Detailed introduction to XSS and CSRF
1. Malicious attackers insert malicious Script code into a Web page. When a user browses the page, the Script code embedded in the Web page will be executed, thereby achieving the purpose of maliciously attacking the user.
1. Workflow
a. Malicious users enter some text in some public areas (for example, the input form of the suggestion submission form or the message public board), which is seen by other users. , but these texts are not only the text they want to input, but also include some scripts that can be executed on the client side. For example:
<script>'Not Safe'</script>
c. Other users see this page containing malicious scripts and execute them to obtain the user's cookies, etc. Sensitive information.
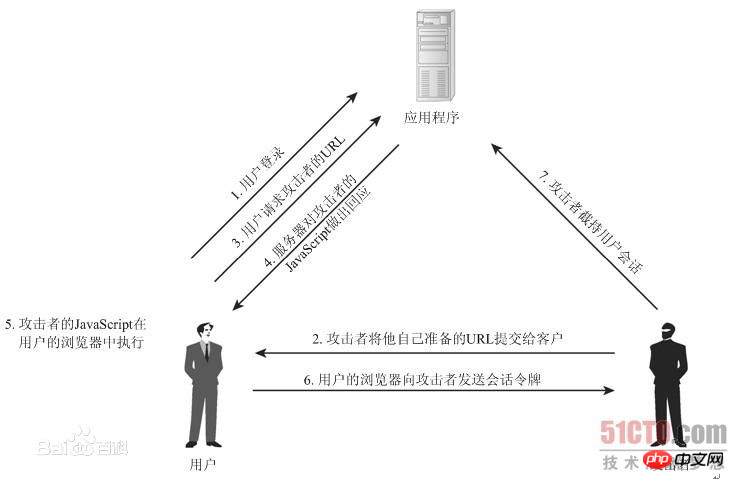
2. Example - Failure to prevent XSS attacks

