Axes and dimensions in numpy
The following article will share with you an understanding of the central axis and dimensions of numpy. It has a good reference value and I hope it will be helpful to everyone. Let's take a look together
NumPy's main object is the homogeneous multidimensional array. It is a table of elements (usually numbers), all of the same type, indexed by a tuple of positive integers. In NumPy dimensions are called axes. The number of axes is rank.
For example, the coordinates of a point in 3D space [1, 2, 1] is an array of rank 1, because it has one axis. That axis has a length of 3. In the example pictured below, the array has rank 2 (it is 2-dimensional). The first dimension (axis) has a length of 2, the second dimension has a length of 3.
[[ 1., 0., 0.], [ 0., 1., 2.]]
ndarray.ndim
The number of array axes, inpython## In the world of #, the number of axes is called rank
>> X = np.reshape(np.arange(24), (2, 3, 4))
# 也即 2 行 3 列的 4 个平面(plane)
>> X
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])shape(x)
(2,3,4)shape(x )[0]
2 orx.shape[0]
2Let’s look at the composition of each plane separately:
>> X[:, :, 0]
array([[ 0, 4, 8],
[12, 16, 20]])
>> X[:, :, 1]
array([[ 1, 5, 9],
[13, 17, 21]])
>> X[:, :, 2]
array([[ 2, 6, 10],
[14, 18, 22]])
>> X[:, :, 3]
array([[ 3, 7, 11],
[15, 19, 23]])reshpae is a method in the array object, used to change the shape of the array.
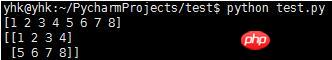
Two-dimensional array
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a d=a.reshape((2,4)) print d
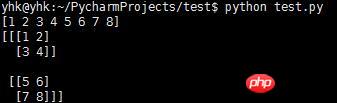
Three-dimensional array
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a f=a.reshape((2, 2, 2)) print f
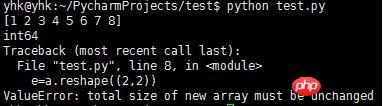
 ##The principle of shape change is that the array elements cannot change, for example, it is written like this Wrong because the array elements have changed.
##The principle of shape change is that the array elements cannot change, for example, it is written like this Wrong because the array elements have changed.
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a print a.dtype e=a.reshape((2,2)) print e
 Note: The new array generated by reshape and the original array share the same memory, that is to say, if one is changed elements of the array, the other array will also be changed.
Note: The new array generated by reshape and the original array share the same memory, that is to say, if one is changed elements of the array, the other array will also be changed.
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf-8 import numpy as np a=np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]) print a e=a.reshape((2, 4)) print e a[1]=100 print a print e

a=np.arange(0, 60, 10) >>>a array([0,10,20,30,40,50]) >>>a.reshape(-1,1) array([[0], [10], [20], [30], [40], [50]])
If written as a.reshape(1,1), an error will be reported##ValueError:cannot reshape array of size 6 into shape (1,1)
>>> a = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]])
>>> np.reshape(a, (3,-1)) # the unspecified value is inferred to be 2
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])# 下面是两张2*3大小的照片(不知道有几张照片用-1代替),如何把所有二维照片给摊平成一维
>>> image = np.array([[[1,2,3], [4,5,6]], [[1,1,1], [1,1,1]]])
>>> image.shape
(2, 2, 3)
>>> image.reshape((-1, 6))
array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
The difference between array and asarray in numpy
The above is the detailed content of Axes and dimensions in numpy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to update numpy version
Nov 28, 2023 pm 05:50 PM
How to update numpy version
Nov 28, 2023 pm 05:50 PM
How to update the numpy version: 1. Use the "pip install --upgrade numpy" command; 2. If you are using the Python 3.x version, use the "pip3 install --upgrade numpy" command, which will download and install it, overwriting the current NumPy Version; 3. If you are using conda to manage the Python environment, use the "conda install --update numpy" command to update.
 How to quickly check numpy version
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:23 AM
How to quickly check numpy version
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:23 AM
Numpy is an important mathematics library in Python. It provides efficient array operations and scientific calculation functions and is widely used in data analysis, machine learning, deep learning and other fields. When using numpy, we often need to check the version number of numpy to determine the functions supported by the current environment. This article will introduce how to quickly check the numpy version and provide specific code examples. Method 1: Use the __version__ attribute that comes with numpy. The numpy module comes with a __
 Which version of numpy is recommended?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 04:58 PM
Which version of numpy is recommended?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 04:58 PM
It is recommended to use the latest version of NumPy1.21.2. The reason is: Currently, the latest stable version of NumPy is 1.21.2. Generally, it is recommended to use the latest version of NumPy, as it contains the latest features and performance optimizations, and fixes some issues and bugs in previous versions.
 Step-by-step guide on how to install NumPy in PyCharm and get the most out of its features
Feb 18, 2024 pm 06:38 PM
Step-by-step guide on how to install NumPy in PyCharm and get the most out of its features
Feb 18, 2024 pm 06:38 PM
Teach you step by step to install NumPy in PyCharm and make full use of its powerful functions. Preface: NumPy is one of the basic libraries for scientific computing in Python. It provides high-performance multi-dimensional array objects and various functions required to perform basic operations on arrays. function. It is an important part of most data science and machine learning projects. This article will introduce you to how to install NumPy in PyCharm, and demonstrate its powerful features through specific code examples. Step 1: Install PyCharm First, we
 Upgrading numpy versions: a detailed and easy-to-follow guide
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:39 PM
Upgrading numpy versions: a detailed and easy-to-follow guide
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:39 PM
How to upgrade numpy version: Easy-to-follow tutorial, requires concrete code examples Introduction: NumPy is an important Python library used for scientific computing. It provides a powerful multidimensional array object and a series of related functions that can be used to perform efficient numerical operations. As new versions are released, newer features and bug fixes are constantly available to us. This article will describe how to upgrade your installed NumPy library to get the latest features and resolve known issues. Step 1: Check the current NumPy version at the beginning
 How to install numpy
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
How to install numpy
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
Numpy can be installed using pip, conda, source code and Anaconda. Detailed introduction: 1. pip, enter pip install numpy in the command line; 2. conda, enter conda install numpy in the command line; 3. Source code, unzip the source code package or enter the source code directory, enter in the command line python setup.py build python setup.py install.
 Numpy version selection guide: why upgrade?
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:34 AM
Numpy version selection guide: why upgrade?
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:34 AM
With the rapid development of fields such as data science, machine learning, and deep learning, Python has become a mainstream language for data analysis and modeling. In Python, NumPy (short for NumericalPython) is a very important library because it provides a set of efficient multi-dimensional array objects and is the basis for many other libraries such as pandas, SciPy and scikit-learn. In the process of using NumPy, you are likely to encounter compatibility issues between different versions, then
 Numpy installation guide: Solving installation problems in one article
Feb 21, 2024 pm 08:15 PM
Numpy installation guide: Solving installation problems in one article
Feb 21, 2024 pm 08:15 PM
Numpy installation guide: One article to solve installation problems, need specific code examples Introduction: Numpy is a powerful scientific computing library in Python. It provides efficient multi-dimensional array objects and tools for operating array data. However, for beginners, installing Numpy may cause some confusion. This article will provide you with a Numpy installation guide to help you quickly solve installation problems. 1. Install the Python environment: Before installing Numpy, you first need to make sure that Py is installed.






