 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to share the method of converting solar calendar to lunar calendar in Python
How to share the method of converting solar calendar to lunar calendar in Python
How to share the method of converting solar calendar to lunar calendar in Python
This article mainly introduces the method of converting the Gregorian calendar (solar calendar) to the lunar calendar (lunar calendar) in Python, involving the principles of the lunar calendar algorithm and Python date operation related operating skills. Friends in need can refer to the following
Examples of this article Python implements the method of converting the Gregorian calendar (solar calendar) to the lunar calendar (lunar calendar). Share it with everyone for your reference. The details are as follows:
Two important points:
1. The table lookup method is used to convert the Gregorian calendar to the lunar calendar (line 126)
2. Are astronomical methods used for solar terms? (Line 176)
Running chart (The background is hao123 perpetual calendar)
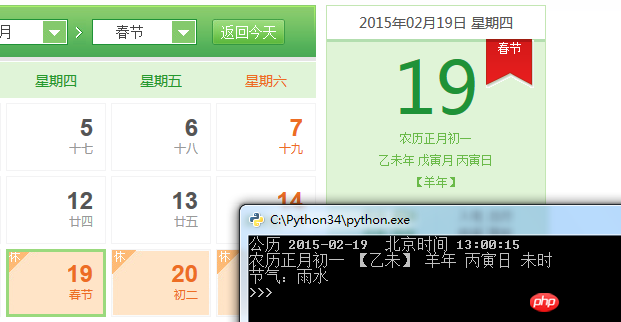

##Source code:
# lunar.py
# 2015/02/27 罗兵
import datetime
class Lunar(object):
#******************************************************************************
# 下面为阴历计算所需的数据,为节省存储空间,所以采用下面比较变态的存储方法.
#******************************************************************************
#数组g_lunar_month_day存入阴历1901年到2050年每年中的月天数信息,
#阴历每月只能是29或30天,一年用12(或13)个二进制位表示,对应位为1表30天,否则为29天
g_lunar_month_day = [
0x4ae0, 0xa570, 0x5268, 0xd260, 0xd950, 0x6aa8, 0x56a0, 0x9ad0, 0x4ae8, 0x4ae0, #1910
0xa4d8, 0xa4d0, 0xd250, 0xd548, 0xb550, 0x56a0, 0x96d0, 0x95b0, 0x49b8, 0x49b0, #1920
0xa4b0, 0xb258, 0x6a50, 0x6d40, 0xada8, 0x2b60, 0x9570, 0x4978, 0x4970, 0x64b0, #1930
0xd4a0, 0xea50, 0x6d48, 0x5ad0, 0x2b60, 0x9370, 0x92e0, 0xc968, 0xc950, 0xd4a0, #1940
0xda50, 0xb550, 0x56a0, 0xaad8, 0x25d0, 0x92d0, 0xc958, 0xa950, 0xb4a8, 0x6ca0, #1950
0xb550, 0x55a8, 0x4da0, 0xa5b0, 0x52b8, 0x52b0, 0xa950, 0xe950, 0x6aa0, 0xad50, #1960
0xab50, 0x4b60, 0xa570, 0xa570, 0x5260, 0xe930, 0xd950, 0x5aa8, 0x56a0, 0x96d0, #1970
0x4ae8, 0x4ad0, 0xa4d0, 0xd268, 0xd250, 0xd528, 0xb540, 0xb6a0, 0x96d0, 0x95b0, #1980
0x49b0, 0xa4b8, 0xa4b0, 0xb258, 0x6a50, 0x6d40, 0xada0, 0xab60, 0x9370, 0x4978, #1990
0x4970, 0x64b0, 0x6a50, 0xea50, 0x6b28, 0x5ac0, 0xab60, 0x9368, 0x92e0, 0xc960, #2000
0xd4a8, 0xd4a0, 0xda50, 0x5aa8, 0x56a0, 0xaad8, 0x25d0, 0x92d0, 0xc958, 0xa950, #2010
0xb4a0, 0xb550, 0xb550, 0x55a8, 0x4ba0, 0xa5b0, 0x52b8, 0x52b0, 0xa930, 0x74a8, #2020
