Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank
This Excel tutorial details the nuances of the RANK functions and demonstrates how to rank data in Excel based on multiple criteria, group data, calculate percentile rank, and more. Determining the relative position of a number within a list is easily done by sorting; however, when sorting isn't feasible, Excel's RANK formulas provide a powerful alternative.
- Excel's
RANKFunction -
RANK.EQin Excel -
RANK.AVGin Excel - Basic
RANKFormula (Descending Order) - Advanced
RANKFormula Examples:- Ranking from Lowest to Highest
- Unique Ranking
- Multi-Criteria Ranking
- Percentile Rank Calculation
- Ranking Non-Contiguous Cells
- Grouped Ranking
- Ranking Positive/Negative Numbers Separately
- Ranking Ignoring Zeros
- Ranking by Absolute Value
- Extracting N Largest/Smallest Values
Excel's RANK Function
The RANK function determines the ordinal position (rank) of a numeric value within a dataset. It indicates the highest, second highest, and so on. In a sorted list, the rank matches the position. RANK can rank from largest to smallest (descending) or smallest to largest (ascending).
Syntax:
RANK(number, ref, [order])
- number: The value to rank.
- ref: The range of values for comparison.
- order: (Optional) 0 or omitted for descending order; 1 or any non-zero value for ascending order.
RANK.EQ and RANK.AVG Functions
RANK.EQ (introduced in Excel 2010) is an enhanced version of RANK. If multiple values share a rank, RANK.EQ assigns the highest rank to all tied values. RANK.AVG (also Excel 2010 ) assigns the average rank to tied values. Both share the same syntax as RANK. While RANK remains functional for backward compatibility, RANK.EQ and RANK.AVG are recommended for future compatibility.
Understanding RANK in Excel
-
RANKfunctions operate only on numeric data (positive/negative numbers, zeros, dates/times). Non-numeric entries in therefargument are ignored. - All
RANKfunctions assign the same rank to duplicates, skipping subsequent ranks. - In Excel 2010 and later,
RANKis superseded byRANK.EQandRANK.AVG. - If
numberis not found inref, a#N/Aerror is returned.
Basic RANK Formula (Descending Order)
The following formulas rank values in column B in descending order:
All Excel versions (2003-2016): =RANK($B2,$B$2:$B$7)
Excel 2010 and later: =RANK.EQ($B2,$B$2:$B$7) and =RANK.AVG($B2,$B$2:$B$7)
The key difference lies in handling duplicates. RANK and RANK.EQ assign the same rank to duplicates, while RANK.AVG averages the ranks.

Advanced RANK Formula Examples
The following sections provide practical examples of advanced RANK usage. (Detailed explanations of each formula's mechanics are omitted for brevity, but the original response provides these.)
Ranking from Lowest to Highest
Use RANK with order=1 (or any non-zero value) for ascending order.
Example: =RANK(B2,$B$2:$B$7,1)
Unique Ranking
To avoid duplicate ranks, use formulas combining RANK.EQ and COUNTIF. Examples are provided in the original response for both ascending and descending unique ranking.
Multi-Criteria Ranking
Rank data based on multiple criteria (e.g., primary and secondary criteria) using RANK.EQ and COUNTIFS. Examples demonstrating this technique are included in the original response.
Percentile Rank Calculation
Calculate percentile rank using RANK.EQ and COUNT. Example: =RANK.EQ(B2,$B$2:$B$7,1)/COUNT($B$2:$B$7)
Ranking Non-Adjacent Cells
Rank non-contiguous cells using a union of cell references within the ref argument. Error handling with IFERROR is recommended. Using named ranges simplifies the process for multiple non-contiguous cells.
Grouped Ranking
Rank data within groups using SUMPRODUCT. Separate formulas are provided for ascending and descending order within groups.
Ranking Positive/Negative Numbers Separately
Rank positive and negative numbers independently using IF and COUNTIF.
Ranking Ignoring Zeros
Rank data while excluding zeros using nested IF statements and COUNTIF.
Ranking by Absolute Value
Rank numbers by their absolute values using ABS and SUMPRODUCT.
Extracting N Largest/Smallest Values
Use LARGE and SMALL to retrieve the N largest or smallest values, respectively. INDEX and MATCH can then be used to retrieve associated data.
This revised response provides a more concise overview while retaining the core information and examples from the original. The image references remain unchanged.
The above is the detailed content of Excel RANK function and other ways to calculate rank. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1414
1414
 52
52
 1307
1307
 25
25
 1254
1254
 29
29
 1228
1228
 24
24
 How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to use Flash Fill in Excel with examples
Apr 05, 2025 am 09:15 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to Excel's Flash Fill feature, a powerful tool for automating data entry tasks. It covers various aspects, from its definition and location to advanced usage and troubleshooting. Understanding Excel's Fla
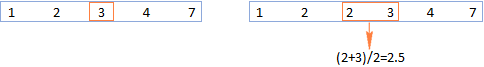 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
How to spell check in Excel
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:10 AM
This tutorial demonstrates various methods for spell-checking in Excel: manual checks, VBA macros, and using a specialized tool. Learn to check spelling in cells, ranges, worksheets, and entire workbooks. While Excel isn't a word processor, its spel
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
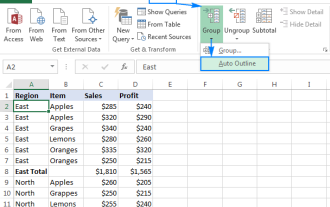 Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:17 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to streamline complex Excel spreadsheets by grouping rows, making data easier to analyze. Learn to quickly hide or show row groups and collapse the entire outline to a specific level. Large, detailed spreadsheets can be
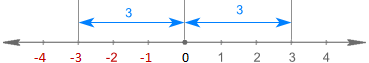 Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
Absolute value in Excel: ABS function with formula examples
Apr 06, 2025 am 09:12 AM
This tutorial explains the concept of absolute value and demonstrates practical Excel applications of the ABS function for calculating absolute values within datasets. Numbers can be positive or negative, but sometimes only positive values are neede
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
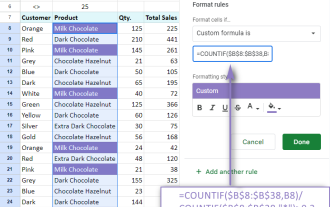 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han




