批改状态:合格
老师批语:
| 原始类型 | 代表 | 引用类型 | 代表 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| number | 数值类型 | array | 数组类型 | |
| string | 字符串类型 | object | 对象类型 | |
| Boolean | 布尔类型 | function | 函数类型 | |
| undefined | 代表没有,变量的默认值 | |||
| null | 空,没有的意思 |
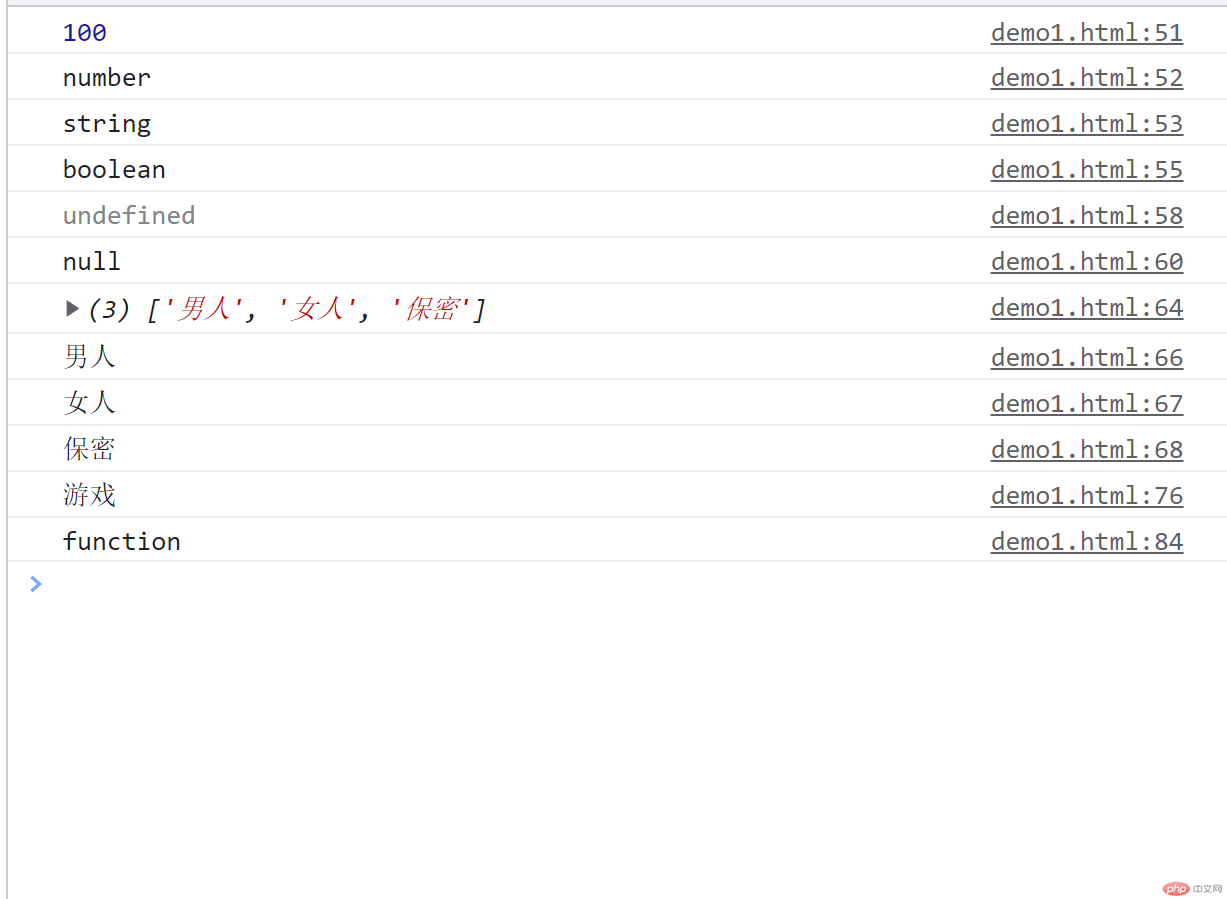
<script>//数值类型console.log(100);console.log(typeof 100); //返回 number数值类型console.log(typeof "php.cn"); //返回string字符串类型let a = false; //false/true 布尔类型console.log(typeof a);//undefined 变量的默认值let b; //undefined 变量的默认值console.log(b); //undefined 变量的默认值let c = "null"; //null代表空没有的意思console.log(c);//-----------------------------//// 引用类型const d = ["男人", "女人", "保密"];console.log(d); // 得到三个值 0=男人1等于女人2=保密// 如果需要拿到第一个值对应的是 0=男人console.log(d[0]); //男人console.log(d[1]); //女人console.log(d[2]); //保密//-----------------------------////对象类型let e = {youxi: "游戏",xiazai: "下载",hobbdy: "爱好",};console.log(e.youxi);//-----------------------------//// 函数//添加函数function hanshu1() {}// 赋予参数xfunction hanshu2(x) {// 查询x是否函数类型console.log(typeof x);}hanshu2(hanshu1);</script>
if(条件) {语句;}条件成立,执行语句
举例 如果分数达到60即为及格,if判断if (fenshu>=80),console.log(‘及格’)。
let fenshu=60;console.log(fenshu>=60);if (fenshu>=60){console.log('及格')}
if (条件) {语句1;}else{语句2;}条件成立,执行语句1 ,条件不成立,执行语句2。
举例设为分数70输出的是及格成绩优良,如果设为70以下即输出不及格
fenshu = 70;if (fenshu>=70){console.log('及格成绩优良');}else{console.log('及格成绩一般');}
多分支
//多分支:if - else if - else if - elsefenshu=65;//如果分数大于60小于70 判断为成绩一般if(fenshu>=60 && fenshu <70){console.log('成绩一般');}//如果分数大于70小于80 判断为成绩良好else if (fenshu >= 70 && fenshu < 80) {console.log('成绩良好');}//如果分数大于80小于90 判断为成绩优秀else if (fenshu >= 80 && fenshu < 90) {console.log('成绩优秀');}//如果分数大于90小于100 判断为成绩牛逼else if (fenshu >= 90 && fenshu < 100) {console.log('成绩牛逼');}//如果分数大于100小于10 判断为作弊else if (fenshu >= 100 || fenshu < 10) {console.log('作弊');}
