likely to be arbitrage, so the competition is fierce.
Examples of the operating principle of triangle arbitrage:
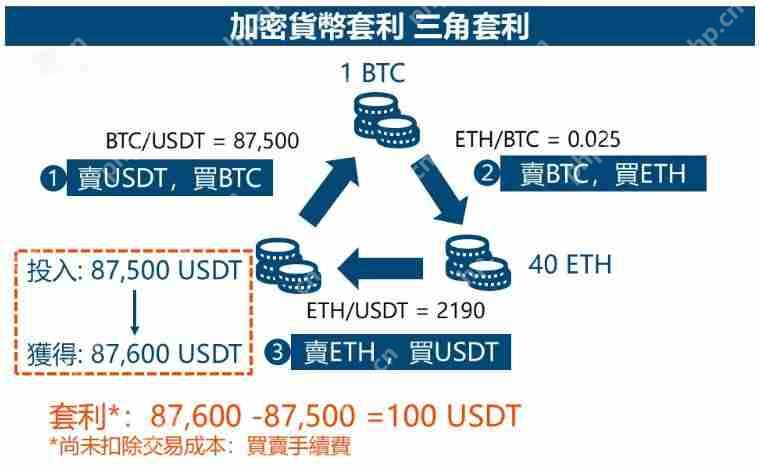
Assumptions:
- BTC/USDT price = 87,500
- ETH/BTC price = 0.025
- ETH/USDT price = 2190
Operation steps:
- Buy 1 BTC with 87500 USDT
- Buy 40 ETH with 1 BTC
- Sell 40 ETH Buy back 87,600 USDT
Profit: 87,600 USDT – 87,500 USDT = 100 USDT
The final USDT is obtained more than the USDT you invested in at the beginning. If you still make a profit after deducting transaction costs, it means that the arbitrage is successful.
3. Spot contract arbitrage
Spot and futures of cryptocurrency are usually highly correlated (but not necessarily 100% related).
Therefore, when shorting spot/long contracts or long spot/short contracts at the same time, the risk of price fluctuations will theoretically be locked.
As cryptocurrency contract transactions are perpetual contract transactions, there will be funding rates (Funding Rate). After locking in the risk of the price spread, it is possible to earn funds rates.
Cryptocurrency spot contract arbitrage is mainly not affected by price fluctuations and earn perpetual contract funding rates
Currently, the mainstream contract transactions in cryptocurrencies will not expire, so they are designed with a perpetual contract funding rate. According to the supply demand of long and short contracts, one of the parties will decide to go long or short, and pay a fee to the other party regularly (for example, the funding rate may be 0.005% every 8 hours, 0.015% per day, etc.).
The capital fee rate will float according to the current supply and demand situation, and the fee rate may be high and low.
In theory, you can continue to earn the capital rate by extending it for a long time, but this is limited to the opportunity to receive the capital rate, and sometimes it may also cost you money, causing losses.
In the market, sometimes the long contracts may pay to contract short sellers (fewer short sellers), but sometimes the other hand may pay to long sellers (fewer long sellers). Therefore, spot contract arbitrage can be profitable in some cases, but it is not always completely risk-free, but depends on the current capital fee rate.
In terms of experience, in the long market, spot contract arbitrage has more opportunities to make profits and earn capital fees. At this time, most of the time in the market, the long ones are higher than those in the short ones.
However, in the short market, spot contract arbitrage may also suffer losses, and the capital fee rate becomes negative.
Examples of the operation principle of spot contract arbitrage:
Assumptions:
- Spot BTC price = 87,500 USDT
- Perpetual contract BTC price = 87,550 USDT
- Fund rate = 0.02% paid every 8 hours (contract long, pay to contract short)
Operation steps:
- Buy 1BTC in the spot market
- Short 1BTC in the Perpetual Contract Market
- Funding rate, you can receive every day: 0.02% × 24 ÷ 8 × 87,550 = 52.53 /
Annualized rate of return*: 52.53 × 365 ÷ (87,500 87,550) = 10.95% *The actual remuneration must be deducted from transaction costs.
As long as the spot and contract prices fluctuate consistently and there is no big deviation, there is no need to worry about changes in the BTC market price, because you are already long for spot and short contracts to lock in the price difference and become a neutral strategy (delta neutral).
Assuming that for 10 days, spot BTC will rise to 87,900, and contract BTC will also rise to 87,950, assuming that the capital fee rate will remain unchanged during the period (0.02%/8 hours) at this time:
- Spot unrealized income = 87,900 – 87,500 = 400
- Unrealized income from contract = 87,550 – 87,950 = -400
- Unrealized profits for futures and contracts = 400 (-400) = 0
- Fund rate income = 0.02%× 24 ÷ 8 × 87550 ×10 days = 525.3*
- Final Profit and Loss = 400 – 400 525.3 = 525.3 USDT
*Teaching examples: Use the USDT value of BTC to roughly estimate the value, and the calculation does not take into account the increase in BTC during the period.