1 pinglu = [] # 评论列表 2 3 #提交表单 4 def commit(request): 5 if request.method == 'GET': 6 return render(request, 'commit.html') 7 else: 8 com = request.POST.get('commit') 9 pinglu.append(com)10 return redirect('/index.html/')11 12 13 #查看评论页面14 def index(request):15 return render(request, 'index.html', {'commit': pinglu})
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <h1>评论</h1> 9 <form action="/commit.html/" method="post">10 <input type="text" name="commit">11 <input type="submit" value="sumbit"> {{ error }}12 </form>13 </body>14 </html>
 commit.html
commit.html
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <h1>评论</h1> 9 {% for item in commit %}10 <div>{{ item|safe }}</div>11 {# item后加safe,默认数据安全,django不会做特殊处理#}12 {% endfor %}13 </body>14 </html>
 index.html
In the above example, if you enter the following content on the commit.html page and submit:
index.html
In the above example, if you enter the following content on the commit.html page and submit:
<script> alert('恶意脚本') </script>3. Prevent XSS attacks 
- The most direct way is not to use safe
-
## for uncontrollable input in the html page
{# <div>{{ item|safe }}</div>#}<div>{{ item }}</div>Copy after login
-
def commit(request):if request.method == 'GET':return render(request, 'commit.html')else: com = request.POST.get('commit')if '<script>' in com: # 过滤“<script>”关键字,防止恶意代码的提交return render(request, 'commit.html', {'error': '此条评论有毒,已被和谐'})else: pinglu.append(com)return redirect('/index.html/')Copy after login
 2. CSRF
2. CSRF
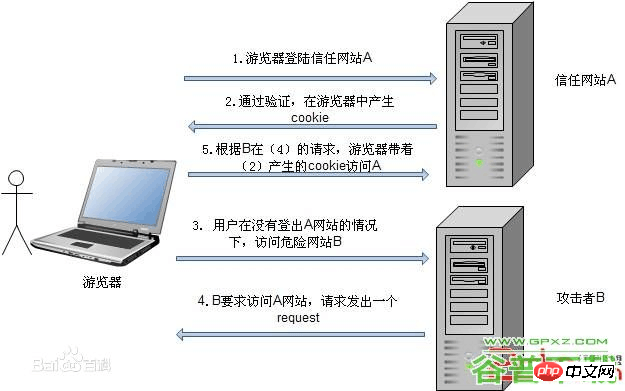
CSRF (Cross-site request forgery) cross-site request forgery, also known as "One Click Attack" or Session Riding, often abbreviated as CSRF or XSRF, is a malicious exploitation of a website. Although it sounds like cross-site scripting (XSS), it is very different from XSS, which exploits trusted users within a site, while CSRF exploits trusted websites by disguising requests from trusted users. Compared with XSS attacks, CSRF attacks tend to be less popular (so resources to prevent them are also quite scarce) and difficult to prevent, so they are considered more dangerous than XSS.
1. Workflow
The attack works by including links or scripts in pages accessed by authorized users:
2. How to prevent in django
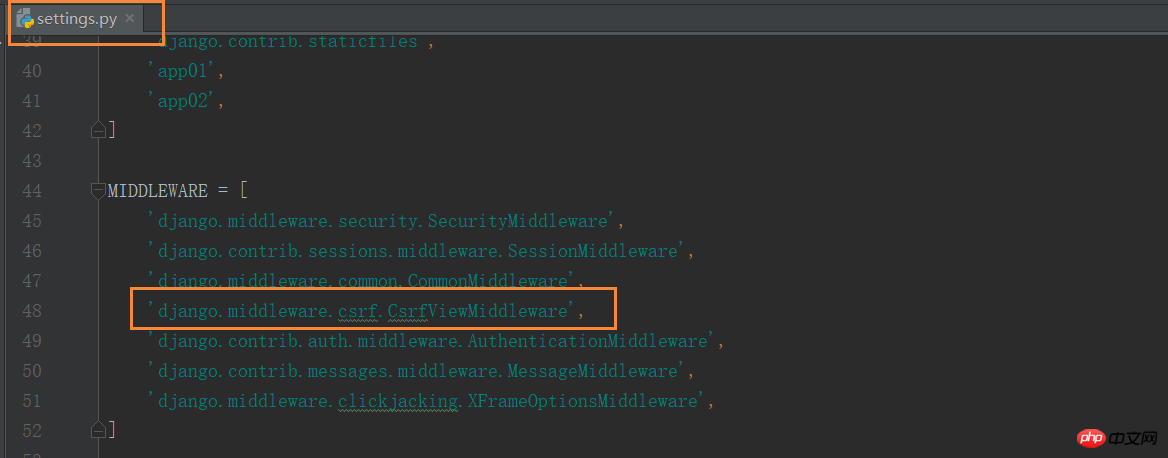
 Django implements the function of preventing cross-site request forgery for users, which is completed through the middleware django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware. The anti-cross-site request forgery function in Django is divided into global and local.
Django implements the function of preventing cross-site request forgery for users, which is completed through the middleware django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware. The anti-cross-site request forgery function in Django is divided into global and local.
Global:
Enable middleware django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddlewarefrom django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt,csrf_protect
@csrf_protect,为当前函数强制设置防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中没有设置全局中间件
@csrf_exempt,取消当前函数防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中设置了全局中间件。
3. django中的具体应用方法
form表单中添加
{%csrf_token%}
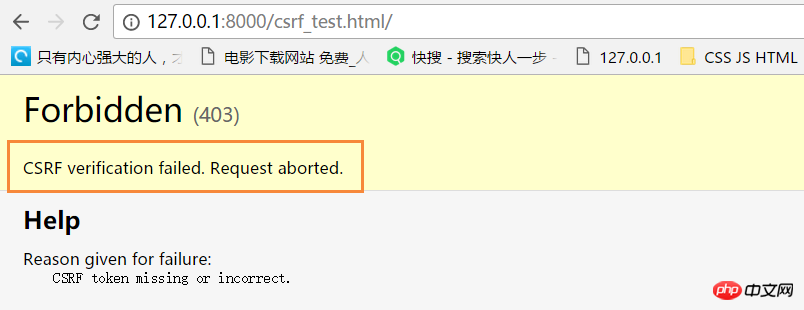
若form表单中未添加{% csrf_token %},则会报403错误。
#settings.py中打开MIDDLEWARE设置'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',


1 from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect2 3 def csrf_test(request):4 if request.method == 'GET':5 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')6 else:7 return HttpResponse('ok')

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">10 <input type="submit" value="submit">11 </form>12 13 </body>14 </html>
修改csef_test.html:


