批改状态:未批改
老师批语:
1.while
2.for
3.for..of
4.for…in
5.forEach()/map()
循环的三要素
1.循环入口
2.条件:true开始,false结束
3.更新条件,避免死循环
循环用于数组和对象
1.while
arr = [1, "php", "朱老师", 30];console.log(arr.length);//初始化循环入口let num = 0;//循环条件:变量num 只要小于数组长度,执行{语句块}while (num < arr.length) {console.log(`这是数组元素arr[${num}]的值:` + arr[`${num}`]);//条件更新num++;}
2.for
为while 循环的语法糖
arr = [1, "php", "朱老师", 30];for (let num = 0; num < arr.length; num++) {console.log(`这是数组元素arr[${num}]的值:` + arr[`${num}`]);}
3.for of:循环 遍历“数组”
大多数场景下,我们只关注值,忽略索引
arr = [1, "php", "朱老师", 30];for (let index of arr) {// 1. index = arr[0], 输出 value// 2. index = arr[1], 输出 value// 3. index = arr[2], 输出 value// 4.index = arr[3], false / end// index: 循环变量,用于接收每一次的要被遍历的值console.log(index);}
4.for...in
用于遍历 “对象”
无法直接使用 ‘对象名.属性名 ’获取属性值,要使用‘对象名[索引]’才能获取属性值
teacher = {id: 1,name: "朱老师",cls: "php",day: 30,"e mail": "151@qq.com",};for (let no in teacher) {// console.log(no);//console.log(teacher[no]);//无法直接使用 ‘对象名.属性名 ’获取属性值,要使用‘对象名[索引]’才能获取属性值console.log(`${no}=>${teacher[no]}`);}
5.forEach / map
这两个函数都是用于遍历 ‘数组’
区别在于 forEach没有返回值,map有返回值
forEach是一个回调函数
forEach函数用法:数组名.forEach(function (值,索引,数组名称))
forEach回调函数的参数,函数值必选,索引和数组名称可选
arr = [1, "php", "朱老师", 30];arr.forEach(function (items, index, arr) {console.log(items, index, arr);});arr.forEach(function (items) {console.log(items);});//回调函数一般会用箭头函数来代替res = arr.map(function (item) {return item;});//使用箭头函数得到相同的结果//使用map函数有返回值,返回的值为一个数组res = arr.map((item) => item);console.log(res);
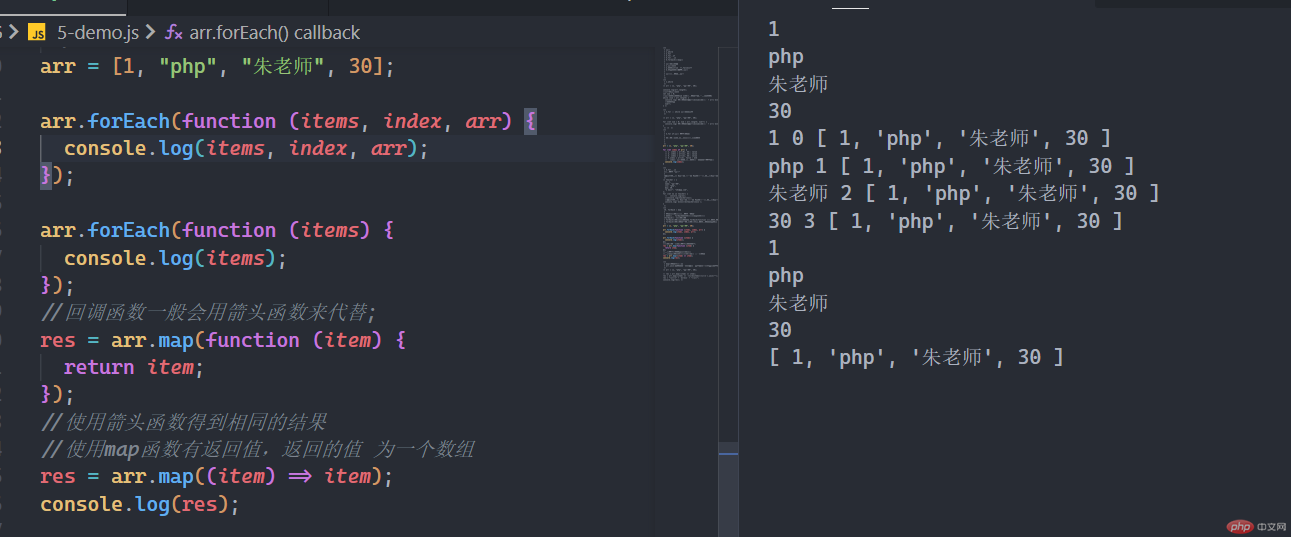
map函数的应用场景
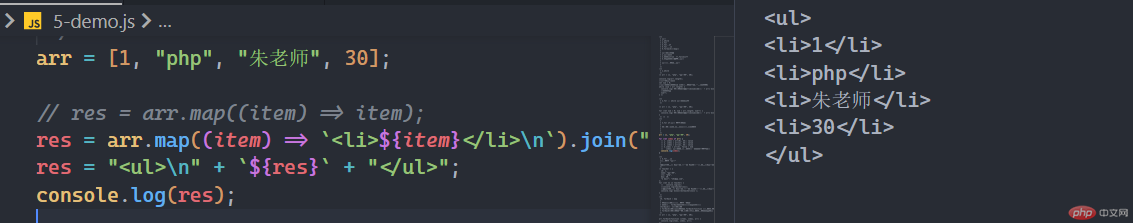
arr.join:将数组的所有元素添加到字符串中,以指定的分隔符字符串分隔。
