Filling of graphic colors and lines in Matplotlib
Matplotlib is a Python 2D plotting library that can generate publication-quality graphics in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments on a variety of platforms.

In the previous Matplotlib data visualization tutorial, we will introducehow to create stacked charts and pie charts. What I bring to you today is the filling of graphic colors and lines.
Color
The first change we want to make is to change plt.title to stock variable.
plt.title(stock)
Now, let’s introduce how to change the label color. We can do this by modifying our axis object:
ax1.xaxis.label.set_color('c') ax1.yaxis.label.set_color('r')
If we run this, we'll see that the labels change color, just like in the words.
Next, we can specify specific numbers for the axes to be displayed, rather than an automatic selection like this:
ax1.set_yticks([0,25,50,75])
Next, I want to introduce padding. What fill does is fill the color between the variable and a value of your choice. For example, we can do this:
ax1.fill_between(date, 0, closep)
So here, our code is:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import urllib
import datetime as dt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
def bytespdate2num(fmt, encoding='utf-8'):
strconverter = mdates.strpdate2num(fmt)
def bytesconverter(b):
s = b.decode(encoding)
return strconverter(s)
return bytesconverter
def graph_data(stock):
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((1,1), (0,0))
stock_price_url = 'http://chartapi.finance.yahoo.com/instrument/1.0/'+stock+'/chartdata;type=quote;range=10y/csv'
source_code = urllib.request.urlopen(stock_price_url).read().decode()
stock_data = []
split_source = source_code.split('\n')
for line in split_source:
split_line = line.split(',')
if len(split_line) == 6:
if 'values' not in line and 'labels' not in line:
stock_data.append(line)
date, closep, highp, lowp, openp, volume = np.loadtxt(stock_data,
delimiter=',',
unpack=True,
converters={0: bytespdate2num('%Y%m%d')})
ax1.fill_between(date, 0, closep)
for label in ax1.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
label.set_rotation(45)
ax1.grid(True)#, color='g', linestyle='-', linewidth=5)
ax1.xaxis.label.set_color('c')
ax1.yaxis.label.set_color('r')
ax1.set_yticks([0,25,50,75])
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.title(stock)
plt.legend()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.09, bottom=0.20, right=0.94, top=0.90, wspace=0.2, hspace=0)
plt.show()
graph_data('EBAY')The result is:
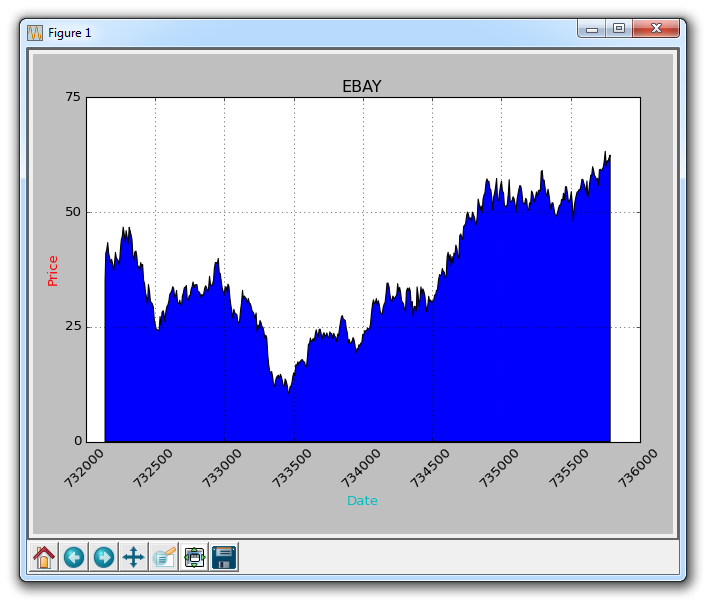
filled one The problem is, we might end up covering everything. We can solve it with transparency:
ax1.fill_between(date, 0, closep)
Now, let’s introduce conditional fill. Let's assume the starting position on the chart is where we start buying eBay. Here, if the price is below this price, we can pad up to the original price, and then if it exceeds the original price, we can pad down. We could do this:
ax1.fill_between(date, closep[0], closep)
would generate:
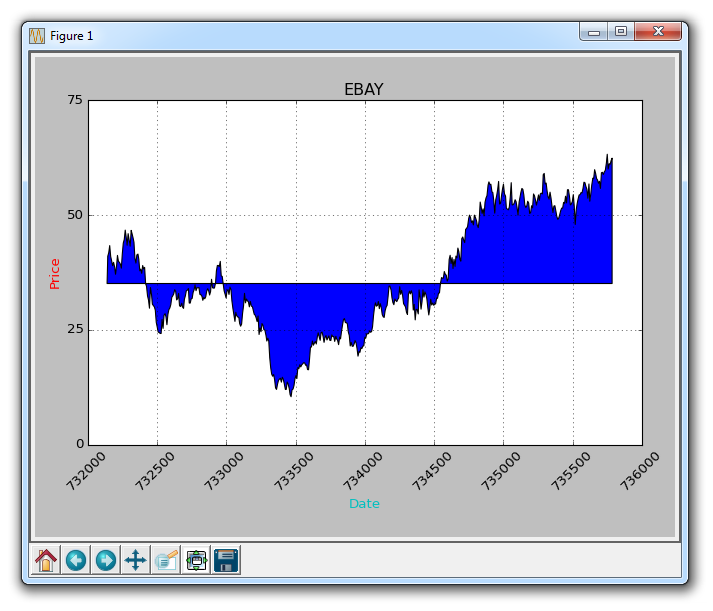
If we wanted to show the gains/losses with red and green fills compared to the original price , green filling is used for rising (note: the color of foreign stock markets is opposite to domestic), red filling is used for falling? no problem! We can add a where parameter like this:
ax1.fill_between(date, closep, closep[0],where=(closep > closep[0]), facecolor='g', alpha=0.5)
Here, we fill the area between the current price and the original price, where the current price is higher than the original price. We give it a green foreground color because this is a rise, and we use a slight transparency.
