 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of examples of dictionary implementation using the zipper method
Detailed explanation of examples of dictionary implementation using the zipper method
Detailed explanation of examples of dictionary implementation using the zipper method
Dictionary:
is also called a hash table. Its biggest feature is the time complexity of finding its corresponding value through key It is O(1).
How to use lists to implement dictionaries in Python?
The biggest problem in using lists to implement dictionaries is to solvehashConflict, if you get the same position in the list by calculating different keys, what should you do at this time?
The simplest way is to use the zipper method.
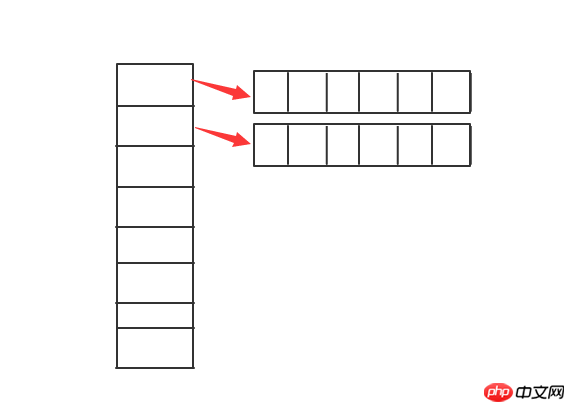
The zipper method: Add another list at each position in a list, so that even if there is Hash conflicts can also be stored. When the selected hashfunction is good enough and the number of
num is large enough, it can ensure that there is only one element in each list. Calculate the location of the element based on the key, and then get the value to achieve
to O(1) time.
class MyDict:
def __init__(self, num=100): # 指定列表大小
self._num = num
self._lst = []
for _ in range(self._num):
self._lst.append([])
def update(self, key, value): # 添加 key-value
key_index = hash(key) % self._num
for i, (k, v) in enumerate(self._lst[key_index]):
if key == k:
self._lst[key_index][i] = [key, value]
break
else:
self._lst[key_index].append([key, value])
def get(self, key): # 根据指定的 key 弹出值
key_index = hash(key) % self._num
for k, v in self._lst[key_index]:
if k == key:
return v
else:
raise KeyError('No such {} key'.format(key))
def pop(self, key): # 根据 key 弹出元素 并且删除
key_index = hash(key) % self._num
for i, (k, v) in enumerate(self._lst[key_index]):
if k == key:
result = v
self._lst.pop[self._num](i)
return result
else:
raise KeyError('No such {} key'.format(key))
def __getitem__(self, key): # 可以通过下标来取值
key_index = hash(key) % self._num
for k, v in self._lst[key_index]:
if k == key:
return v
else:
raise KeyError('No such {} key'.format(key))
def keys(self): # 取得所有的key
for index in range(self._num):
for k, v in self._lst[index]:
yield k
def values(self): # 取得所有的 value
for index in range(self._num):
for k, v in self._lst[index]:
yield v
def items(self): # 取得所有的条目
for index in range(self._num):
for item in self._lst[index]:
yield itemThe time found through key can be seen in the picture below
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of examples of dictionary implementation using the zipper method. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python and C each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1) Python is suitable for rapid development and data processing due to its concise syntax and dynamic typing. 2)C is suitable for high performance and system programming due to its static typing and manual memory management.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Is it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Pythonlistsarepartofthestandardlibrary,whilearraysarenot.Listsarebuilt-in,versatile,andusedforstoringcollections,whereasarraysareprovidedbythearraymoduleandlesscommonlyusedduetolimitedfunctionality.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Python for Web Development: Key Applications
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key Applications
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Key applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code