arr = [1, "php", "朱老师", 30];// res = arr.map((item) => item);res = arr.map((item) => `<li>${item}</li>\n`).join("");res = "<ul>\n" + `${res}` + "</ul>";console.log(res);
//1.参数不足时,使用默认参数
/ let num = (a, b = 0) => a + b;
console.log(num(3)); /
//2.参数过多时,使用剩余参数
*剩余参数:…数组变量(…rest)
将多余的参数打包在rest数组中
1.参数不足时,使用默认参数
let num = (a, b = 0) => a + b;console.log(num(3));
2.参数过多时,使用剩余参数
剩余参数:...数组变量(...rest)将多余的参数打包在rest数组中
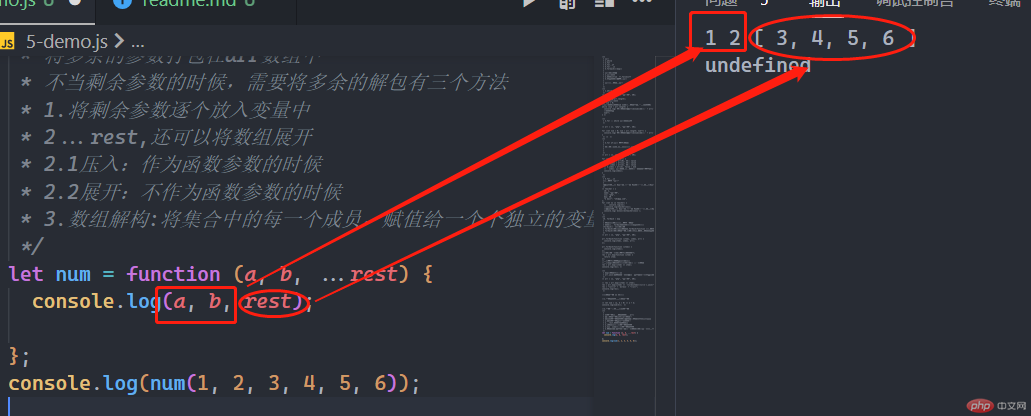
将剩余参数的解包有三个方法
1.将剩余参数逐个放入变量中
2…rest,还可以将数组展开
2.1压入:作为函数参数的时候
2.2展开:不作为函数参数的时候
3.数组解构:将集合中的每一个成员,赋值给一个个独立的变量
let num = function (a, b, ...rest) {console.log(a, b, rest);};console.log(num(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
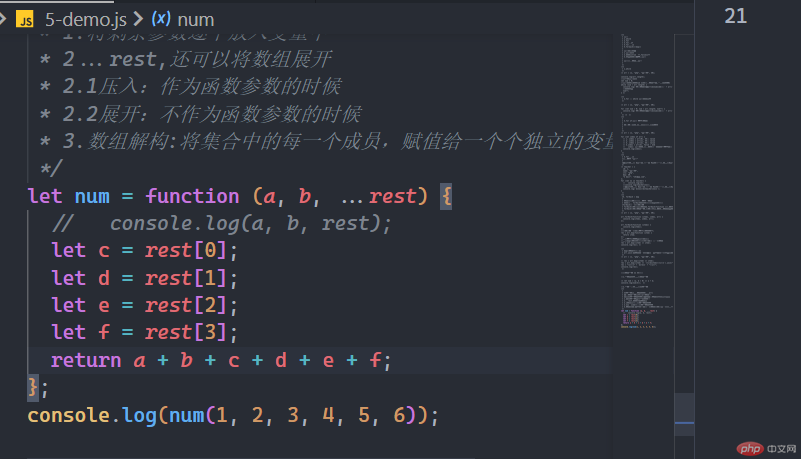
将剩余参数解包有三个方法
1.将它们逐个放入变量中
let num = function (a, b, ...rest) {// console.log(a, b, rest);let c = rest[0];let d = rest[1];let e = rest[2];let f = rest[3];return a + b + c + d + e + f;};console.log(num(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
2….rest,还可以将数组展开
let num = function (a, b, ...rest) {// console.log(a, b, rest);/* let c = rest[0];let d = rest[1];let e = rest[2];let f = rest[3];return a + b + c + d + e + f;*/let tmp = [a, b, ...rest];//得到一个新的数组let sum = 0; //累加器for (let a = 0; a < tmp.length; a++) {sum += tmp[a];}return sum;};console.log(num(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
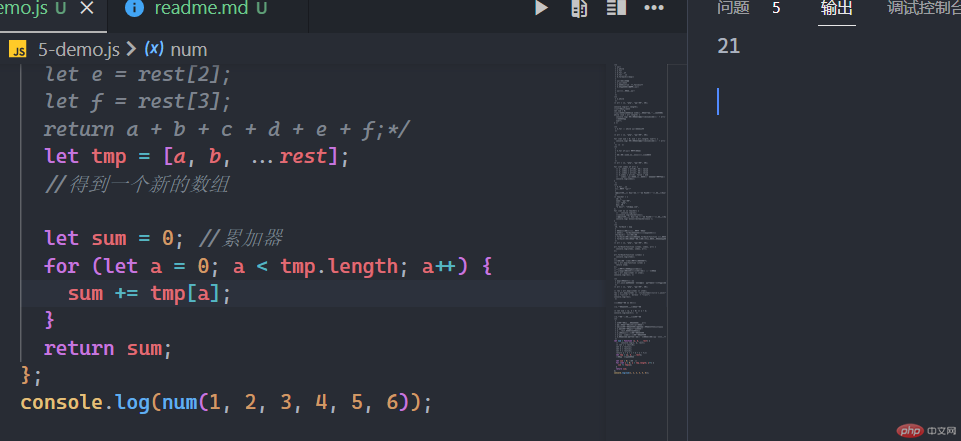
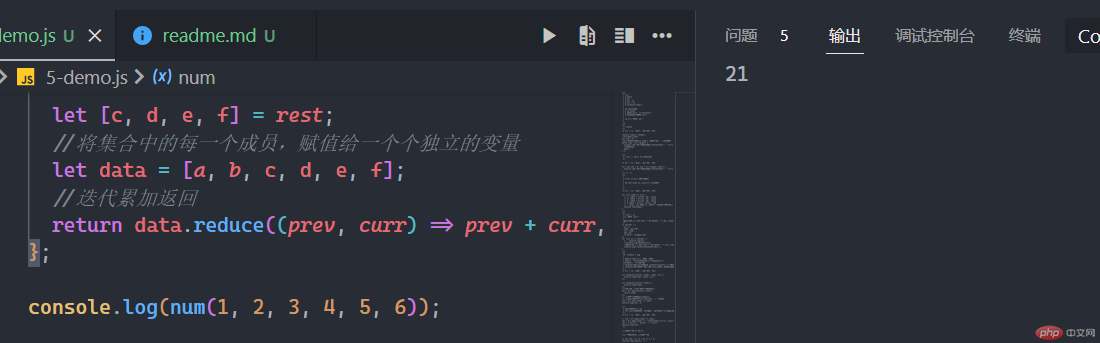
3.数组解构:将集合中的每一个成员,赋值给一个个独立的变量
let num = function (a, b, ...rest) {let [c, d, e, f] = rest;//将集合中的每一个成员,赋值给一个个独立的变量let data = [a, b, c, d, e, f];//迭代累加返回return data.reduce((prev, curr) => prev + curr, 0);};console.log(num(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6));