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 <input type="submit" value="submit">12 </form>13 14 </body>15 </html>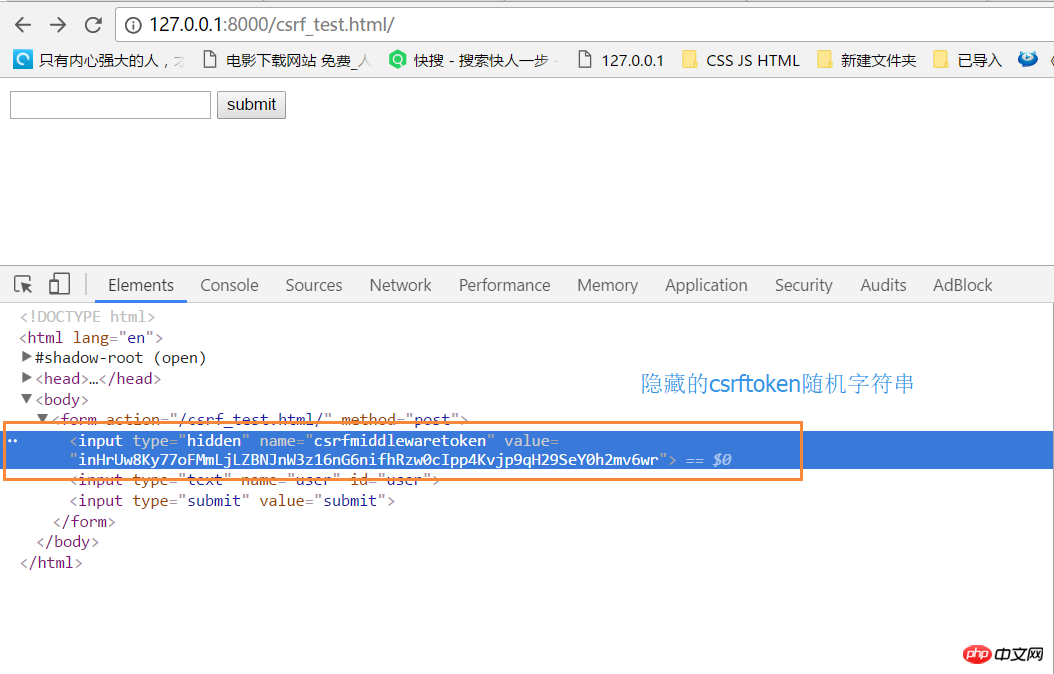
全站禁用,即将settings.py中的 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware' 注释掉即可
基于FBV视图的局部禁用和使用

1 #settings.py 2 #启用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt 6 7 8 @csrf_exempt 9 def csrf_test(request):10 if request.method == 'GET':11 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')12 else:13 return HttpResponse('ok')

1 #settings.py 2 #禁用 #'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_protect 6 7 8 @csrf_protect 9 def csrf_test(request):10 if request.method == 'GET':11 return render(request, 'csrf_test.html')12 else:13 return HttpResponse('ok')基于CBV视图的(只能局部使用或禁用类,不能在类方法里局部使用或禁用


1 #settings.py 2 #禁用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views import View 6 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_protect 7 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 8 9 10 @method_decorator(csrf_protect, name='dispatch')11 class Foo(View):12 def get(self, request):13 pass14 15 def post(self, request):16 pass
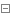
1 #settings.py 2 #启用 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 3 4 5 from django.views import View 6 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt 7 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 8 9 10 @method_decorator(csrf_exempt, name='dispatch')11 class Foo(View):12 def get(self, request):13 pass14 15 def post(self, request):16 pass
Ajax提交数据时,携带CSRF


1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 {# <input type="submit" value="submit">#}12 <a onclick="submitForm();">Ajax提交表单</a>13 </form>14 15 <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.js"></script>16 <script>17 function submitForm() {18 var csrf = $("input[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val()19 var user = $("#user").val()20 $.ajax({21 url: '/csrf_test.html/',22 type: 'POST',23 data: {"user": user, "csrfmiddlewaretoken": csrf},24 success: function (arg) {25 console.log(arg);26 }27 })28 }29 </script>30 </body>31 </html>

