 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in Python
How to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in Python
How to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in Python
This time I will show you how to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in python Get up and take a look. The meaning of the question is roughly to find a local peak in an n*m two-dimensional array. The peak value is required to be greater than the four adjacent elements (outside the array boundary is regarded as negative infinity). For example, if we finally find the peak value A[j][i], then A[j][i] > A[j 1][i ] && A[j][i] > A[j-1][i] && A[j][i] > A[j][i 1] && A[j][i] > A[ j][i-1]. Returns the coordinates and value of this peak.
Of course, the simplest and most direct method is to traverse all array elements to determine whether they are peak values. The time complexity is O(n^2) Then optimize a little more to find the value of each row (column) Maximum value, and then find the peak value of the maximum value column through the dichotomy method (the specific method can be seen inOne-dimensional array
finding the peak value). The time complexity of this algorithm is O(logn)What is discussed here is an algorithm with a complexity of O(n). The algorithm idea is divided into the following steps:1. Find "Tian "Character. Including the four outer edges and the two horizontal and vertical edges in the middle (the green part in the picture), compare their sizes and find the position of the maximum value.
(7 in the picture)
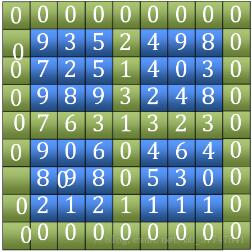
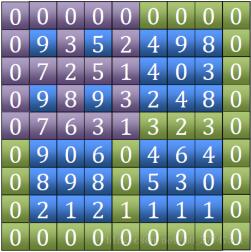
As to why there must be a peak within the range we choose, you can think of it this way, first we have a circle, we It is known that there is at least one element in a circle that is greater than all the elements in this circle. So, is there a maximum value in this circle?
It may be a bit convoluted, but if you think about it more, you should be able to understand it, and you can also use mathematical proof by contradiction to prove it. After we understand the algorithm, the next step is to implement the code. The language I use here is python (I am new to python, so please forgive me for some usages that may not be concise enough). Let’s start with the code:import numpy as np
def max_sit(*n): #返回最大元素的位置
temp = 0
sit = 0
for i in range(len(n)):
if(n[i]>temp):
temp = n[i]
sit = i
return sit
def dp(s1,s2,e1,e2):
m1 = int((e1-s1)/2)+s1 #row
m2 = int((e2-s1)/2)+s2 #col
nub = e1-s1
temp = 0
sit_row = 0
sit_col = 0
for i in range(nub):
t = max_sit(list[s1][s2+i], #第一排
list[m1][s2+i], #中间排
list[e1][s2+i], #最后排
list[s1+i][s2], #第一列
list[s1+i][m2], #中间列
list[s1+i][e2], #最后列
temp)
if(t==6):
pass
elif(t==0):
temp = list[s1][s2+i]
sit_row = s1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==1):
temp = list[m1][s2+i]
sit_row = m1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==2):
temp = list[e1][s2+i]
sit_row = e1
sit_col = s2+i
elif(t==3):
temp = list[s1+i][s2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_row = s2
elif(t==4):
temp = list[s1+i][m2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_col = m2
elif(t==5):
temp = list[s1+i][e2]
sit_row = s1+i
sit_col = m2
t = max_sit(list[sit_row][sit_col], #中
list[sit_row-1][sit_col], #上
list[sit_row+1][sit_col], #下
list[sit_row][sit_col-1], #左
list[sit_row][sit_col+1]) #右
if(t==0):
return [sit_row-1,sit_col-1]
