 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of iterator and generator instance methods in Python
Detailed explanation of iterator and generator instance methods in Python
Detailed explanation of iterator and generator instance methods in Python
This article mainly introduces the relevant information on detailed examples of iterators and generators in Python. Friends in need can refer to
Python Detailed explanation of iterators and generator examples in Python
This article summarizes some related knowledge of iterators and generators in Python by focusing on different application scenarios and their solutions, as follows:
1. Manually traverse the iterator
Application scenario: I want to traverse all the elements in an iterableobject, but I don’t want to use a for loop
Solution: Use next()function, and catch the StopIteration exception
def manual_iter():
with open('/etc/passwd') as f:
try:
while True:
line=next(f)
if line is None:
break
print(line,end='')
except StopIteration:
pass#test case items=[1,2,3] it=iter(items) next(it) next(it) next(it)
2. Agent iteration
Application scenario: Want to perform an iterative operation directly on a container object containing a list, tuple or other iterable object
Solution: Define an iter() method to perform the iterative operation Proxy to the object inside the container
Example:
class Node:
def init(self,value):
self._value=value
self._children=[]
def repr(self):
return 'Node({!r})'.fromat(self._value)
def add_child(self,node):
self._children.append(node)
def iter(self):
#将迭代请求传递给内部的_children属性
return iter(self._children)#test case if name='main': root=Node(0) child1=Node(1) child2=Nide(2) root.add_child(child1) root.add_child(child2) for ch in root: print(ch)
3. Reverse iteration
Application scenario: Want to iterate a sequence in reverse
Solution: Use the built-in reversed() function or implement reversed() on a custom class
Example 1
a=[1,2,3,4]
for x in reversed(a):
print(x) #4 3 2 1
f=open('somefile')
for line in reversed(list(f)):
print(line,end='')
#test case
for rr in reversed(Countdown(30)):
print(rr)
for rr in Countdown(30):
print(rr)Example 2
class Countdown:
def init(self,start):
self.start=start
#常规迭代
def iter(self):
n=self.start
while n > 0:
yield n
n -= 1
#反向迭代
def reversed(self):
n=1
while n <p style="text-align: left;"><strong>4. Selective iteration</strong></p><p style="text-align: left;">Application scenario: I want to traverse an iterable object, but I am not interested in some elements at the beginning of it and want to skip</p><p style="text-align: left;">Solution : Use itertools.dropwhile()</p><p style="text-align: left;">Example 1</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">with open('/etc/passwd') as f:
for line in f:
print(line,end='')Example 2
from itertools import dropwhile
with open('/etc/passwd') as f:
for line in dropwhile(lambda line:line.startwith('#'),f):
print(line,end='')5. Iterate multiple sequences simultaneously
Application scenario: Want to iterate multiple sequences at the same time and take an element from one sequence each time
Solution: Use the zip() function


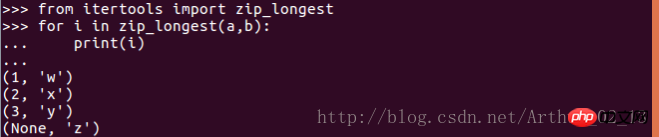
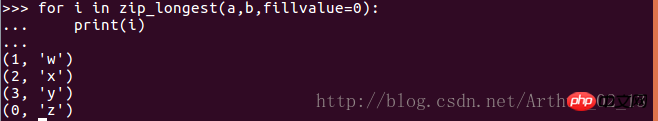
6. Iteration of elements on different collections
Application scenario: Want to perform the same operation on multiple objects, but these objects are in different containers
Solution: Use the itertool.chain() function
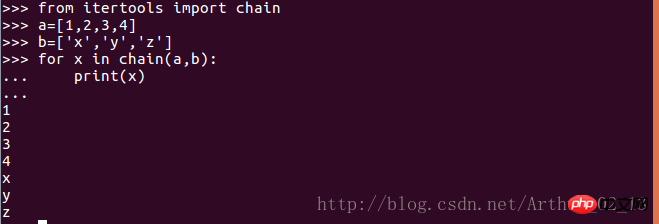
7. Expand nested sequences
Application scenario: Want to expand a multi-level nested sequence into a single-level list
Solution: Use RecursionGenerator containing yield from statement
Example
from collections import Iterable def flatten(items,ignore_types=(str,bytes)): for x in items: if isinstance(x,Iterable) and not isinstance(x,ignore_types): yield from flatten(x) else: yield x
#test case items=[1,2,[3,4,[5,6],7],8] for x in flatten(items): print(x)
Thank you for reading, I hope it can help everyone, thank you for your support of this site!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of iterator and generator instance methods in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1324
1324
 25
25
 1272
1272
 29
29
 1251
1251
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Pythonlistsarepartofthestandardlibrary,whilearraysarenot.Listsarebuilt-in,versatile,andusedforstoringcollections,whereasarraysareprovidedbythearraymoduleandlesscommonlyusedduetolimitedfunctionality.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Is it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.