Lines
We still can't apply labels to polygonal data (like fills), but we can implement empty lines as before, so we can:
ax1.plot([],[],linewidth=5, label='loss', color='r',alpha=0.5) ax1.plot([],[],linewidth=5, label='gain', color='g',alpha=0.5) ax1.fill_between(date, closep, closep[0],where=(closep > closep[0]), facecolor='g', alpha=0.5) ax1.fill_between(date, closep, closep[0],where=(closep < closep[0]), facecolor='r', alpha=0.5)
This gives us some padding, as well as empty lines for handling labels, which we intend to display in the legend. The complete code here is:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npimport urllib
import datetime as dt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
def bytespdate2num(fmt, encoding='utf-8'):
strconverter = mdates.strpdate2num(fmt)
def bytesconverter(b):
s = b.decode(encoding)
return strconverter(s)
return bytesconverter
def graph_data(stock):
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((1,1), (0,0))
stock_price_url = 'http://chartapi.finance.yahoo.com/instrument/1.0/'+stock+'/chartdata;type=quote;range=10y/csv'
source_code = urllib.request.urlopen(stock_price_url).read().decode()
stock_data = []
split_source = source_code.split('\n')
for line in split_source:
split_line = line.split(',')
if len(split_line) == 6:
if 'values' not in line and 'labels' not in line:
stock_data.append(line)
date, closep, highp, lowp, openp, volume = np.loadtxt(stock_data,
delimiter=',',
unpack=True,
converters={0: bytespdate2num('%Y%m%d')})
ax1.plot_date(date, closep,'-', label='Price')
ax1.plot([],[],linewidth=5, label='loss', color='r',alpha=0.5)
ax1.plot([],[],linewidth=5, label='gain', color='g',alpha=0.5)
ax1.fill_between(date, closep, closep[0],where=(closep > closep[0]), facecolor='g', alpha=0.5)
ax1.fill_between(date, closep, closep[0],where=(closep < closep[0]), facecolor='r', alpha=0.5)
for label in ax1.xaxis.get_ticklabels():
label.set_rotation(45)
ax1.grid(True)#, color='g', linestyle='-', linewidth=5)
ax1.xaxis.label.set_color('c')
ax1.yaxis.label.set_color('r')
ax1.set_yticks([0,25,50,75])
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.title(stock)
plt.legend()
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.09, bottom=0.20, right=0.94, top=0.90, wspace=0.2, hspace=0)
plt.show()
graph_data('EBAY')Now our result is:
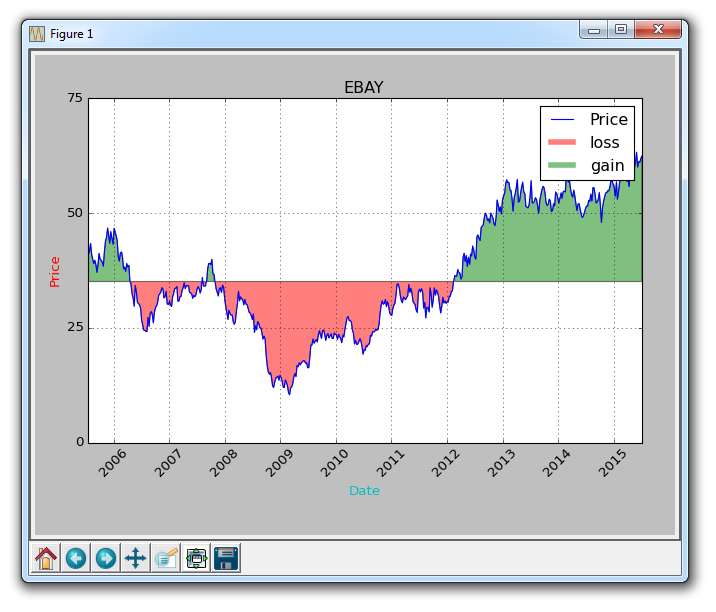
The above is the detailed content of Filling of graphic colors and lines in Matplotlib. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.






