Algorithm summary of Photoshop Gaussian blur filter
recently felt that some netizens' research on Gaussian blur filter is now summarized as follows. Gaussian blur is a kind of digital image template processing method. Its template is calculated based on a two-dimensional normal distribution (Gaussian distribution) function.
The normal distribution was first obtained by A. Demoivre in finding the asymptotic formula of the binomial distribution. C.F. Gauss derived it from another angle when studying measurement error. P.S. Laplace and Gauss studied its properties. Hence the name Gaussian blur.
Function definition of one-dimensional normal distribution:
Distribution of type random variables, the first parameter μ is the mean value of the random variable that follows the normal distribution , the second parameter σ2 is the variance of this random variable, so the normal distribution is recorded as N(μ, σ2). The probability rule of a random variable that follows a normal distribution is that the probability of taking a value near μ is high, and the probability of taking a value that is farther away from μ is smaller; the smaller σ, the more concentrated the distribution is near μ, and the larger σ, the smaller the distribution. dispersion. The characteristics of the density function of the normal distribution are: symmetric about μ, reaching a maximum value at μ, taking a value of 0 at positive (negative) infinity, and having an inflection point at μ±σ. Its shape is high in the middle and low on both sides, and the image is a bell-shaped curve above the x-axis. When μ = 0, σ2 = 1, it is called the standard normal distribution, recorded as N (0, 1). 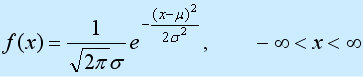
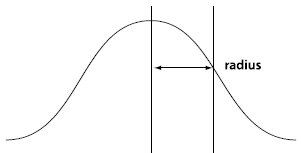
Based on this formula, we can calculate the Gaussian templates under different radii. In fact, the templates are infinite, but they will approach 0 far away from the center. For example, we calculate r A normalized Gaussian template when =0.7:
高斯模板(guass radius=0.700000)
在网络上众所周知流传的高斯3*3模板实际上是对高斯曲面的一个整数除法形式的近似:
1 2 1
2 4 2 /16
1 2 1
Actual verification, we found that this 3*3 template is actually an approximation of the Gaussian radius when it is about 0.849. When r=0.849, its 3*3 normalized template is (in MATLAB, enter h=fspecial('gaussian', 3, 0.849);You can get this template): 0.062467 0.125000 0.062467
0.125000 0.250131 0.125000 0.062467 0.125000 0.06246 7## Then we can use imfilter in Matlab to perform Gaussian blur processing on the image:
img = imread('c:\demo.bmp'); h = fspecial('gaussian', 3, 0.849);
subplot(121), imshow(img); title('Original image')
subplot(122), imshow(img2); title('After Gaussian blur')
# The effect is as follows: We can use it in Matlab as follows Statement to draw Gaussian surface:
Matlab code for drawing Gaussian surface
http:/ /www.php.cn/
-->%math.h>include
stdio.h>
define## N 3 3 / * Template size: (2N+1) * (2N+1) */
void main(){
double a[2*N+1][2*N+1]; /* Gaussian template*/ /* Gaussian radius: [0.1, 250] */
double A=1/
(2*##M_PI*r*r); int i,j; for(i=-
1*
N;i N;i++) for(j=-1 *N;j
N;j++)a[i+N][j+N]=A *exp((-1)*(i*i+j*j)/ (2*r*r));
}
case 'gaussian' % Gaussian filter
siz = (p2-1)/2; %注:p2即模板边长,默认值为33
std = p3; %注:p3即高斯半径,默认为为0.5
[x,y] = meshgrid(-siz(2):siz(2),-siz(1):siz(1));
arg = -(x.*x + y.*y)/(2*std*std);
h = exp(arg);
h(h<eps*max(h(:))) = 0;
sumh = sum(h(:)); %注:模板归一化
if sumh ~= 0,
h = h/sumh;
end;
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1418
1418
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 Photoshop's Value: Weighing the Cost Against Its Features
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Photoshop's Value: Weighing the Cost Against Its Features
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Photoshop is worth the investment because it provides powerful features and a wide range of application scenarios. 1) Core functions include image editing, layer management, special effects production and color adjustment. 2) Suitable for professional designers and photographers, but amateurs may consider alternatives such as GIMP. 3) Subscribe to AdobeCreativeCloud can be used as needed to avoid high one-time spending.
 Advanced Photoshop Tutorial: Master Retouching & Compositing
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Advanced Photoshop Tutorial: Master Retouching & Compositing
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Photoshop's advanced photo editing and synthesis technologies include: 1. Use layers, masks and adjustment layers for basic operations; 2. Use image pixel values to achieve photo editing effects; 3. Use multiple layers and masks for complex synthesis; 4. Use "liquefaction" tools to adjust facial features; 5. Use "frequency separation" technology to perform delicate photo editing, these technologies can improve image processing level and achieve professional-level effects.
 Photoshop for Web Design: Advanced Techniques for UI/UX
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Photoshop for Web Design: Advanced Techniques for UI/UX
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Photoshop can be used in web design to create high-fidelity prototypes, design UI elements, and simulate user interactions. 1. Use layers, masks and smart objects for basic design. 2. Simulate user interaction through animation and timeline functions. 3. Use scripts to automate the design process and improve efficiency.
 Photoshop's Key Features: A Deep Dive
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Photoshop's Key Features: A Deep Dive
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Key features of Photoshop include layers and masks, adjustment tools, filters and effects. 1. Layers and masks allow independent editing of image parts. 2. Adjust tools such as brightness/contrast can modify image tone and brightness. 3. Filters and effects can quickly add visual effects. Mastering these features can help creative professionals achieve their creative vision.
 Using Photoshop: Creative Possibilities and Practical Uses
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Using Photoshop: Creative Possibilities and Practical Uses
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Photoshop is very practical and creative in practical applications. 1) It provides basic editing, repairing and synthesis functions, suitable for beginners and professionals. 2) Advanced features such as content recognition fill and layer style can improve image effects. 3) Mastering shortcut keys and optimizing layer structure can improve work efficiency.
 Is Photoshop Free? Understanding Subscription Plans
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Is Photoshop Free? Understanding Subscription Plans
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Photoshop is not free, but there are several ways to use it at low cost or free: 1. The free trial period is 7 days, and you can experience all functions during this period; 2. Student and teacher discounts can cut costs by half, and school proof is required; 3. The CreativeCloud package is suitable for professional users and includes a variety of Adobe tools; 4. PhotoshopElements and Lightroom are low-cost alternatives, with fewer functions but lower prices.
 Photoshop Advanced Typography: Creating Stunning Text Effects
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Photoshop Advanced Typography: Creating Stunning Text Effects
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:15 AM
In Photoshop, you can create text effects through layer styles and filters. 1. Create a new document and add text. 2. Apply layer styles such as shadows and outer glow. 3. Use filters such as wave effects and add bevel and relief effects. 4. Use masks to adjust the effect range and intensity to optimize the visual impact of the text effect.
 The Core Purpose of Photoshop: Creative Image Design
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
The Core Purpose of Photoshop: Creative Image Design
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
Photoshop’s core use in creative image design is its powerful functionality and flexibility. 1) It allows designers to transform creativity into visual reality through layers, masks and filters. 2) Basic usages include cropping, resizing and color correction. 3) Advanced usages such as layer styles, blend modes and smart objects can create complex effects. 4) Common mistakes include improper layer management and excessive use of filters, which can be solved by organizing layers and using filters reasonably. 5) Performance optimization and best practices include rational use of layers, regular saving of files, and using shortcut keys.