语法糖
多分支的语法糖: switch、双分支的语法糖: condition ? true : false**
fenshu=65;switch (true) {case fenshu>=60 && fenshu <70:console.log('成绩一般');break;case fenshu >= 70 && fenshu < 80:console.log('成绩良好');break;case fenshu >= 80 && fenshu < 90:console.log('成绩优秀');break;case enshu >= 90 && fenshu < 100:console.log('成绩牛逼');//如果分数大于100小于10 判断为作弊case fenshu >= 100 || fenshu < 10:console.log('作弊');}
while循环:
1.while循环首先检查条件
2.如果条件为真,则循环中的语句执行
3.这个顺序一直重复直到条件为假
<script>const time =['早上','下午','晚上'];console.log(time);console.log(time.length);console.log(time.length - 1);console.log(time[time.length - 1]);console.log(time[time.length]);let a = 0;let length = time.length;// if (a < length) {// console.log(time[a]);// a = a + 1;// }// if (a < length) {// console.log(time[a]);// a+=1;// }// if (a < length) {// console.log(time[a]);// a++;// }// else {// console.log('遍历结束');// }// 简写语法while (a<length){console.log(time[a]);//更新a++;}</script>

do-while循环:
1.do-while循环在循环的最后检查条件
2.这就意味着do-while循环能保证至少循环能执行一次
a = 0;//while循环在开头检查条件,do-while循环在循环的结尾检查条件,至少代码执行一次 不管真假do {console.log(time[a]);// 必须要更新循环条件,否则进入死循环a++;} while (a > length);
for 循环、while 的简写
for( let a =0; a<length;a++){console.log(time[a]);}
for of查看数组的值
for( let item of time){console.log('time: ' + item);}

keys/只看键/索引
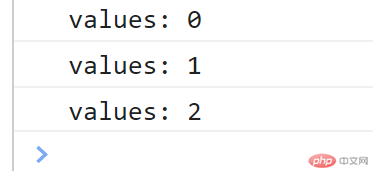
for( let item of time.keys()){console.log('values: ' + item);}

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号