1.默认单值返回
2.多值返回(数组,对象)
多值返回
const items = [{ id: 1, name: '西瓜', price: 20 },{ id: 2, name: '苹果', price: 30 },{ id: 3, name: '橘子', price: 40 },{ id: 4, name: '香蕉', price: 50 },{ id: 5, name: '樱桃', price: 60 },]// 根据输入的商品id,返回指定的商品集合// 1,2,返回西瓜,苹果// 声明函数const getFruits = function (items, ...nums) {// console.log(nums)// 结果返回的数组let res = []// 循环nums// 拿到要获取的id,去遍历items数组,将满足条件的成员,添加到res数组中for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {// 根据id,遍历当前商品集合items.forEach(function (item) {if (item.id === nums[i]) {// push(x):向数组的尾部追加内容res.push(item)}})}return res}// 调用let result = getFruits(items, 1, 3, 5)console.table(result)
可以将数组中的值或对象的属性取出,赋值给其他变量。
语法:
左边: 模板, 数组用 […], 对象用 {…}
右边: 值(数组,对象)
数组解构
/**当变量数量 > 值的数量 时,变量使用默认值当变量数量 < 值的数量 时,使用剩余参数 ...rest*/const x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];const [y, z] = x;console.log(y); // 1console.log(z); // 2
对象解构
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };const { a, b } = obj;// 等同于下面的语句// const a = obj.a;// const b = obj.b;// 默认变量名和属性相同// let { id, username } = { id: 1, username: '朱老师' }// 变量与当前作用域中的变量命名冲突时,用别名访问let { id, uname: username } = { id: 1, uname: '朱老师' }console.log(id, username)
对象解构应用场景:
1.克隆对象
let obj = { id: 1, uname: "朱老师" };let { ...obj1 } = obj;console.log(obj1); // { id: 1, uname: '朱老师' }console.log(obj1 === obj); //false
2.解构传参
let show = function (user) {// user 是 objectreturn `${user.uname}: ( ${user.email} )`}user = { uname: '张老师', email: 'zhang@php.cn' }console.log(show(user))// 使用对象解构来简化传参show = function ({ uname, email }) {return `${uname}: ( ${email} )`}console.log(show(user))

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号