How to multiply in Excel: numbers, cells, entire columns
This tutorial demonstrates various methods for performing multiplication in Excel, leveraging both the multiplication symbol and built-in functions. We'll cover multiplying numbers, cells, columns, and rows, as well as incorporating multiplication into more complex calculations.
- Multiplying in Excel using the Multiplication Symbol
- Multiplying Numbers
- Multiplying Cells
- Multiplying One Column by Another
- Multiplying Two Rows
- Using the PRODUCT Function for Multiplication
- Multiplying a Cell by a Percentage
- Multiplying a Column by a Number
- Combining Multiplication and Summation
- Multiplication within Array Formulas
- Streamlining Calculations in Excel
Multiplication with the Asterisk Operator
The simplest method involves the asterisk (*) as the multiplication operator. This approach efficiently handles numbers, individual cells, and entire columns or rows.
Multiplying Numbers:
Begin by typing an equals sign (=) in a cell, followed by the numbers to be multiplied, separated by asterisks. For example: =2*5
Excel supports multiple arithmetic operations within a single formula, adhering to the standard order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).

Multiplying Cells:
Replace numbers with cell references to multiply cell values. For instance, to multiply A2 and B2: =A2*B2. Multiplying multiple cells is achieved by adding more references, separated by asterisks: =A2*B2*C2.

Multiplying Columns:
Enter the multiplication formula (=A2*B2, for example) in the topmost cell of the result column. Double-click the small square at the bottom-right corner of the cell to automatically fill the formula down the column. Relative cell references adjust automatically for each row.


Multiplying Rows:
While less common, row multiplication is straightforward. Enter the formula (=B1*B2 for example) in the leftmost cell of the result row. Drag the fill handle (the small square) to the right to copy the formula across the desired cells.


The PRODUCT Function
For multiplying multiple cells or ranges, the PRODUCT function offers a concise solution: PRODUCT(number1, [number2], ...) where arguments can be numbers, cells, or ranges. For example: =PRODUCT(A2:C2) or =PRODUCT(A2:C2,3).

Multiplying by Percentages
Multiplying by percentages is done directly within the formula: =50*10% (or =A1*10% for a cell reference). Alternatively, use the decimal equivalent: =50*0.1.

Multiplying a Column by a Number
To multiply a column by a constant, enter the constant in a separate cell (e.g., A2). Use absolute cell referencing (=$A$2) in your multiplication formula (e.g., =C2*$A$2) to prevent the reference from changing when copied down the column.

Combining Multiplication and Summation (SUMPRODUCT)
The SUMPRODUCT function efficiently handles multiplying and summing multiple pairs of values: =SUMPRODUCT(B2:B5,C2:C5).

Multiplication in Array Formulas
For more complex scenarios, embed multiplication within an array formula (entered with Ctrl Shift Enter). For example, =SUM(B2:B5*C2:C5) calculates the sum of products. Other functions like AVERAGE, MAX, and MIN can also be used with array formulas.

Streamlining Calculations with Add-ins
Add-ins can simplify calculations. Tools like the "Calculate" feature in the Ultimate Suite for Excel allow for quick multiplication and other operations with a few clicks.




This comprehensive guide provides various techniques for efficient multiplication in Excel, catering to different needs and skill levels.
The above is the detailed content of How to multiply in Excel: numbers, cells, entire columns. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1319
1319
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
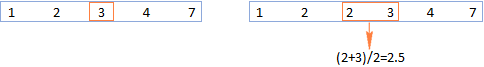 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
This tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
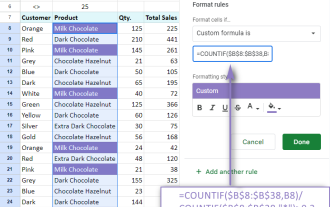 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examples
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Master Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
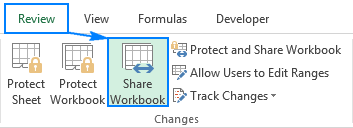 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple users
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image file
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
This tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
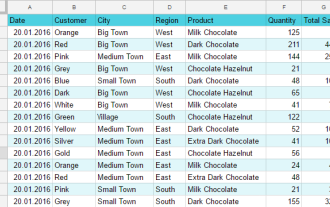 Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
Google sheets chart tutorial: how to create charts in google sheets
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:06 AM
This tutorial shows you how to create various charts in Google Sheets, choosing the right chart type for different data scenarios. You'll also learn how to create 3D and Gantt charts, and how to edit, copy, and delete charts. Visualizing data is cru
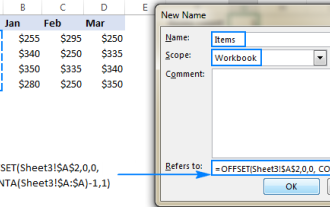 Excel dynamic named range: how to create and use
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:19 AM
Excel dynamic named range: how to create and use
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:19 AM
This tutorial shows you how to create and use dynamic named ranges in Excel, automatically updating calculations as your data changes. Unlike static named ranges, dynamic ranges adjust to include new data without manual intervention. Last week's tut
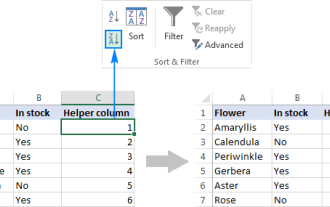 How to flip data in Excel columns and rows (vertically and horizontally)
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:05 AM
How to flip data in Excel columns and rows (vertically and horizontally)
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:05 AM
This tutorial demonstrates several efficient methods for vertically and horizontally flipping tables in Excel, preserving original formatting and formulas. While Excel lacks a direct "flip" function, several workarounds exist. Flipping Dat
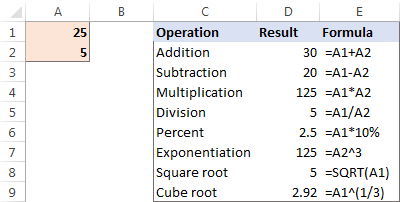 How to do calculations in Excel
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:20 AM
How to do calculations in Excel
Apr 11, 2025 am 10:20 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform arithmetic calculations within Microsoft Excel and modify the order of operations in your formulas. Excel's capabilities extend far beyond simple addition; it can handle complex calculations, thanks to its h