elif(t==1):
sit_row-=1
elif(t==2):
sit_row+=1
elif(t==3):
sit_col-=1
elif(t==4):
sit_col+=1
if(sit_row<m1):
e1 = m1
else:
s1 = m1
if(sit_col<m2):
e2 = m2
else:
s2 = m2
return dp(s1,s2,e1,e2)
f = open("demo.txt","r")
list = f.read()
list = list.split("\n") #对行进行切片
list = ["0 "*len(list)]+list+["0 "*len(list)] #加上下的围墙
for i in range(len(list)): #对列进行切片
list[i] = list[i].split()
list[i] = ["0"]+list[i]+["0"] #加左右的围墙
list = np.array(list).astype(np.int32)
row_n = len(list)
col_n = len(list[0])
ans_sit = dp(0,0,row_n-1,col_n-1)
print("找到峰值点位于:",ans_sit)
print("该峰值点大小为:",list[ans_sit[0]+1,ans_sit[1]+1])
f.close()string
. The specific conversion process can be seen in my previous blog -Converting a string to a two-dimensional array in python . (It should be noted that if the list after splitting in windows environment does not have an empty tail, there is no need to add the sentence list.pop()). Some changes are that I added a "0" wall around the two-dimensional array. Adding a wall eliminates the need to consider boundary issues when we judge peak values. max_sit(*n) function is used to find the position of the maximum value among multiple values and return its position. Python's built-in max function can only return the maximum value, so you still need to write it yourself, *n means Indefinite length parameters, because I need to use this function when comparing Tian and Ten (judging peak values)
def max_sit(*n): #返回最大元素的位置 temp = 0 sit = 0 for i in range(len(n)): if(n[i]>temp): temp = n[i] sit = i return sit
def dp(s1,s2,e1,e2): m1 = int((e1-s1)/2)+s1 #row m2 = int((e2-s1)/2)+s2 #col
for i in range(nub): t = max_sit(list[s1][s2+i], #第一排 list[m1][s2+i], #中间排 list[e1][s2+i], #最后排 list[s1+i][s2], #第一列 list[s1+i][m2], #中间列 list[s1+i][e2], #最后列 temp) if(t==6): pass elif(t==0): temp = list[s1][s2+i] sit_row = s1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==1): temp = list[m1][s2+i] sit_row = m1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==2): temp = list[e1][s2+i] sit_row = e1 sit_col = s2+i elif(t==3): temp = list[s1+i][s2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = s2 elif(t==4): temp = list[s1+i][m2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = m2 elif(t==5): temp = list[s1+i][e2] sit_row = s1+i sit_row = m2
t = max_sit(list[sit_row][sit_col], #中 list[sit_row-1][sit_col], #上 list[sit_row+1][sit_col], #下 list[sit_row][sit_col-1], #左 list[sit_row][sit_col+1]) #右 if(t==0): return [sit_row-1,sit_col-1] elif(t==1): sit_row-=1 elif(t==2): sit_row+=1 elif(t==3): sit_col-=1 elif(t==4): sit_col+=1
if(sit_row<m1): e1 = m1 else: s1 = m1 if(sit_col<m2): e2 = m2 else: s2 = m2 return dp(s1,s2,e1,e2)
大体的思路就是从中间位置起找相邻4个点中最大的点,继续把该点来找相邻最大点,最后一定会找到一个峰值点,有兴趣的可以看一下,上代码:
#!/usr/bin/python3
def dp(n):
temp = (str[n],str[n-9],str[n-1],str[n+1],str[n+9]) #中 上 左 右 下
sit = temp.index(max(temp))
if(sit==0):
return str[n]
elif(sit==1):
return dp(n-9)
elif(sit==2):
return dp(n-1)
elif(sit==3):
return dp(n+1)
else:
return dp(n+9)
f = open("/home/nancy/桌面/demo.txt","r")
list = f.read()
list = list.replace(" ","").split() #转换为列表
row = len(list)
col = len(list[0])
str="0"*(col+3)
for x in list: #加围墙 二维变一维
str+=x+"00"
str+="0"*(col+1)
mid = int(len(str)/2)
print(str,mid)
p = dp(mid)
print (p)
f.close()相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of How to obtain the local peak value of a two-dimensional array in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.





