How to use Vue to develop time conversion instructions?
Let’s implement such a Vue custom instruction v-time to convert the timestamp passed in the expression into relative time in real time. Below I bring you a real-time time conversion instruction using Vue. Friends who need it can refer to it
Preface
Recently In other words, if you see a certain function of a website, you can probably guess what the business logic behind it is, and if you can develop an identical function, then your front-end skills are considered to be advanced. Advanced level. For example, the topic we are going to talk about today: How to use Vue to develop a real-time time conversion instruction?
The next text starts from here~
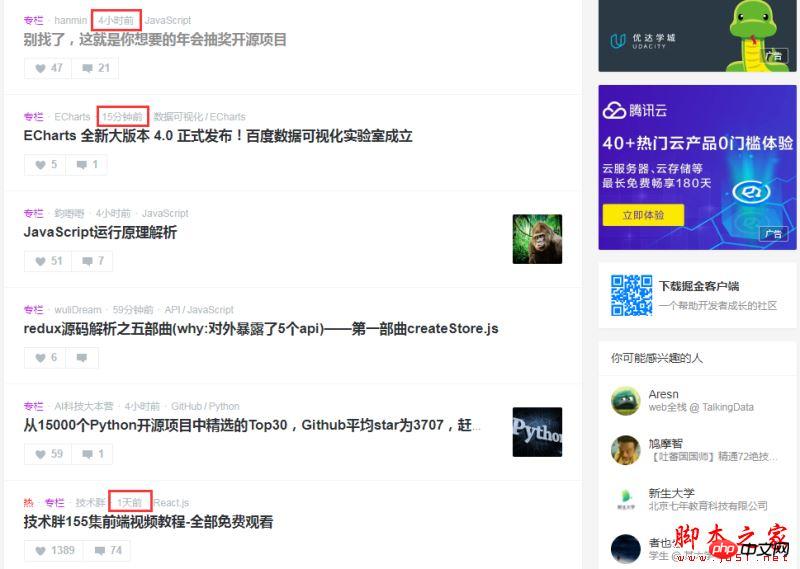
As shown in the picture above (I intercepted part of the home page of a technical community), you can see that using Check the time text with a red border. When many websites publish updates, there will be a relative time converted from the local time. So do you know the principle behind the implementation of this function? If you are interested, please prepare melon seeds and tea and continue reading.
Generally, the storage time format on the server is Unix timestamp. For example, the timestamp of 2018-01-17 06:00:00 is 1516140000. After the front end gets the data, it converts it into a sustainable time format and then displays it. In order to show real-time, in some social products, it will even be converted in real time into different formats such as seconds ago, minutes ago, hours ago, etc., because this is better than directly converting into years, months, days, hours, minutes, etc. In seconds, it appears more user-friendly and the experience is more humane.
Today, we will implement such a Vue custom instruction v-time to convert the timestamp passed in the expression into relative time in real time. In order to facilitate the demonstration effect, we defined two times during initialization.
First look at the html structure:
<p id="app" v-cloak> <p v-time="timeNow"></p> <p v-time="timeBefore"></p> </p>
and initialize a Vue instance:
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
timeNow:(new Date()).getTime(),
timeBefore:686219755822
}
})timeNow is the current time, timeBefore is a hard-coded time: 1991-09- 30.
Let’s first analyze the logic of time conversion:
1 minute ago, “just now” was displayed.
Between 1 minute and 1 hour, "xx minutes ago" is displayed.
Between 1 hour and 1 day, "xx hours ago" is displayed.
Between 1 day and 1 month (31 days), "xx days ago" is displayed.
If it is greater than 1 month, it will display "xx year xx month xx day".
Listed in this way, the logic will be clear at a glance. In order to make the judgment simpler, we uniformly use timestamps for size judgment here. Before writing the instruction v-time, we need to write a series of time-related functions. We declare an object Time and encapsulate them all in it.
