 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of the difference between assets and static in vue2.0 resource files
Detailed explanation of the difference between assets and static in vue2.0 resource files
Detailed explanation of the difference between assets and static in vue2.0 resource files
This article mainly introduces the difference between vue2.0 resource file assets and static. Now I will share it with you and give you a reference.
Resource file processing
In our project structure, there are two resource file paths, namely: src/assets and static/. So what is the difference between the two?
Webpacked Resources
In order to answer this question, we first need to understand how webpack handles static resources. In the *.vue component, all templates and css will be parsed by vue-html-loader and css-loader to find the URL of the resource.
For example, in  and background: url(./logo.png), "./logo.png", they are all relative resources Paths will be parsed into module dependencies by Webpack.
and background: url(./logo.png), "./logo.png", they are all relative resources Paths will be parsed into module dependencies by Webpack.
Since logo.png is not JavaScript, when it is regarded as a module dependency, we need to use url-loader and file-loader for processing. The template already has these loaders configured, so you can use relative/module paths without worrying about deployment issues. Since these resources may be inlined/copied/renamed at build time, they are essentially part of your source code. This is why we recommend placing static resources processed by webpack under the /src path like other source files. In fact, you don't even need to put them all under /src/assets: you can organize the file structure based on module/component usage. For example, you can put each component and its static resources in its own directory.
Resource processing rules
Relative URLs, e.g. ./assets/logo.png will be interpreted as a module dependency. They will be replaced by an automatically generated URL based on your Webpack output configuration. URLs without a prefix, e.g. assets/logo.png will be treated as relative URLs and converted to ./assets/logo.png
URLs prefixed with ~ will be treated as module requests, similar to require( 'some-module/image.png'). Use this prefix if you want to take advantage of Webpack's module handling configuration. For example, if you have a path resolution for assets, you need to use  to ensure that the resolution is correct. URLs relative to the root directory, e.g. /assets/logo.png will not be processed
to ensure that the resolution is correct. URLs relative to the root directory, e.g. /assets/logo.png will not be processed
Get the resource path in Javascript
In order to allow Webpack to return the correct For the resource path, you need to use require('./relative/path/to/file.jpg'), which will be parsed by file-loader and then the processed URL will be returned. For example:
computed: {
background () {
return require('./bgs/' + this.id + '.jpg')
}
}Note that in the above example, all images under the ./bgs/ path will be included in the final build. This is because Webpack cannot guess it. Which of them will be used at runtime, so all of them will be included.
"Real" static resources
As a comparison, files under static/ will not be processed by Webpack: they use the same file name, Copy directly to the final path. You must use absolute paths to reference these files, depending on build.assetsPublicPath and build.assetsSubDirectory added in config.js.
For example, the default value below is:
// config/index.js
module.exports = {
// ...
build: {
assetsPublicPath: '/',
assetsSubDirectory: 'static'
}
}All files placed in the static/ directory should use absolute URLs Referenced by /static/[filename]. If you change the value of assetSubDirectory to assets, then these URLs will become /assets/[filename]
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future.
Related articles:
Using ajax to change page content and address bar URL without refreshing
AJAX processing method for XML returned by the server
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the difference between assets and static in vue2.0 resource files. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 vue3+vite assets dynamically introduce images and solve the problem of incorrect image path not being displayed after packaging
May 10, 2023 pm 05:55 PM
vue3+vite assets dynamically introduce images and solve the problem of incorrect image path not being displayed after packaging
May 10, 2023 pm 05:55 PM
The official default configuration of vite. If the resource file is packaged in the assets folder, the hash value will be added to the image name. However, if it is imported directly through: src="imgSrc", it will not be parsed during packaging, causing the development environment to be imported normally. , we see the problem of not being displayed after packaging. In fact, we don’t want the resource files to be compiled by wbpack. It will be easier to put the images in the public directory. Whether it is a development environment or a production environment, the root directory can always be used to keep the image path consistent. , this is consistent with webpack. Seeing this, maybe the problem is solved. If you really need to put static files in assets in Vite, let’s look down:
 What is the function and usage of static in C language
Jan 31, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
What is the function and usage of static in C language
Jan 31, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
The role and usage of static in C language: 1. Variable scope; 2. Life cycle; 3. Internal function; 4. Modify global variables; 5. Modify function; 6. Other uses; Detailed introduction: 1. Variable scope, when If there is the static keyword before a variable, then the scope of the variable is limited to the file in which it is declared. In other words, the variable is a "file-level scope", which is very useful for preventing the "duplicate definition" problem of variables; 2. Life cycle, static variables are initialized once when the program starts executing, and destroyed when the program ends, etc.
