批改状态:合格
老师批语:

css:层叠样式表,用来设置页面中元素的样式、布局。
h1 {color: violet;border: 1px solid #000;}
h1:选择器{...}:声明块,由一个或多个样式声明组成,各声明由分号分隔h1 + {...}:选择器 + 声明块 = 规则
1、内部样式
<style>h1 {/* 声明:属性和值组成 */color: violet;border: 1px solid #000;}</style>
2、外部样式
3、内联样式
<h1 style="color: violet;">css真的非常好玩</h1>
4、小结
内部样式:通过 style 引入,仅适用于当前页面(html 文档)外部样式:适用于所有引入了这个 css 样式表的 html 文档,使用 link 标签内联样式:也叫 行内样式 通过标签的style属性,仅适用于当前的页面中的指定的元素html 页面
<!--导入公共样式表--><link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
css 样式表
小结
<body><!--示范结构代码--><ul><li id="foo">item1</li><li class="on">item2</li><li id="foo">item3</li><li class="on">item4</li><li class="on">item5</li></ul></body>
1、标签选择器
<style>/* 标签选择器,返回一组 */li {background-color: violet;}</style>

2、类选择器
<style>/* 类选择器: 返回一组(所有 class = "on" 的标签) */li[class="on"] {background-color: violet;}/* class选择器可简化为 . */.on {background-color: violet;}</style>
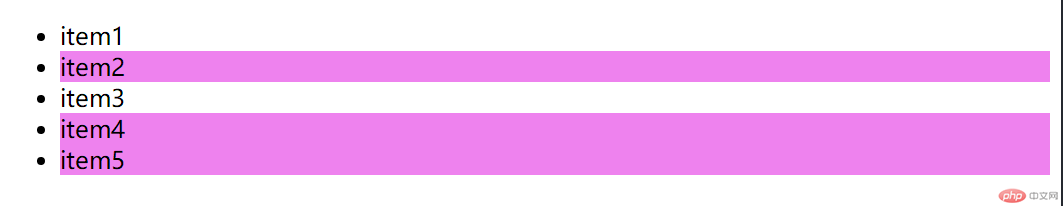
3、id 选择器
<style>/* id选择器: 返回一个 */li[id="foo"] {background-color: violet;}/* 因为浏览器不检查id的唯一性,必须由开发者自行保证 *//* id选择器使用 # 简化 */#foo {background-color: violet;}</style>

4、上下文选择器
因为 html 是一个结构化的文档:每个元素在文档中有确切的位置
因此,可以根据元素的上下文环境来选择元素
<body><!--示范结构代码--><ul><li>item1</li><li class="start">item2</li><li>item3</li><li>item4<ul><li>item4-1</li><li>item4-2</li><li>item4-3</li></ul></li><li>item5</li></ul></body>
后代选择器
<style>/* 后代选择器: 所有ul下的li层级 */ul li {background-color: lightblue;}</style>

子元素选择器
<style>/* 子元素选择器: 仅父子层级 *//* 选择 body 下的 ul 标签 中的 所有 li 标签 */body > ul > li {background-color: teal;}</style>
注:如果没有其他选择器对里层的 li 进行选择,这里的 item4 下的 li 也会被选择

同级相邻选择器
<style>/* 同级相邻选择器: 仅选中与之相邻的第一个兄弟元素 *//* 根据 item2 的类名,选择与之相邻的 li,最终选中 item3 *//* 也可以写成 .start+*,选择与 .start 相邻的任意一个元素 */.start + li {background-color: lightgreen;}</style>
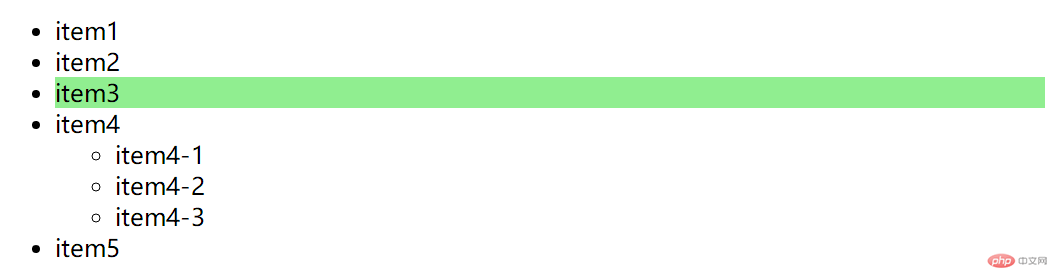
同级所有选择器
<style>/* 同级所有选择器: 选中与之相邻的后面所有兄弟元素 */.start ~ li {background-color: yellow;}</style>

