Custom Data Validation in Excel : formulas and rules
This tutorial demonstrates how to create custom data validation rules in Excel. We'll explore several examples, including formulas to restrict input to numbers, text, text starting with specific characters, unique entries, and more.
Yesterday's tutorial introduced Excel Data Validation's purpose and basic built-in rules. Today, we delve into advanced custom validation using formulas.
Key Topics:
- Creating custom formula-based validation rules
- Number-only validation
- Text-only validation
- Validation for text starting with specific characters
- Validation for entries containing specific text
- Preventing duplicate entries
- Date and time validation formulas
- Troubleshooting custom validation issues
Creating Custom Data Validation with Formulas
While Excel offers built-in rules, custom formulas provide greater flexibility. Here's how to create them:
- Select the cells needing validation.
- Access the Data Validation dialog (Data tab > Data Tools group > Data Validation, or Alt D L).
- Choose "Custom" from the "Allow" dropdown in the "Settings" tab.
- Enter your validation formula in the "Formula" box.
- Click "OK".

You can also add custom input messages and error alerts. Remember: Data validation only checks new data entered after the rule is created. To identify pre-existing invalid data, use the "Circle Invalid Data" feature.
Examples of Custom Validation Formulas:
Number-Only Validation:
Use =ISNUMBER(C2) (where C2 is the first cell in your range). This accepts integers, decimals, dates, and times (which Excel stores as numbers).

Text-Only Validation:
Use =ISTEXT(D2) (where D2 is the first cell).

Text Starting with Specific Characters:
Use COUNTIF with wildcards. For example, =COUNTIF(A2,"AA-*") allows entries starting with "AA-". For multiple prefixes (e.g., "AA-" or "BB-"), use =COUNTIF(A2,"AA-*") COUNTIF(A2,"BB-*"). For case-sensitive validation, use =EXACT(LEFT(A2,3),"AA-").



Entries Containing Specific Text:
Use ISNUMBER(SEARCH("AA",A2)) (case-insensitive) or ISNUMBER(FIND("AA",A2)) (case-sensitive) to allow entries containing "AA".

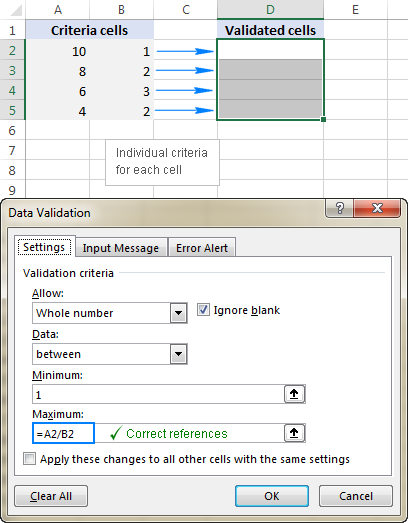
Unique Entries (No Duplicates):
Use =COUNTIF($A$2:$A$6,A2) (case-insensitive). Note the use of absolute and relative references.

Date and Time Validation:
Use built-in date rules or custom formulas like =AND(C2>=DATE(2017,7,1),C2 for dates within a specific range. For weekdays/weekends, use <code>WEEKDAY(C2,2) (weekdays) or <code>WEEKDAY(C2,2)>5 (weekends). Use TODAY() and NOW() for validation relative to the current date and time.




Troubleshooting:
If your validation isn't working, check:
- Formula correctness: Test the formula separately.
- Blank cells: Ensure your formula handles blank cells correctly.
- Cell references: Use absolute ($A$1) or relative (A1) references appropriately.

Download the practice workbook for further exploration.
The above is the detailed content of Custom Data Validation in Excel : formulas and rules. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1418
1418
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to streamline complex Excel spreadsheets by grouping rows, making data easier to analyze. Learn to quickly hide or show row groups and collapse the entire outline to a specific level. Large, detailed spreadsheets can be
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
 Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
This tutorial shows you how to create various charts in Google Sheets, choosing the right chart type for different data scenarios. You'll also learn how to create 3D and Gantt charts, and how to edit, copy, and delete charts. Visualizing data is cru
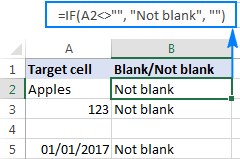 Excel: If cell contains formula examples
Apr 09, 2025 am 09:04 AM
Excel: If cell contains formula examples
Apr 09, 2025 am 09:04 AM
This tutorial demonstrates various Excel formulas to check if a cell contains specific values, including text, numbers, or parts of strings. It covers scenarios using IF, ISTEXT, ISNUMBER, SEARCH, FIND, COUNTIF, EXACT, SUMPRODUCT, VLOOKUP, and neste
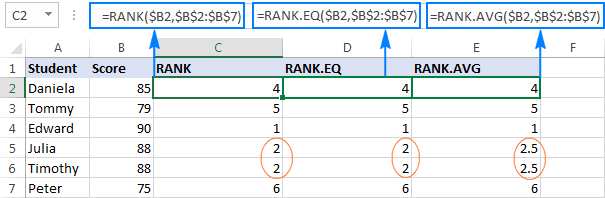 Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:35 AM
Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:35 AM
This Excel tutorial details the nuances of the RANK functions and demonstrates how to rank data in Excel based on multiple criteria, group data, calculate percentile rank, and more. Determining the relative position of a number within a list is easi