 Practical application scenarios and usage skills of the static keyword in C language
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
Practical application scenarios and usage skills of the static keyword in C language
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
Practical application scenarios and usage skills of the static keyword in C language 1. Overview static is a keyword in C language, used to modify variables and functions. Its function is to change its life cycle and visibility during program running, making variables and functions static. This article will introduce the actual application scenarios and usage techniques of the static keyword, and illustrate it through specific code examples. 2. Static variables extend the life cycle of variables. Using the static keyword to modify local variables can extend their life cycle.
 How to use static, this, super, and final in Java
Apr 18, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use static, this, super, and final in Java
Apr 18, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
1. static Please look at the following program first: publicclassHello{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//(1)System.out.println("Hello, world!");//(2)}} Have seen this Segment programs are familiar to most people who have studied Java. Even if you have not learned Java but have learned other high-level languages, such as C, you should be able to understand the meaning of this code. It simply outputs "Hello, world" and has no other use. However, it shows the main purpose of the static keyword.
 How to use Java modifiers abstract, static and final
Apr 26, 2023 am 09:46 AM
How to use Java modifiers abstract, static and final
Apr 26, 2023 am 09:46 AM
Modifier abstract (abstract) 1. Abstract can modify a class (1) The class modified by abstract is called an abstract class (2) Syntax: abstractclass class name {} (3) Features: Abstract classes cannot create objects separately, but they can be declared Reference the abstract class name reference name; (4) Abstract classes can define member variables and member methods (5) Abstract classes have constructors. When used to create subclass objects, jvm creates a parent class object by default; abstract constructor methods apply Applied when jvm creates parent class object. 2. Abstract can modify methods (1) The method modified by asbtract is called an abstract method (2) Syntax: access modifier abstract return value
 The role of static
Jan 24, 2024 pm 04:08 PM
The role of static
Jan 24, 2024 pm 04:08 PM
The functions of static: 1. Variables; 2. Methods; 3. Classes; 4. Other uses; 5. Multi-threaded environment; 6. Performance optimization; 7. Singleton mode; 8. Constants; 9. Local variables; 10. Memory Layout optimization; 11. Avoid repeated initialization; 12. Use in functions. Detailed introduction: 1. Variables, static variables. When a variable is declared as static, it belongs to the class level, not the instance level, which means that no matter how many objects are created, only one static variable exists, and all objects share this Static variables and so on.
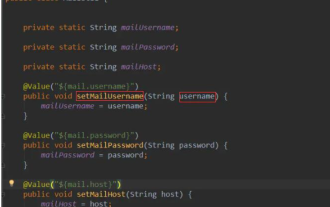 How Springboot reads custom pro files and injects static variables
May 30, 2023 am 09:07 AM
How Springboot reads custom pro files and injects static variables
May 30, 2023 am 09:07 AM
Springboot reads the pro file and injects static static variables mailConfig.properties#Server mail.host=smtp.qq.com#Port number mail.port=587#Email account mail.userName=hzy_daybreak_lc@foxmail.com#Email authorization code mail.passWord =vxbkycyjkceocbdc#Time delay mail.timeout=25000#Sender mail.emailForm=hzy_daybreak_lc@foxmail.com#Sender mai
 What is the static method of php
Oct 31, 2022 am 09:40 AM
What is the static method of php
Oct 31, 2022 am 09:40 AM
The "static" in php static static methods means that these properties and methods can be called directly without instantiating the class; static is a keyword used to modify the properties and methods of the class, and its usage syntax is such as "class Foo {public static $my_static = 'hello';}".





