Parsing of React components and state|props
One of the pain points of reading source code is that you will fall into the dilemma of not straightening out the backbone. This series of articles implements a (x)react while straightening out the backbone content of the React framework (JSX/virtual DOM/components/... )
Components are functions
In the previous article JSX and Virtual DOM, the process of rendering JSX to the interface was explained and the corresponding code was implemented. The code call is as follows:
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
const element = (
<p>
hello<span>world!</span>
</p>
)
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('root')
)In this section, we will continue to explore the process of component rendering to the interface. Here we introduce the concept of components. A component is essentially a function. The following is a standard component code:
import React from 'react'
// 写法 1:
class A {
render() {
return <p>I'm componentA</p>
}
}
// 写法 2:无状态组件
const A = () => <p>I'm componentA</p>
ReactDOM.render(<a></a>, document.body)<a name="componentA"></a> is the way to write JSX. Same as the previous article, babel converts it into the form of React.createElement(). The conversion result is as follows:
React.createElement(A, null)
You can see that when JSX is a custom component , the first parameter after createElement becomes a function, and <a name="componentA"></a> is printed in repl, and the result is as follows:
{
attributes: undefined,
children: [],
key: undefined,
nodeName: ƒ A()
}Note that it is returned at this time nodeName in Virtual DOM has also become a function. Based on these clues, we transformed the previous render function.
function render(vdom, container) {
if (_.isFunction(vdom.nodeName)) { // 如果 JSX 中是自定义组件
let component, returnVdom
if (vdom.nodeName.prototype.render) {
component = new vdom.nodeName()
returnVdom = component.render()
} else {
returnVdom = vdom.nodeName() // 针对无状态组件:const A = () => <p>I'm componentsA</p>
}
render(returnVdom, container)
return
}
}At this point, we have completed the processing logic of the component.
Implementation of props and state
In component A in the previous section, no properties and states were introduced. We hope that properties (props) can be transferred between components and that components can Record the state (state).
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class A extends Component {
render() {
return <p>I'm {this.props.name}</p>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<a></a>, document.body)In the above code, we see that the A function inherits from Component. Let's construct this parent class Component and add state, props, setState and other attribute methods to it, so that subclasses can inherit them.
function Component(props) {
this.props = props
this.state = this.state || {}
}First, we pass the props outside the component into the component and modify the following code in the render function:
function render(vdom, container) {
if (_.isFunction(vdom.nodeName)) {
let component, returnVdom
if (vdom.nodeName.prototype.render) {
component = new vdom.nodeName(vdom.attributes) // 将组件外的 props 传进组件内
returnVdom = component.render()
} else {
returnVdom = vdom.nodeName(vdom.attributes) // 处理无状态组件:const A = (props) => <p>I'm {props.name}</p>
}
...
}
...
}After completing the transfer of props between components, let’s talk about state. In react In this example, setState is used to complete the change of component state. Subsequent chapters will delve into this API (asynchronous). Here is a simple implementation as follows:
function Component(props) {
this.props = props
this.state = this.state || {}
}
Component.prototype.setState = function() {
this.state = Object.assign({}, this.state, updateObj) // 这里简单实现,后续篇章会深入探究
const returnVdom = this.render() // 重新渲染
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML = null
render(returnVdom, document.getElementById('root'))
}Although the setState function has been implemented at this time, document.getElementById('root') It is obviously not what we want to write the node in setState. We transfer the dom node related to the _render function:
Component.prototype.setState = function(updateObj) {
this.state = Object.assign({}, this.state, updateObj)
_render(this) // 重新渲染
}Naturally, the reconstruction is related to it The render function:
function render(vdom, container) {
let component
if (_.isFunction(vdom.nodeName)) {
if (vdom.nodeName.prototype.render) {
component = new vdom.nodeName(vdom.attributes)
} else {
component = vdom.nodeName(vdom.attributes) // 处理无状态组件:const A = (props) => <p>I'm {props.name}</p>
}
}
component ? _render(component, container) : _render(vdom, container)
}The purpose of separating the _render function from the render function is to allow the _render logic to be called in the setState function. The complete _render function is as follows:
function _render(component, container) {
const vdom = component.render ? component.render() : component
if (_.isString(vdom) || _.isNumber(vdom)) {
container.innerText = container.innerText + vdom
return
}
const dom = document.createElement(vdom.nodeName)
for (let attr in vdom.attributes) {
setAttribute(dom, attr, vdom.attributes[attr])
}
vdom.children.forEach(vdomChild => render(vdomChild, dom))
if (component.container) { // 注意:调用 setState 方法时是进入这段逻辑,从而实现我们将 dom 的逻辑与 setState 函数分离的目标;知识点: new 出来的同一个实例
component.container.innerHTML = null
component.container.appendChild(dom)
return
}
component.container = container
container.appendChild(dom)
}Let us use the following use case to run the written react!
