 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of DB-API for Python connection to database learning
Detailed explanation of DB-API for Python connection to database learning
Detailed explanation of DB-API for Python connection to database learning
Before the Python DB-API, the application interfaces between databases were very confusing and the implementations were different. If the project needs to replace the database, it will require a lot of modifications, which is very inconvenient. The emergence of Python DB-API is to solve such problems. This article mainly introduces the relevant information of DB-API for Python to connect to the database. Friends in need can refer to it.
Preface
Everyone knows that if you want to connect to a database in Python, whether it is MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL or SQLite, use Cursors are always used, so you have to learn Python DB-API.
All Python database interface programs comply with the Python DB-API specification to a certain extent. DB-API defines a series of necessary objects and database access methods to provide consistent access interfaces for various underlying database systems and various database interface programs. Since DB-API provides a consistent access interface for different databases, porting code between different databases becomes an easy task.
Python connection database process:
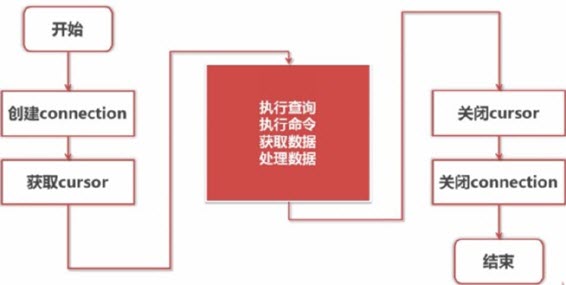
##Create using connect connection connection
The parameters of the connect function are as follows:
- user Username
- password Password
- host Hostname
- database Database name
- dsn Data source name
Of course, different database interface programs may have some differences, and not all are implemented strictly in accordance with the specifications. For example, MySQLdb uses the db parameter instead of the database parameter recommended by the specification to indicate the database to be accessed:
Parameters available when connecting to MySQLdb
- host: database host name. The default is the local host
- user: database Login name. The default is the current user
- passwd: The secret of database login. The default is empty
- db: The database name to be used. None Default value
- port: TCP port used by MySQL service. The default is 3306
- charset: Database encoding
Parameters available when connecting to psycopg2:
- ##dbname – database name (dsn connection mode)
- database – database name
- user – username
- password – password
- host – Server address (if the default connection Unix Socket is not provided)
- port – Connection port (default 5432)
- close(): Close this connect object. After closing, no further operations can be performed unless the connection is created again
- commit(): Submit the current transaction. If the database supports transactions and there is no commit after adding, deleting or modifying, the database will rollback by default
- ##rollback( ): Cancel the current transaction
- cursor(): Create a cursor object
cursor cursor object has the following properties and methods:
Common methods:
- fetchone(): Get the next row of the result set
- fetchmany([size = cursor.arraysize]): Get the next few rows of the result set
- fetchall(): Get all the remaining rows of the result set
- excute(sql[, args]): Execute a database query or command
- excutemany(sql, args):Execute multiple database queries or commands
- Common properties:
- arraysize: How many records are fetched at one time using the fetchmany() method, the default is 1
- lastrowid: Equivalent to PHP's last_inset_id()
##__iter__(): Create an iterable object (optional)
-
next(): Get the next row of the result set (if iteration is supported)
nextset(): Move to the next result set (if it is supported)
callproc(func[,args]): Call a stored procedure
setinputsizes(sizes): Set the maximum input value (must exist, but the specific implementation is Optional)
setoutputsizes(sizes[,col]): Set the maximum buffer size for large column fetch
##Other properties:
- description: Returns the cursor activity status (tuple containing 7 elements): (name, type_code, display_size, internal_size, precision, scale, null_ok) only name and type_cose is required
- rowcount: The number of rows created or affected by the most recent execute()
- messages: The information returned by the database after the cursor is executed Tuple (optional)
- rownumber: The index of the row where the cursor is located in the current result set (the starting row number is 0)
Error definition in DB-API only
Hierarchical relationship of error classes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
Database operation example
The code is as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 |
|

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Is it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python and C each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1) Python is suitable for rapid development and data processing due to its concise syntax and dynamic typing. 2)C is suitable for high performance and system programming due to its static typing and manual memory management.
 Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Pythonlistsarepartofthestandardlibrary,whilearraysarenot.Listsarebuilt-in,versatile,andusedforstoringcollections,whereasarraysareprovidedbythearraymoduleandlesscommonlyusedduetolimitedfunctionality.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed Look
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed Look
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python's applications in scientific computing include data analysis, machine learning, numerical simulation and visualization. 1.Numpy provides efficient multi-dimensional arrays and mathematical functions. 2. SciPy extends Numpy functionality and provides optimization and linear algebra tools. 3. Pandas is used for data processing and analysis. 4.Matplotlib is used to generate various graphs and visual results.
 Python for Web Development: Key Applications
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key Applications
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Key applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code