When the principal remains unchanged, the funding rate of the perpetual contract can be obtained.
In actual operation, there will still be handling fee loss costs, and you also need to pay attention to the direction risks of the capital rate. The capital rate will change with the market conditions, and sometimes it will reverse to the short seller pays to the long seller.
4. Spot futures arbitrage
Spot futures arbitrage is to use the price difference between the same asset in "spot" and "futures" to converge to conduct arbitrage. First buy low and sell high to lock the price difference. When the futures expire, the theoretical price difference will converge to 0, and then simultaneously close the position and hold it to achieve profits.
The futures mentioned here are cryptocurrency futures (such as futures issued by CME), rather than cryptocurrency contracts. The futures and contracts are both called Futures in English, but there are differences in details between the two.
- Futures will expire, the contract specifications are large, there is no capital fee rate, and trading at futures brokers.
- Perpetual contracts, contract specifications are flexible, with funding rates, and are usually traded on cryptocurrency exchanges.
Examples of the operating principles of spot futures arbitrage:
Assumptions:
- Cryptocurrency Exchange BTC Spot Price = 87,500
- Futures Exchange BTC Futures Price = 87,700
- BTC futures expiration settlement date is 2 weeks later
Operation steps:
- Buy 1BTC in the spot market
- Short 1BTC in the futures market
- Spot and futures are closed simultaneously during settlement in 2 weeks
During settlement, you can make a profit regardless of the BTC market price. Use the following 3 different maturity date BTC prices as an example to illustrate:
Assumption 1: BTC rises sharply to 100,000, and when futures expire, it returns to the spot price, and the futures and spot prices are consistent.
- Spot income = 100,000 – 87,500 = 12,500
- Futures earnings = 87,700 – 100,000 = -12,300
- Realize profit* = 125,00 (-12,300) = 200 *The actual reward must be deducted from transaction costs
Assumption 2: BTC falls to 80,000, and the futures return to the spot price when they expire.
- Spot income = 80,000 – 87,500 = -7,500
- Futures Income = 87,700 – 80,000 = 7,700
- Realize profit* = -7,500 7,700 = 200 *The actual reward must be deducted from transaction costs
Assumption 3: BTC price has not fluctuated significantly and remains at 87,600, and the futures return to the spot price when they expire.
- Spot income = 87,600 – 87,500 = 100
- Futures earnings = 87,700 – 87,600 = 100
- Realize profit* = 100 100 = 200 *The actual reward must be deducted from transaction costs
From the above example, we can see that since the futures will return to the spot price when they expire and the price difference converges to 0, you can lock the price difference by buying spot short futures at the beginning of trading and making a profit at the settlement date.
However, when operating spot futures arbitrage, you must pay attention to the transaction costs, including whether the reference sources of the commodity prices tracked by different exchanges are the same, the exchange trading fees, etc.
What are the risks of cryptocurrency arbitrage?
The biggest risk of cryptocurrency arbitrage is the risk on execution, and arbitrage sounds ideal.
In theory, arbitrage is risk-free, but there are still execution challenges in the real market. The actual transaction may not be as good as expected, or even the transaction fails.
The risks of cryptocurrency arbitrage include:
Risk 1. Trading delay: The transaction cannot be completed instantly
Cryptocurrency trading is not completed instantly every time, and the market price is highly volatile. If the buy and sell orders cannot be traded at the same time, price changes may occur due to delayed transactions.
The price spread originally planned to make may narrow or even reverse, resulting in arbitrage failure or loss.
Risk 2. Insufficient liquidity: The result is that the transaction cannot be completed at the current price
For example, after you place an order on both sides at the same time, the transaction is completed on one side and the other side has not yet been completed. This is possible.
Or when the liquidity of the trading market is insufficient (the trading volume is too low) will affect the transaction price, resulting in slippage, and the transaction price is better than the expected price difference.
The originally calculated price difference will narrow or disappear due to insufficient liquidity, affecting the arbitrage results.
Risk 3. Transaction costs: handling fees, transfer gas fees, taxes
True profit and loss of cryptocurrency arbitrage = Locked spread – Transaction fees
Transaction costs are an important factor affecting profitability. Transaction costs are too high, such as transaction fees, transfer and withdrawal of Gas fees, and tax costs in some countries, which will significantly reduce the profit margin of cryptocurrency arbitrage.
In the case of a small price difference, excessive transaction fees will directly consume the expected profit, which may make the arbitrage unenforceable.
When calculating arbitrage transactions, all these derivative transaction costs must be taken into account in advance.
Risk 4. Fund rate risk and spot contract volatility inconsistent risk
This risk mainly occurs in spot contract arbitrage strategies.
