批改状态:合格
老师批语:

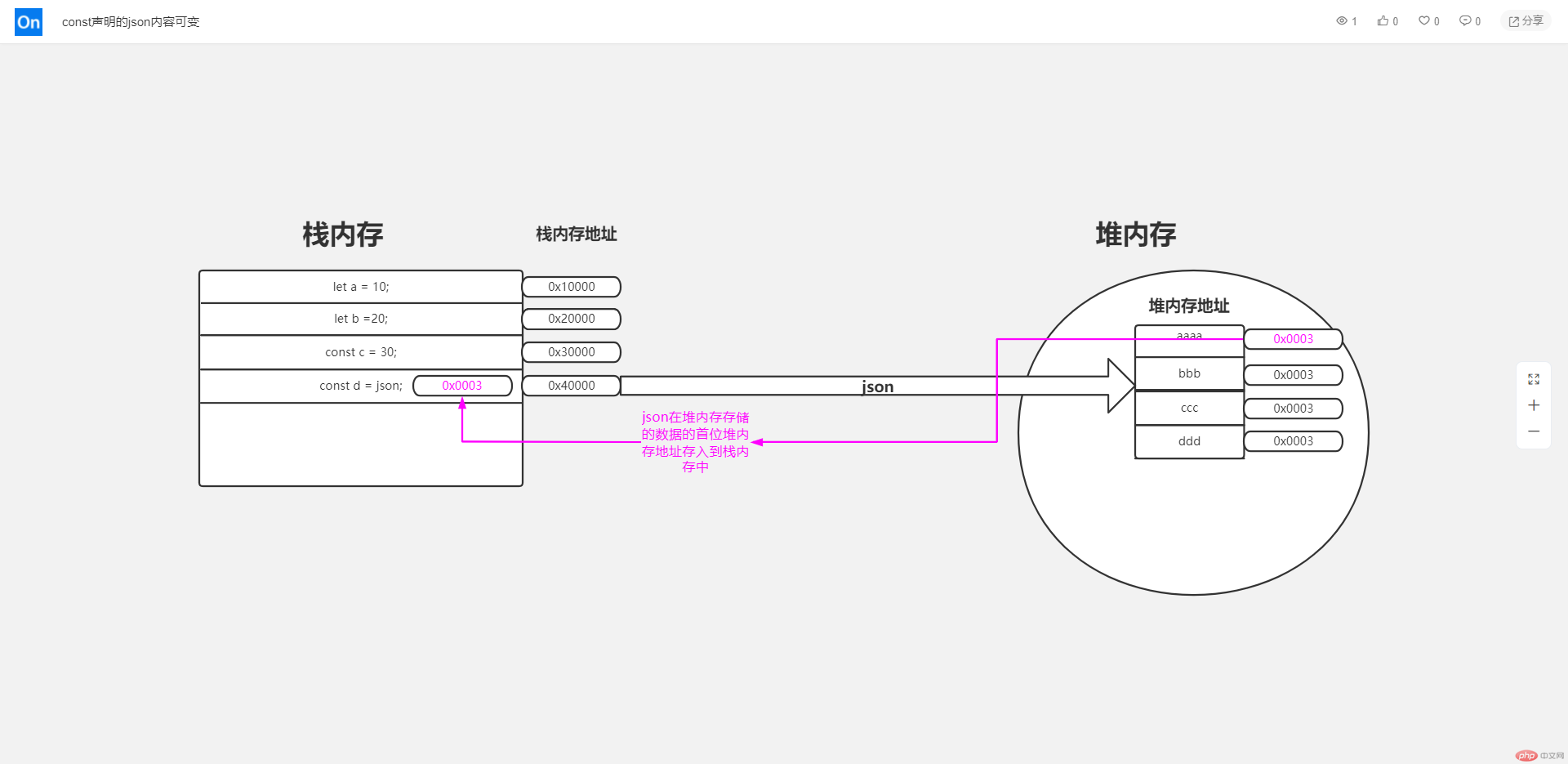
所有声明的变量、常量 会放到栈内存 每个内存都有一个地址 每个地址都是 16 进制
比较大的数据比如 json 都会在堆内存开辟一块空间,空间里也有各个内存,也会有一个地址,但这个 json 所赋值给的 let 的变量或 const 的常量是仍旧存在于栈内存的,他在栈内存里存的只是堆内存的空间里内存的首地址,堆内空间内存的地址不可变,但是里面的内容是可变的
用两个`反引号包裹可以使用${}的形式添加变量,相如换行等无需再用 html 代码替换,直接输入即可
let name = "zhangsirui";let age = 30;let jsx = `我叫${name}我今年${age}岁`;console.log(jsx);
输出:
我叫 zhangsirui
我今年 30 岁
一般来说函数都是用 function 声明,用箭头函数可以使用=>代替 function,使代码变的更简洁
function add (a,b){return a + b;}
// 用箭头函数let add = (a,b)=>{return a + b;};
箭头函数使用时需要注意以下几点
let add = (a,b)=>a + b;
let info = ()=>'info';let add = (a,b)=>a + b;
let name = name => `我的名字是${name}`;
let info = () => ({name:"admin",age:30});
let info = () => this;//可以看到this一直往上指到了window对象
for in 是遍历的数组的索引 for of 是遍历的数组的元素值 for in 更适合遍历对象 for of 更适合遍历数组
// for inlet good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];let goods1 = [];let sum = 0;for (n in good) {if (good[n] >= 10) {goods1.push(good[n]);}}
// for oflet good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];for (n of good) {if (n >= 0) {goods1.push(n * 0.5);sum += n * 0.5;}}
filter 过滤器 把符合条件的值过滤出来
let good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];let goods1 = good.filter(function (n) {return n >= 10;});// filter过滤器进阶let goods1jj = good.filter((n) => n >= 10);
map 映射 把每个元素处理 处理完了把每个处理后的结果返回
let good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];let goods1 = good.filter((n) => n >= 10);let goods2 = goods1.map(function (n) {return n * 0.5;});// map 映射进阶let goods2jj = goods1.map((n) => n * 0.5);
reduce(function(a,b){},c)
let good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];let goods1 = good.filter((n) => n >= 10);let goods2 = goods1.map((n) => n * 0.5);let sum = goods2.reduce(function (a, b) {return a + b;});// reduce进阶let sumjj = goods2.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
let url = ["https://www.baidu.com/", "http://www.baidu.com/", "https://www.php.cn/"];url.forEach((item) => {if (item.startsWith("https")) {console.log("安全");} else {console.log("err:链接不安全,暂不支持");}});url.forEach((item) => (item.endsWith("cn") ? console.log("网站支持") : console.log("网站不支持")));
链式调用
let good = [4, 12, 20, 34, 56, 5, 8, 45, 10];let sum = good.filter((n) => n >= 10).map((n) => n * 0.5).reduce((a, b) => a + b);
class Person {constructor(name, age, gender) {this.name = "name";this.age = age;this.gender = gender;}//声明方法say() {console.log(this.name);}}