class A extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 1
}
}
click() {
this.setState({
count: ++this.state.count
})
}
render() {
return (
<p>
<button>Click Me!</button>
</p><p>{this.props.name}:{this.state.count}</p>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<a></a>,
document.getElementById('root')
)The rendering is as follows:
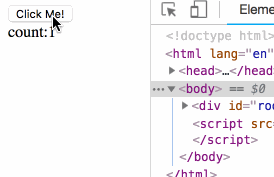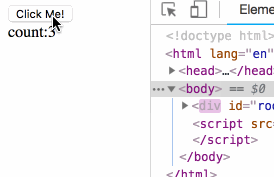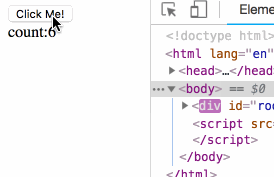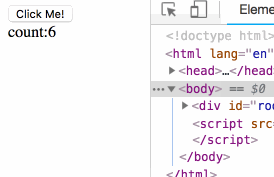
At this point, we have implemented the logic of the props and state parts.
Summary
Components are functions; when JSX is a custom component, the first parameter in React.createElement(fn, ..) after babel conversion becomes a function , except that other logic is the same as when it is an html element in JSX;
In addition, we have encapsulated apis such as state/props/setState into the parent class React.Component, so that they can be called in subclasses these properties and methods.
The above is the entire content of this article. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's study. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of config/index.js: configuration in vue
The above is the detailed content of Parsing of React components and state|props. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to call the method of child component in React parent component
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:01 PM
How to call the method of child component in React parent component
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:01 PM
Calling method: 1. Calls in class components can be implemented by using React.createRef(), functional declaration of ref or props custom onRef attribute; 2. Calls in function components and Hook components can be implemented by using useImperativeHandle or forwardRef to throw a child Component ref is implemented.
 In-depth understanding of React's custom Hooks
Apr 20, 2023 pm 06:22 PM
In-depth understanding of React's custom Hooks
Apr 20, 2023 pm 06:22 PM
React custom Hooks are a way to encapsulate component logic in reusable functions. They provide a way to reuse state logic without writing classes. This article will introduce in detail how to customize encapsulation hooks.
 How to debug React source code? Introduction to debugging methods using multiple tools
Mar 31, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
How to debug React source code? Introduction to debugging methods using multiple tools
Mar 31, 2023 pm 06:54 PM
How to debug React source code? The following article will talk about how to debug React source code under various tools, and introduce how to debug the real source code of React in contributors, create-react-app, and vite projects. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 How to set div height in react
Jan 06, 2023 am 10:19 AM
How to set div height in react
Jan 06, 2023 am 10:19 AM
How to set the div height in react: 1. Implement the div height through CSS; 2. Declare an object C in the state and store the style of the change button in the object, then get A and reset the "marginTop" in C. That is Can.
 Why React doesn't use Vite as the first choice for building apps
Feb 03, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
Why React doesn't use Vite as the first choice for building apps
Feb 03, 2023 pm 06:41 PM
Why doesn’t React use Vite as the first choice for building applications? The following article will talk to you about the reasons why React does not recommend Vite as the default recommendation. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 7 great and practical React component libraries (shared under pressure)
Nov 04, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
7 great and practical React component libraries (shared under pressure)
Nov 04, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
This article will share with you 7 great and practical React component libraries that are often used in daily development. Come and collect them and try them out!
 10 practical tips for writing cleaner React code
Jan 03, 2023 pm 08:18 PM
10 practical tips for writing cleaner React code
Jan 03, 2023 pm 08:18 PM
This article will share with you 10 practical tips for writing simpler React code. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about the differences in design and implementation between Vuex and Pinia
Dec 07, 2022 pm 06:24 PM
Let's talk about the differences in design and implementation between Vuex and Pinia
Dec 07, 2022 pm 06:24 PM
When developing front-end projects, state management is always an unavoidable topic. The Vue and React frameworks themselves provide some capabilities to solve this problem. However, there are often other considerations when developing large-scale applications, such as the need for more standardized and complete operation logs, time travel capabilities integrated in developer tools, server-side rendering, etc. This article takes the Vue framework as an example to introduce the differences in the design and implementation of the two state management tools, Vuex and Pinia.






