A brief discussion on jquery's on() binding event and off() unbinding event
The
off() function is used to remove the event handler of one or more events bound to an element. The
off() function is mainly used to unblock the event processing function bound by the on() function.
This function belongs to the jQuery object (instance).
Syntax
This function is added in jQuery 1.7. It mainly has the following two forms of usage:
Usage 1:
jQueryObject.off( [ events [, selector ] [, handler ] ] )
Usage 2:
jQueryObject.off( eventsMap [, selector ] ) The
parameters
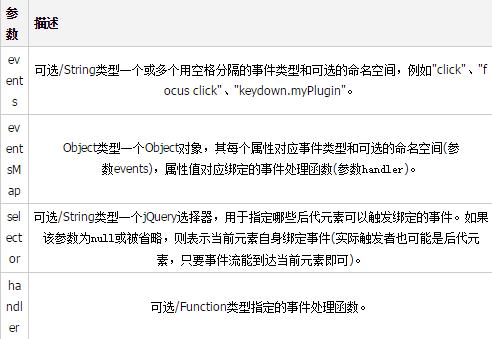
off() function will remove the event handler of the events event bound to the descendant element selector on the current matching element.
If the selector parameter is omitted, the event handler bound to any element is removed.
The parameter selector must be consistent with the selector passed in when adding binding through the on() function.
If the parameter handler is omitted, all event handlers bound to the specified event type of the specified element will be removed.
If all parameters are omitted, it means to remove any event handlers of any event type bound to any element on the current element.
Return value
The return value of the off() function is of jQuery type, returning the current jQuery object itself.
In fact, the parameters of the off() function are all filtering conditions, and only event processing functions that match all parameter conditions will be removed. The more parameters there are, the more qualifications there are and the smaller the range that is removed.
off() method code example:
Easily overlooked point: the unbinding event of the element off, where the selector must be consistent with the selector used when on binds the event.
html code
<input id="btn1" type="button" value="点击1" /> <input id="btn2" type="button" value="点击2" /> <a id="a1" href="#">CodePlayer</a>
jquery code executed when the page is loaded
function btnClick1(){
alert( this.value + "-1" );
}
function btnClick2(){
alert( this.value + "-2" );
}
var $body = $("body");
// 给按钮1绑定点击
$body.on("click", "#btn1", btnClick1 );
// 给按钮2绑定点击
$body.on("click", "#btn2", btnClick2 );
//为所有a元素绑定click、mouseover、mouseleave事件
$body.on("click mouseover mouseleave", "a", function(event){
if( event.type == "click" ){
$body.off("click", "#btn1");//取消btn1的绑定事件。成功执行
alert("点击事件");
alert("ddd");
}else if( event.type == "mouseover" ){
$(this).css("color", "red");
}else{
$(this).css("color", "blue");
}
});
// 移除body元素为所有button元素的click事件绑定的事件处理函数btnClick2
// 点击按钮,btnClick1照样执行
$body.off("click", ":button", btnClick2);
// 点击按钮1,不会执行任何事件处理函数
// $body.off("click", "#btn1");
// 注意: $body.off("click", ":button"); 无法移除btn1的点击事件,off()函数指定的选择器必须与on()函数传入的选择器一致。
// 移除body元素为所有元素(包括button和<a>元素)的click事件绑定的所有处理函数
// 点击按钮或链接,都不会触发执行任何事件处理函数
// $("body").off("click");
// 移除body元素为所有元素的任何事件绑定的所有处理函数
// 点击按钮,或点击链接或者鼠标移入/移出链接,都不会触发执行任何事件处理函数
// $("body").off( );
on() function is used to bind event handlers to one or more events of the specified element.
In addition, you can also pass some additional required data to the event handler function.
Starting from jQuery 1.7, the on() function provides all the functions required to bind event handlers, and is used to uniformly replace the previous event functions such as bind(), delegate(), live(), etc.
Even if it is a newly added element after executing the on() function, as long as it meets the conditions, the bound event handling function will be effective for it.
In addition, this function can bind multiple event handlers to the same element and the same event type. When an event is triggered, jQuery will execute the bound event processing functions in the order of binding.
To remove an event bound via on(), use the off() function. If you want to attach an event, execute it only once, and then delete itself, use the one() function.
This function belongs to jQuery object (instance).
Syntax
This function is added in jQuery 1.7. It mainly has the following two forms of usage:
Usage 1:
jQueryObject.on( events [, selector ] [, data ], handler )
Usage 2:
jQueryObject.on( eventsMap [, selector ] [ , data ] )
parameter
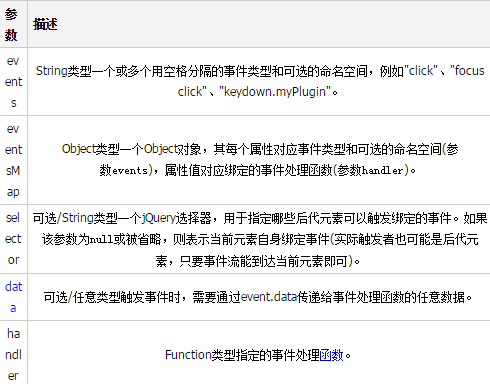
For the optional namespace in parameter events, please refer to the sample code below.