0x6aa0, 0xad50, 0x4da8, 0x4b60, 0x9570, 0xa4e0, 0xd260, 0xe930, 0xd530, 0x5aa0, #2030
0x6b50, 0x96d0, 0x4ae8, 0x4ad0, 0xa4d0, 0xd258, 0xd250, 0xd520, 0xdaa0, 0xb5a0, #2040
0x56d0, 0x4ad8, 0x49b0, 0xa4b8, 0xa4b0, 0xaa50, 0xb528, 0x6d20, 0xada0, 0x55b0, #2050
]
#数组gLanarMonth存放阴历1901年到2050年闰月的月份,如没有则为0,每字节存两年
g_lunar_month = [
0x00, 0x50, 0x04, 0x00, 0x20, #1910
0x60, 0x05, 0x00, 0x20, 0x70, #1920
0x05, 0x00, 0x40, 0x02, 0x06, #1930
0x00, 0x50, 0x03, 0x07, 0x00, #1940
0x60, 0x04, 0x00, 0x20, 0x70, #1950
0x05, 0x00, 0x30, 0x80, 0x06, #1960
0x00, 0x40, 0x03, 0x07, 0x00, #1970
0x50, 0x04, 0x08, 0x00, 0x60, #1980
0x04, 0x0a, 0x00, 0x60, 0x05, #1990
0x00, 0x30, 0x80, 0x05, 0x00, #2000
0x40, 0x02, 0x07, 0x00, 0x50, #2010
0x04, 0x09, 0x00, 0x60, 0x04, #2020
0x00, 0x20, 0x60, 0x05, 0x00, #2030
0x30, 0xb0, 0x06, 0x00, 0x50, #2040
0x02, 0x07, 0x00, 0x50, 0x03 #2050
]
START_YEAR = 1901
# 天干
gan = '甲乙丙丁戊己庚辛壬癸'
# 地支
zhi = '子丑寅卯辰巳午未申酉戌亥'
# 生肖
xiao = '鼠牛虎兔龙蛇马羊猴鸡狗猪'
# 月份
lm = '正二三四五六七八九十冬腊'
# 日份
ld = '初一初二初三初四初五初六初七初八初九初十十一十二十三十四十五十六十七十八十九二十廿一廿二廿三廿四廿五廿六廿七廿八廿九三十'
# 节气
jie = '小寒大寒立春雨水惊蛰春分清明谷雨立夏小满芒种夏至小暑大暑立秋处暑白露秋分寒露霜降立冬小雪大雪冬至'
def __init__(self, dt = None):
'''初始化:参数为datetime.datetime类实例,默认当前时间'''
self.localtime = dt if dt else datetime.datetime.today()
def sx_year(self): # 返回生肖年
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = self.ln_year() - 3 - 1 # 农历年份减3 (说明:补减1)
year = year % 12 # 模12,得到地支数
return self.xiao[year]
def gz_year(self): # 返回干支纪年
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = self.ln_year() - 3 - 1 # 农历年份减3 (说明:补减1)
G = year % 10 # 模10,得到天干数
Z = year % 12 # 模12,得到地支数
return self.gan[G] + self.zhi[Z]
def gz_month(self): # 返回干支纪月(未实现)
pass
def gz_day(self): # 返回干支纪日
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
C = ct.year // 100 #取世纪数,减一
y = ct.year % 100 #取年份后两位(若为1月、2月则当前年份减一)
y = y - 1 if ct.month == 1 or ct.month == 2 else y
M = ct.month #取月份(若为1月、2月则分别按13、14来计算)
M = M + 12 if ct.month == 1 or ct.month == 2 else M
d = ct.day #取日数
i = 0 if ct.month % 2 == 1 else 6 #取i (奇数月i=0,偶数月i=6)
#下面两个是网上的公式
# http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=MbTKmhrTHTOAz735gi37tEtwd29zqE9GJ92cZQZd0X8uFO5XgmyMKQru6aetzcGadqekzKd3nZHVS99rewya6q
# 计算干(说明:补减1)
G = 4 * C + C // 4 + 5 * y + y // 4 + 3 * (M + 1) // 5 + d - 3 - 1
G = G % 10
# 计算支(说明:补减1)
Z = 8 * C + C // 4 + 5 * y + y // 4 + 3 * (M + 1) // 5 + d + 7 + i - 1
Z = Z % 12
#返回 干支纪日
return self.gan[G] + self.zhi[Z]
def gz_hour(self): # 返回干支纪时(时辰)
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
#计算支
Z = round((ct.hour/2) + 0.1) % 12 # 之所以加0.1是因为round的bug!!