上下文选择器小结
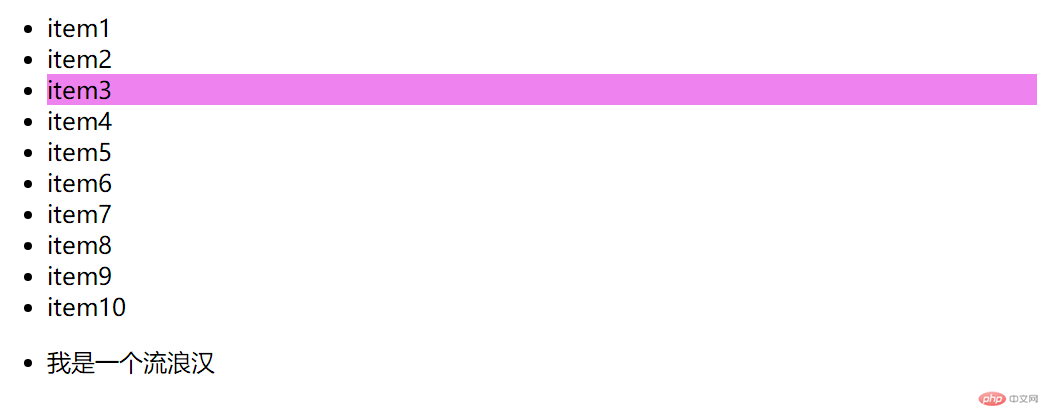
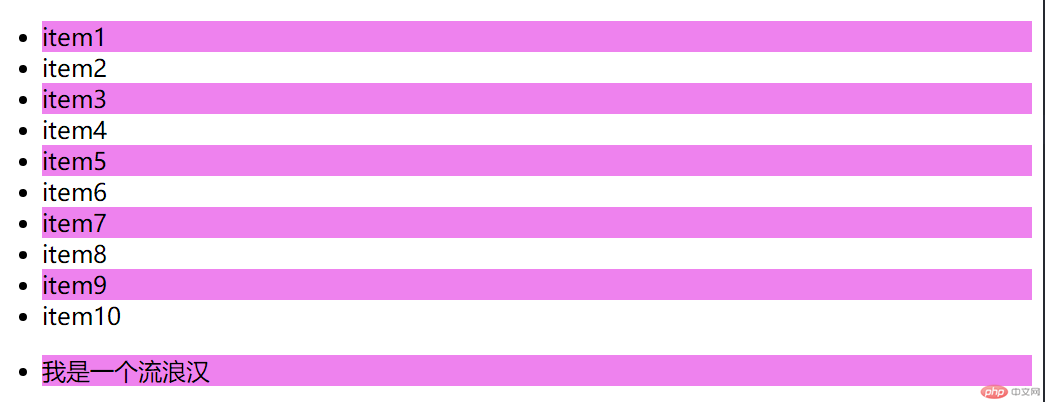
<body><!--示范结构代码--><ul class="list"><li>item1</li><li>item2</li><li>item3</li><li>item4</li><li>item5</li><li>item6</li><li>item7</li><li>item8</li><li>item9</li><li>item10</li></ul><ul><li>我是一个流浪汉</li></ul></body>
1、结构伪类选择器
(1)正向获取元素::nth-of-type(an+b)
匹配任意位置的元素
<style>/* an+b: an是起点,b是偏移量,n = (0,1,2,3...) *//* 匹配第3个 li (0 * n + 3) */ul li:nth-of-type(0n + 3) {background-color: violet;}/* 0乘以任何数都等于0,通常直接写偏移量就可以 */ul li:nth-of-type(3) {background-color: violet;}</style>

匹配所有元素
<style>/* 选择所有元素 */ul li:nth-of-type(1n) {background-color: violet;}/* 如果只是为了全选,这样做没意义,还不如标签选择器来得直接,但是一旦带上偏移量就完全不同了 *//* 选择第三个及之后的所有元素 */ul li:nth-of-type(1n + 3) {background-color: violet;}/* 1乘以任何数都等于自己,所以省去1 */ul li:nth-of-type(n + 3) {background-color: violet;}</style>

(2)反向获取元素:nth-last-of-type(an+b)
<style>/* 反向获取任意位置的元素: `nth-last-of-type(an+b)` *//* 获取倒数三个元素 */ul li:nth-last-of-type(-n + 3) {background-color: violet;}/* -n没有意义,可以直接写 3 */ul li:nth-last-of-type(3) {background-color: violet;}</style>

(3)奇偶数
<style>/* 选择偶数行 */ul li:nth-of-type(2n) {background-color: violet;}/* 2*0 = 02*1 = 22*2 = 42*3 = 6 *//* 选择奇数行 *//* 或 2n+1 */ul li:nth-of-type(2n-1) {background-color: violet;}/* 也可以用关键字方式 *//* 偶数行: even */ul li:nth-of-type(even) {background-color: violet;}/* 奇数行: odd */ul li:nth-of-type(odd) {background-color: violet;}</style>


(4)语法糖(为简化而生的语法方式)
:nth-of-type(an+b)这是最核心的一个选择器,其它的相关选择器都是它的语法糖。:nth-last-of-type(),:first-of-type,:last-of-type,这些都是快捷方式。
<style>/* 选择第一个子元素: :first-of-type *//* :nth-of-type(1) 的语法糖 :first-of-type */ul li:first-of-type {background-color: violet;}/* -------------------------------------------- *//* 选中最后一个: :last-of-type */ul li:last-of-type {background-color: violet;}/* -------------------------------------------- *//* 选中最后一个 ul 中的 li */ul:last-of-type li:first-of-type {background-color: violet;}/* 如果只想匹配父元素中唯一子元素,使用:`only-of-type` 就可快速实现(用的不多) */ul li:only-of-type {background-color: violet;}</style>

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号