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>csef_test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <form action="/csrf_test.html/" method="post"> 9 {% csrf_token %}10 <input type="text" name="user" id="user">11 {# <input type="submit" value="submit">#}12 <a onclick="submitForm();">Ajax提交表单</a>13 </form>14 15 <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.js"></script>16 {#专门处理cookie的插件,提取cookie字符串#}17 <script src="/static/jquery.cookie.js"></script>18 19 {#csrf数据放于data中#}20 {#<script>#}21 {# function submitForm() {#}22 {# var csrf = $("input[name='csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val();#}23 {# var user = $("#user").val();#}24 {# $.ajax({#}25 {# url: '/csrf_test.html/',#}26 {# type: 'POST',#}27 {# data: {"user": user, "csrfmiddlewaretoken": csrf},#}28 {# success: function (arg) {#}29 {# console.log(arg);#}30 {# }#}31 {# })#}32 {# }#}33 {#</script>#}34 35 {#csrf数据放于请求头中#}36 <script>37 function submitForm() {38 var csrf = $.cookie('csrftoken');39 var user = $("#user").val();40 $.ajax({41 url: '/csrf_test.html/',42 type: 'POST',43 headers: {'X-CSRFToken': csrf},44 data: {"user": user},45 success: function (arg) {46 console.log(arg);47 }48 })49 }50 </script>51 52 53 54 </body>55 </html>注意:{% csrf_token %}和cookie中的csrftoken值不一样。
form表单中的隐藏csrf_token

cookie中

The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to XSS and CSRF. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
How to check django version
Dec 01, 2023 pm 02:25 PM
Steps to check the Django version: 1. Open a terminal or command prompt window; 2. Make sure Django has been installed. If Django is not installed, you can use the package management tool to install it and enter the pip install django command; 3. After the installation is complete , you can use python -m django --version to check the Django version.
 Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django vs. Flask: A comparative analysis of Python web frameworks
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Django and Flask are both leaders in Python Web frameworks, and they both have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. This article will conduct a comparative analysis of these two frameworks and provide specific code examples. Development Introduction Django is a full-featured Web framework, its main purpose is to quickly develop complex Web applications. Django provides many built-in functions, such as ORM (Object Relational Mapping), forms, authentication, management backend, etc. These features allow Django to handle large
 Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django Framework Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Django is a complete development framework that covers all aspects of the web development life cycle. Currently, this framework is one of the most popular web frameworks worldwide. If you plan to use Django to build your own web applications, then you need to understand the advantages and disadvantages of the Django framework. Here's everything you need to know, including specific code examples. Django advantages: 1. Rapid development-Djang can quickly develop web applications. It provides a rich library and internal
 How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to upgrade Django version: steps and considerations, specific code examples required Introduction: Django is a powerful Python Web framework that is continuously updated and upgraded to provide better performance and more features. However, for developers using older versions of Django, upgrading Django may face some challenges. This article will introduce the steps and precautions on how to upgrade the Django version, and provide specific code examples. 1. Back up project files before upgrading Djan
 What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
What is the difference between django versions?
Nov 20, 2023 pm 04:33 PM
The differences are: 1. Django 1.x series: This is an early version of Django, including versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8 and 1.9. These versions mainly provide basic web development functions; 2. Django 2.x series: This is the mid-term version of Django, including 2.0, 2.1, 2.2 and other versions; 3. Django 3.x series: This is the latest version series of Django. Including versions 3.0, 3, etc.
 How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check django version
Nov 30, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
How to check the django version: 1. To check through the command line, enter the "python -m django --version" command in the terminal or command line window; 2. To check in the Python interactive environment, enter "import django print(django. get_version())" code; 3. Check the settings file of the Django project and find a list named INSTALLED_APPS, which contains installed application information.
 Is django front-end or back-end?
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
Is django front-end or back-end?
Nov 21, 2023 pm 02:36 PM
django is the backend. Details: Although Django is primarily a backend framework, it is closely related to front-end development. Through features such as Django's template engine, static file management, and RESTful API, front-end developers can collaborate with back-end developers to build powerful, scalable web applications.
 Comparative analysis of PHP Session cross-domain and cross-site request forgery
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:58 PM
Comparative analysis of PHP Session cross-domain and cross-site request forgery
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:58 PM
Comparative analysis of PHPSession cross-domain and cross-site request forgery With the development of the Internet, the security of web applications has become particularly important. PHPSession is a commonly used authentication and session tracking mechanism when developing web applications, while cross-domain requests and cross-site request forgery (CSRF) are two major security threats. In order to protect the security of user data and applications, developers need to understand the difference between Session cross-domain and CSRF, and adopt






