批改状态:未批改
老师批语:
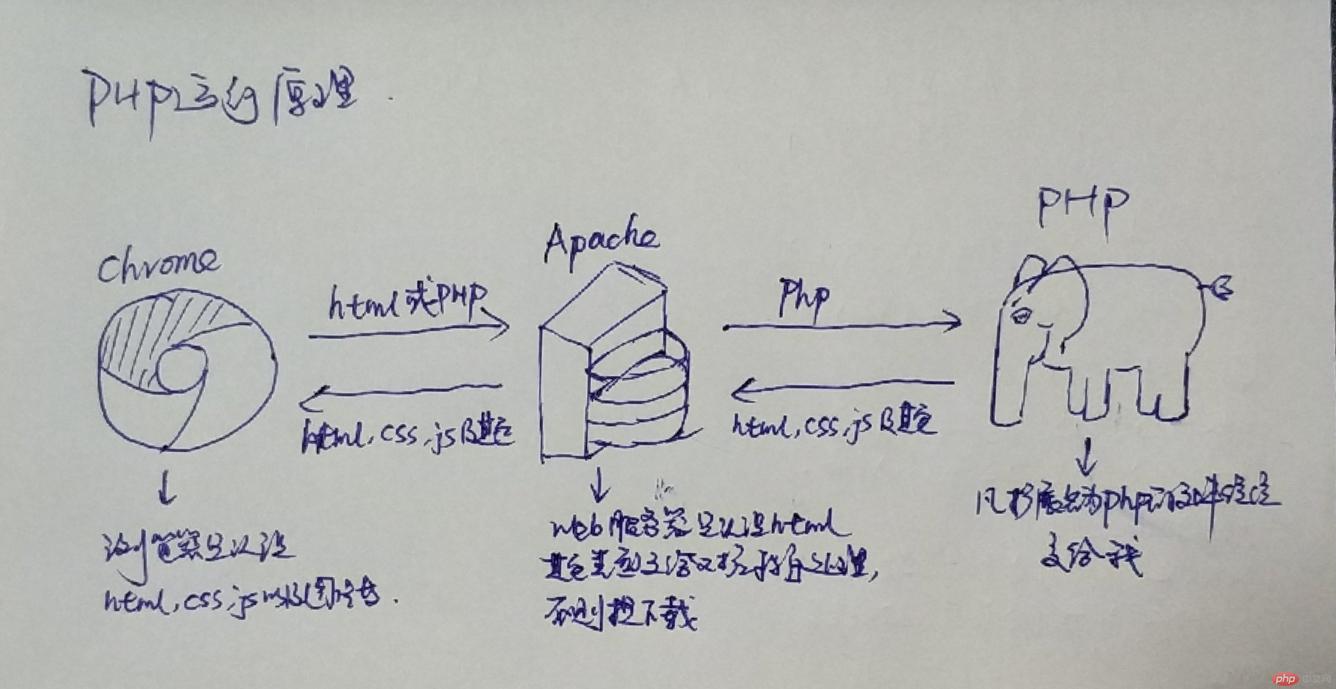
1php运行原理
浏览器、apache以及服务器之间怎么协同工作
2get、post请求类型的区别
get:明文传递
请求参数以键值对的方式,附加到url地址上,称为查询字符串,用`?`号与当前脚本分隔
url格式: `index.php?name=peter&age=30
受url长度限制, `GET`方式传递的数据也是有限制的
服务器端脚本使用预定义变量数组 `$_GET` 进行接收
post:
请求参数放在`header`请求头中发送, url地址看不到请求参数,适合敏感信息(如用户名,密码等)
通常是通过表单提交并, 用来更新服务器上的信息
适合发送大量的数据到服务器端, 长度受到配置文件限制,但比`GET`要大得多
服务器端脚本使用预定义变量数组 `$_POST` 进行接收
实例
get
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>get</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo '<pre>';
if (isset($_GET['email'])) {
print_r($_GET);
}else{
echo "请输入用户名和密码!";
}
?>
<form action="" method="get">
<label for="email">邮箱:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" value="<?=$_GET['email']?:''?>">
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" value="<?=$_GET['password']?:''?>">
<button>登录</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>get</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo '<pre>';
if (isset($_GET['email'])) {
print_r($_GET);
}else{
echo "请输入用户名和密码!";
}
?>
<form action="" method="get">
<label for="email">邮箱:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" value="<?=$_GET['email']?:''?>">
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" value="<?=$_GET['password']?:''?>">
<button>登录</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
post
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>get</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
echo '<pre>';
if (empty($_POST['email'])) {
echo "请输入用户名和密码!";
}else{
print_r($_POST);
}
?>
<form action="" method="post">
<label for="email">邮箱:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" value="<?=$_POST['email']?:''?>">
<label for="password">密码:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" value="<?=$_POST['password']?:''?>">
<button>登录</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号