On the one hand, the price fluctuations of spot contracts may be inconsistent, so long and short may not completely lock the price difference.
In addition, the capital rate is floating, and sometimes it may become a payment of the capital rate instead of charging the capital rate (usually a short market), which is also the risk.
Risk 5. Time risk/limited opportunity
Good arbitrage opportunities are fleeting and need to be able to react quickly enough in a short period of time. If the reaction is not fast enough, the price difference may have disappeared before the order is placed.
In addition, many investors in the market use program trading to automatically detect arbitrage opportunities. It is difficult for ordinary people to manually operate it faster than the reaction speed of trading robots. In the face of fierce competition, it is greatly difficult to successfully seize arbitrage opportunities.
Risk 6. Regulatory Regulations Uncertainty
At present, cryptocurrency arbitrage is not illegal, because it is just a trading strategy, which is actually exactly the same as general trading transactions.
However, the regulation of cryptocurrencies is still changing, and governments have successively introduced new regulations and restrictions, but more regulations may be imposed in the future, resulting in the originally feasible strategies becoming untyped. For example, cross-border capital flow restrictions and certain types of transactions are prohibited, which may affect the operations of cryptocurrency arbitrage.
In addition, cryptocurrency arbitrage involves capital transfer, and some regulators may consider it related to illegal capital flows, so some transactions will be monitored intensified and even frozen funds.
However, on the other hand, due to regulatory factors, if some exchanges are only limited to people of certain nationalities, when there is a price difference on the exchange, only people of that nationality can earn these arbitrage opportunities.
Risk 7. Risk of execution errors or operational errors
Execution of arbitrage transactions requires high timing, but there may be mistakes in practice.
For example, if you place an order for a computer or mobile phone, if the network is unstable, if you place an order, if you make an error in the automatic program or if you have a bug... etc.
The probability of these things may be small, but once they happen, they may cause great harm. Once they happen, they may lose the arbitrage gain accumulated over a long period of time.
When these mistakes occur, one side of the long and short positions of arbitrage trading is not completed, which creates risks.
For mature arbitrage traders, they need to first take into account the processing procedures, risk control methods and inspection methods when an accident occurs, so as not to panic when encountering an accident temporarily.
Cryptocurrency Arbitrage Trading Pipeline
Cryptocurrency arbitrage Whether it is operating exchange arbitrage, triangular arbitrage or spot contract arbitrage, it is necessary to purchase cryptocurrency at the cryptocurrency exchange, trade between one or several different exchanges and earn the price difference.
Virtual Currency Exchange – Centralized Exchange CEX
You can find a centralized exchange and choose a larger exchange in your country.
Or choose from the world's large-scale cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Binance, which currently ranks number one in the world in terms of trading volume.
Please refer to: Binance Exchange Registration/Recharge/Trading Operation Tutorial
Quick focus on cryptocurrency arbitrage
1. The English name of cryptocurrency arbitrage is Crypto Arbitrage, which generally refers to buying and selling the same cryptocurrency on two exchanges at the same time, locking the price difference between the two sides to make profits.
2. There are many strategies for cryptocurrency arbitrage, not limited to exchange arbitrage. For example, triangular arbitrage, spot contract arbitrage and spot futures arbitrage are also cryptocurrency arbitrage.
3. In theory, arbitrage is a risk-free profit, but in the actual market, arbitrage still comes with risks, such as:
- Transaction delay
- Insufficient liquidity
- Transaction Cost
- Fund rate risk
- Time risk/limited opportunities
- Regulatory regulations uncertainty
- Execution errors or operational risks
4. The cryptocurrency arbitrage operation method is to use one or several virtual currency exchanges to trade, and it is recommended to choose from the top and reputable exchanges in the world.
Mr. Market’s experience is that although there are many arbitrage opportunities in the cryptocurrency field, because the information is relatively transparent, many people are trading these arbitrage opportunities. In addition, if you want to earn these arbitrage opportunities, you will also need to automatically programmatic tools to reduce transaction costs as much as possible in order to make a profit.
Finally, although the arbitrage strategy is theoretically low, the main risks occur on the execution side.
Before investing, you should clearly understand the risks behind them, and do not be attracted by words such as low-risk arbitrage/risk-free profit, and ignore the risks that may occur in the actual operation.
What are the articles about cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? This is the end of this article about 4 common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis. For more popular science content related to cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies, please search for previous articles of Script Home or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope everyone will support Script Home in the future!
The above is the detailed content of What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1673
1673
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Recommended websites for free viewing market software. What are the websites for free viewing market software?
May 13, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
Recommended websites for free viewing market software. What are the websites for free viewing market software?