var Time = {
//获取当前时间戳
getUnix:function(){
var date = new Date();
return date.getTime();
},
//获取今天0点0分0秒的时间戳
getTodayUnix:function(){
var date = new Date();
date.setHours(0);
date.setMinutes(0);
date.setSeconds(0);
date.setMilliseconds(0);
return date.getTime();
},
//获取今年1月1日0点0分0秒的时间戳
getYearUnix:function(){
var date = new Date();
date.setMonth(0);
date.setDate(1);
date.setHours(0);
date.setMinutes(0);
date.setSeconds(0);
date.setMilliseconds(0);
return date.getTime();
},
//获取标准年月日
getLastDate:function(time){
var date = new Date(time);
var month = date.getMonth() + 1 < 10 ? '0' + (date.getMonth() + 1) : date.getMonth() + 1;
var day = date.getDate() < 10 ? '0' + date.getDate() : date.getDate();
return date.getFullYear() + '-' + month + '-' + day;
},
//转换时间
getFormatTime:function(timestamp){
var now = this.getUnix(); // 当前时间戳
var today = this.getTodayUnix(); // 今天0点的时间戳
var year = this.getYearUnix(); // 今年0点的时间戳
var timer = (now - timestamp) / 1000; // 转换为秒级时间戳
var tip = '';
if(timer <= 0){
tip = '刚刚';
}else if(Math.floor(timer/60) <= 0){
tip = '刚刚';
}else if(timer < 3600){
tip = Math.floor(timer/60) + '分钟前';
}else if(timer >= 3600 && (timestamp - today >= 0)){
tip = Math.floor(timer/3600) + '小时前';
}else if(timer/86400 <= 31){
tip = Math.ceil(timer/86400) + '天前';
}else{
tip = this.getLastDate(timestamp);
}
return tip;
}
}Of course, if you don’t know much about JavaScript’s Date type, you can first go to runoob.com to learn more.
Then, the Time.getFormatTime() method is required for the custom instruction v-time. The parameter is a millisecond timestamp and returns the organized time format. String.
Finally, let’s see how we use Vue to customize an instruction v-time:
Vue.directive('time',{
bind:function(el, binding){
el.innerHTML = Time.getFormatTime(binding.value);
el.__timeout__ = setInterval(function(){
el.innerHTML = Time.getFormatTime(binding.value);
}, 60000)
},
unbind:function(el){
clearInterval(el.__timeout__);
delete el.__timeout__;
}
})In the bind hook, pass the value of the instruction v-time expression binding.value as a parameter Get the formatted time in the Time.getFormatTime() method, and write the element where the instruction is located through el.innerHTML. The timer el.__timeout__ is triggered every minute, updates the time, and is cleared in the unbind hook.
You may ask, what is this binding.value?
Of course, you can print it on the console through the console.log(binding) method, and it will be clear at a glance.
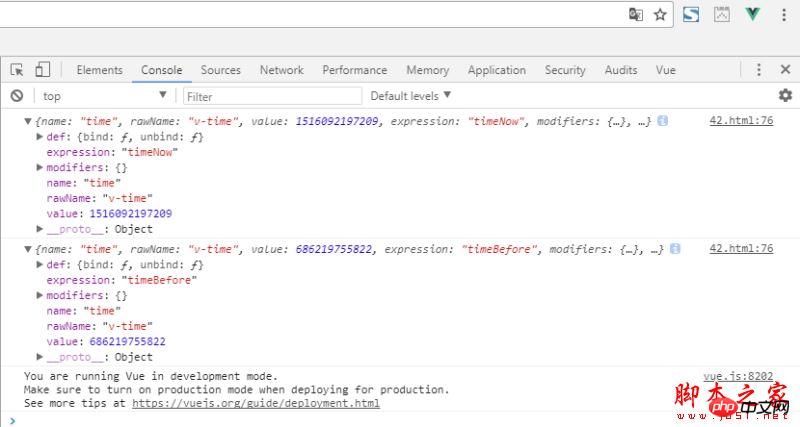
Here, let me first add that the options for custom instructions are composed of several hook functions, including bind, insert, update, componentUpdated, and unbind. The bind and unbind are only called once. Each hook function has several parameters available, such as el and binding we used above.
The elements bound to the el directive can be used to directly manipulate the DOM. Binding is an object that contains many attributes, as shown in the figure above:
name: Instruction name
rawName: Custom instruction
value: The binding value of the instruction
expression: The string form of the binding value
modifiers: an object containing modifiers
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
How to implement page jump in vue and return to the initial position of the original page
Cooperate in vue-router How ElementUI implements navigation
Detailed explanation of introducing elementUI components into the vue project
Refresh and tab switching in vue
How to implement mouse-responsive Taobao animation effect in jQuery
jQuery Implemented mouse response buffer animation effect
The above is the detailed content of How to use Vue to develop time conversion instructions?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.