使用 JSON.stringify(json 对象) 可以把 json 对象转为字符串,使用 JSON.parse(json 字符串)可以把 json 字符串转为 json 对象
let a = "aaa";let b = "bbb";let c = "ccc";let d = function () {console.log("ddd");};// 将a更名为econst obj = { e: a, b, c, d };console.log(obj);let str = JSON.stringify(obj);console.log(str);let o = JSON.parse(str);
let arr = ["one", "two", "three"];let [a, b, c] = ["one", "two", "three"];
const { name, gender, age, say } = {name: "admin",age: 30,gender: "男",say() {return "aaa";},};
const [a, b, c, { x: g, y }, d, e] = ["a", "b", "c", { x: "aaa", y: "bbb" }, "d", "e"];console.log(a, b, c, g, y, d, e);
const {a,b,c,d: [x, y],e,} = { a: "a", b: "b", c: "c", d: ["aaa", "bbb"], e: "e" };console.log(a, b, c, x, y, e);
const [a, b, ...c] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];console.log(a, b, c);
function add(...args) {return args.reduce((a, b) => a + b);}console.log(add(1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 56, 4, 5, 10));console.log(add(...c));
one.js
// 使用export将变量跟函数单个导出export let a = 10;export function add(a, b) {return a + b;}console.log("one.js");
two.js
let b = 20;function add(a, b) {return a + b;}console.log("two.js");// 使用export将变量跟函数打包导出export { b, add };
three.js
let d = 40;function add(a, b) {return a + b;}// 进行缺省导出,一个模块只能有一个缺省导出export default function (...args) {return args.reduce(function (a, b) {return a + b;});}// 导出的时候给函数或者变量更名export { d, add as fun1 };
four.js
let e = 40;function add(a, b) {return a + b;}export default function (...args) {return args.reduce(function (a, b) {return a + b;});}export { e, add as fun2 };
index.js
// 使用解构赋值的方法 用import将变量及函数导入import { a, add } from "./one.js";// 导入的时候给变量或函数更名import { b, add as sum } from "./two.js";// 使用*as可以将所有内容导入,并存放到一个变量中import * as three from "./three.js";import { e, fun2 } from "./four.js";let c = 30;console.log("########");console.log(add(a, b));console.log("########");console.log(sum(b, c));console.log("########");// 从导入的所有内容中调用里面的变量及函数console.log(three["fun1"](c, three["d"]));console.log("########");console.log(three["default"](a, b, c, three["d"]));console.log("########");console.log(fun2(a, e));
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title><!-- 使用module模块化编程需要加上type="module才能生效 --><script src="index.js" type="module"></script></head><body></body></html>

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号