May 13, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
The three recommended free market viewing software websites are: 1. OKX, 2. Binance, 3. Huobi. 1. OKX provides rich market data and user-friendly interface, supporting multiple languages and mobile applications. 2. Binance provides simple design and rich market data, supporting advanced charting tools and mobile applications. 3. Huobi is known for its comprehensive and accurate market data, providing intuitive interfaces and mobile applications.
 Where to buy altcoins? Recommended altcoin trading platform in 2025
May 13, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
Where to buy altcoins? Recommended altcoin trading platform in 2025
May 13, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
The steps to buy altcoins include: 1. Select a reliable trading platform, 2. Register and verify an account, 3. Deposit, 4. Buy altcoins. The recommended trading platforms in 2025 are: 1. Binance, 2. OKX, 3. Huobi, 4. KuCoin, 5. Coinbase. When purchasing altcoins, you need to pay attention to research, risk management and safety measures.
 What is Solayer(LAYER)? Solayer Token Economics and Price Forecast
May 14, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
What is Solayer(LAYER)? Solayer Token Economics and Price Forecast
May 14, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Introduction Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is changing the way users interact with blockchain technology, creating seamless and flexible ways for transactions, lending and earnings creation. Solayer (LAYER) is at the heart of this change, building a protocol that connects liquidity and practicality across multiple blockchains. With the popularity of DeFi and the growing demand for efficient cross-chain infrastructure, Solayer is attracting the attention of traders, developers and investors who are looking for the next major opportunity. This article will explain the concept of Solayer, detail its innovative features and token economics, and look forward to its 2030
 What is the future of VINU coins? VINU coin price analysis and investment strategy in 2025
May 14, 2025 pm 09:30 PM
What is the future of VINU coins? VINU coin price analysis and investment strategy in 2025
May 14, 2025 pm 09:30 PM
Table of Contents What is VitaInu (VINU)? What is VINU token? 2025 VINU Coin Price Forecast VitaInu (VINU) Price Forecast 2025-2030 to 2030 VitaInu (VINU) Price Forecast 2025 VitaInu Price Forecast 2026 VitaInu Price Forecast 2027 VitaInu Price Forecast 2028 VitaInu Price Forecast 2029 VitaInu Price Forecast 2030 VitaInu Price Forecast Interpretation of VINU’s Market Performance
 One article to clarify the role of stablecoins during economic fluctuations
May 14, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
One article to clarify the role of stablecoins during economic fluctuations
May 14, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
You don't need to be an economist to feel the economic turmoil. Prices fall, job stability declines, and everyone seems to be anxious about their financial future. What is a stablecoin? Stablecoins are like life jackets in the crypto world: a digital currency designed to keep its value stable, often linked to stable assets such as the US dollar or gold. Unlike cryptocurrencies with severe price fluctuations such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins pursue stability. When an economic storm strikes, investors will naturally seek stability, and stablecoins just provide this safe-haven asset – free from volatility. Why stablecoins thrive when economic instability is
 What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis
May 14, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
What are the cryptocurrency arbitrage strategies? Four common arbitrage strategies and risk analysis
May 14, 2025 pm 09:18 PM
The English name of cryptocurrency arbitrage is CryptoArbitrage, which refers to a strategy of trading on two exchanges at the same time and making profits by locking the spread on both sides. Cryptocurrency investment has large fluctuations and high risks. Investors want to find strategies that can reduce risks and make profits. Cryptocurrency arbitrage is one of the types of strategies, but is arbitrage strategies really necessarily low risk? What is cryptocurrency arbitrage? When there are different quotes for the same cryptocurrency pair, buy low and sell high at the same time, and use risk-free or extremely low risk to earn the profits of the spread, which is the arbitrage transaction conducted by cryptocurrency arbitrage in the cryptocurrency field, which generally refers to buying and selling on different exchanges.
 XDC and XRP: Which one is more attractive to investment?
May 14, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
XDC and XRP: Which one is more attractive to investment?
May 14, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The two tokens are highlighted by their different use cases and technical characteristics, namely XDC and XRP. Both are in compliance with ISO20022 standards, meaning they comply with global financial messaging standards for seamless interoperability. However, their purpose, market, and the technology differences behind them are significant. In this article, we will compare XDC and XRP in detail to explore their strengths, weaknesses, market potential, and investment considerations in depth. XDC and XRP: Which one is more attractive to investment? Both XDC and XRP are decentralized tokens, but they target different industries and take a unique approach. Here are them
 What should I do if I don't get the account after the recharge of Huobi Huobi? Solution to the recharge of Huobi
May 14, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
What should I do if I don't get the account after the recharge of Huobi Huobi? Solution to the recharge of Huobi
May 14, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
When you recharge on Huobi Huobi platform, if you find that the funds have not arrived, this may cause you to be anxious and confused. Fortunately, there are some specific steps and methods to help you solve this problem. The following are detailed solutions and operating guides to help you quickly find solutions when you encounter the problem of recharge not being received.