Regarding the parameter selector, you can simply understand it as: if the parameter is equal to null or omitted, the event is bound to the current matching element; otherwise, the event is bound to the elements that match the selector among the descendant elements of the current matching element. .
This in the parameter handler points to the DOM element that triggers the event among the descendant elements of the current matching element. If the selector parameter is null or omitted, this points to the current matching element (that is, the element).
on() will also pass in a parameter to the handler: the Event object representing the current event.
The return value of the parameter handler has the same effect as the return value of the DOM native event processing function. For example, the event handler of the "submit" (form submission) event returns false to prevent the form from being submitted.
If the event processing function handler only returns a false value, you can directly set the handler to false.
Return value
The return value of the on() function is of jQuery type, returning the current jQuery object itself.
Important note: The
on() function does not bind event handlers to elements matching the current jQuery object, but binds event handlers to elements in their descendant elements that match the selector parameter of the selector. The on() function does not directly bind events to these descendant elements one by one, but delegates processing to the matching elements of the current jQuery object. Due to the DOM level 2 event flow mechanism, when the descendant element selector triggers an event, the event will be passed to all its ancestor elements in the event bubbling. When the event flow is passed to the current matching element, jQuery will determine which descendant element it is. When an event is triggered, if the element matches the selector, jQuery will capture the event and execute the bound event handler.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference methods: Quick start guide
Feb 27, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Detailed explanation of jQuery reference method: Quick start guide jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used in website development. It simplifies JavaScript programming and provides developers with rich functions and features. This article will introduce jQuery's reference method in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers get started quickly. Introducing jQuery First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the HTML file. It can be introduced through a CDN link or downloaded
 How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
How to use PUT request method in jQuery? In jQuery, the method of sending a PUT request is similar to sending other types of requests, but you need to pay attention to some details and parameter settings. PUT requests are typically used to update resources, such as updating data in a database or updating files on the server. The following is a specific code example using the PUT request method in jQuery. First, make sure you include the jQuery library file, then you can send a PUT request via: $.ajax({u
 In-depth analysis: jQuery's advantages and disadvantages
Feb 27, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
In-depth analysis: jQuery's advantages and disadvantages
Feb 27, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
jQuery is a fast, small, feature-rich JavaScript library widely used in front-end development. Since its release in 2006, jQuery has become one of the tools of choice for many developers, but in practical applications, it also has some advantages and disadvantages. This article will deeply analyze the advantages and disadvantages of jQuery and illustrate it with specific code examples. Advantages: 1. Concise syntax jQuery's syntax design is concise and clear, which can greatly improve the readability and writing efficiency of the code. for example,
 How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery?
Feb 28, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to remove the height attribute of an element with jQuery? In front-end development, we often encounter the need to manipulate the height attributes of elements. Sometimes, we may need to dynamically change the height of an element, and sometimes we need to remove the height attribute of an element. This article will introduce how to use jQuery to remove the height attribute of an element and provide specific code examples. Before using jQuery to operate the height attribute, we first need to understand the height attribute in CSS. The height attribute is used to set the height of an element
 jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page
Feb 28, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Title: jQuery Tips: Quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page In web development, we often need to modify and operate elements on the page. When using jQuery, sometimes you need to modify the text content of all a tags in the page at once, which can save time and energy. The following will introduce how to use jQuery to quickly modify the text of all a tags on the page, and give specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library file and ensure that the following code is introduced into the page: <
 Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags
Feb 28, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Title: Use jQuery to modify the text content of all a tags. jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM operations. In web development, we often encounter the need to modify the text content of the link tag (a tag) on the page. This article will explain how to use jQuery to achieve this goal, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to introduce the jQuery library into the page. Add the following code in the HTML file:
 How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute?
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:03 AM
How to tell if a jQuery element has a specific attribute? When using jQuery to operate DOM elements, you often encounter situations where you need to determine whether an element has a specific attribute. In this case, we can easily implement this function with the help of the methods provided by jQuery. The following will introduce two commonly used methods to determine whether a jQuery element has specific attributes, and attach specific code examples. Method 1: Use the attr() method and typeof operator // to determine whether the element has a specific attribute
 Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
Understand the role and application scenarios of eq in jQuery
Feb 28, 2024 pm 01:15 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library that is widely used to handle DOM manipulation and event handling in web pages. In jQuery, the eq() method is used to select elements at a specified index position. The specific usage and application scenarios are as follows. In jQuery, the eq() method selects the element at a specified index position. Index positions start counting from 0, i.e. the index of the first element is 0, the index of the second element is 1, and so on. The syntax of the eq() method is as follows: $("s