#返回 干支纪时(时辰)
return self.zhi[Z]
def ln_year(self): # 返回农历年
year, _, _ = self.ln_date()
return year
def ln_month(self): # 返回农历月
_, month, _ = self.ln_date()
return month
def ln_day(self): # 返回农历日
_, _, day = self.ln_date()
return day
def ln_date(self): # 返回农历日期整数元组(年、月、日)(查表法)
delta_days = self._date_diff()
#阳历1901年2月19日为阴历1901年正月初一
#阳历1901年1月1日到2月19日共有49天
if (delta_days < 49):
year = self.START_YEAR - 1
if (delta_days <19):
month = 11;
day = 11 + delta_days
else:
month = 12;
day = delta_days - 18
return (year, month, day)
#下面从阴历1901年正月初一算起
delta_days -= 49
year, month, day = self.START_YEAR, 1, 1
#计算年
tmp = self._lunar_year_days(year)
while delta_days >= tmp:
delta_days -= tmp
year += 1
tmp = self._lunar_year_days(year)
#计算月
(foo, tmp) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
while delta_days >= tmp:
delta_days -= tmp
if (month == self._get_leap_month(year)):
(tmp, foo) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
if (delta_days < tmp):
return (0, 0, 0)
return (year, month, delta_days+1)
delta_days -= tmp
month += 1
(foo, tmp) = self._lunar_month_days(year, month)
#计算日
day += delta_days
return (year, month, day)
def ln_date_str(self):# 返回农历日期字符串,形如:农历正月初九
_, month, day = self.ln_date()
return '农历{}月{}'.format(self.lm[month-1], self.ld[(day-1)*2:day*2])
def ln_jie(self): # 返回农历节气
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = ct.year
for i in range(24):
#因为两个都是浮点数,不能用相等表示
delta = self._julian_day() - self._julian_day_of_ln_jie(year, i)
if -.5 <= delta <= .5:
return self.jie[i*2:(i+1)*2]
return ''
#显示日历
def calendar(self):
pass
#######################################################
# 下面皆为私有函数
#######################################################
def _date_diff(self):
'''返回基于1901/01/01日差数'''
return (self.localtime - datetime.datetime(1901, 1, 1)).days
def _get_leap_month(self, lunar_year):
flag = self.g_lunar_month[(lunar_year - self.START_YEAR) // 2]
if (lunar_year - self.START_YEAR) % 2:
return flag & 0x0f
else:
return flag >> 4
def _lunar_month_days(self, lunar_year, lunar_month):
if (lunar_year < self.START_YEAR):
return 30
high, low = 0, 29
iBit = 16 - lunar_month;
if (lunar_month > self._get_leap_month(lunar_year) and self._get_leap_month(lunar_year)):
iBit -= 1
if (self.g_lunar_month_day[lunar_year - self.START_YEAR] & (1 << iBit)):
low += 1
if (lunar_month == self._get_leap_month(lunar_year)):
if (self.g_lunar_month_day[lunar_year - self.START_YEAR] & (1 << (iBit -1))):
high = 30
else:
high = 29
return (high, low)
def _lunar_year_days(self, year):
days = 0
for i in range(1, 13):
(high, low) = self._lunar_month_days(year, i)
days += high
days += low
return days
# 返回指定公历日期的儒略日
def _julian_day(self):
ct = self.localtime #取当前时间
year = ct.year
month = ct.month
day = ct.day
if month <= 2:
month += 12
year -= 1
B = year / 100
B = 2 - B + year / 400
dd = day + 0.5000115740 #本日12:00后才是儒略日的开始(过一秒钟)*/
return int(365.25 * (year + 4716) + 0.01) + int(30.60001 * (month + 1)) + dd + B - 1524.5
# 返回指定年份的节气的儒略日数
def _julian_day_of_ln_jie(self, year, st):
s_stAccInfo =[
0.00, 1272494.40, 2548020.60, 3830143.80, 5120226.60, 6420865.80,
7732018.80, 9055272.60, 10388958.00, 11733065.40, 13084292.40, 14441592.00,
15800560.80, 17159347.20, 18513766.20, 19862002.20, 21201005.40, 22529659.80,
23846845.20, 25152606.00, 26447687.40, 27733451.40, 29011921.20, 30285477.60]
#已知1900年小寒时刻为1月6日02:05:00
base1900_SlightColdJD = 2415025.5868055555
if (st < 0) or (st > 24):
return 0.0
stJd = 365.24219878 * (year - 1900) + s_stAccInfo[st] / 86400.0
return base1900_SlightColdJD + stJd
# 测试
def test(ct=None):
ln = Lunar(ct)
print('公历 {} 北京时间 {}'.format(ln.localtime.date(), ln.localtime.time()))
print('{} 【{}】 {}年 {}日 {}时'.format(ln.ln_date_str(), ln.gz_year(), ln.sx_year(), ln.gz_day(), ln.gz_hour()))
print('节气:{}'.format(ln.ln_jie()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
ct = datetime.datetime(2015,2,19,13,0,15)
test(ct)The above is the detailed content of How to share the method of converting solar calendar to lunar calendar in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.





