Use history to enable ajax to support forward/back/refresh
This time I will bring you how to use history to enable ajax to support forward/back/refresh, and use history to enable ajax to support forward/back/refresh. What are the precautions?The following is a practical case, let’s take a look one time.
Foreword:
Nowadays, the front-end and back-end basically realize the interaction of front-end and back-end interface data through ajax. However, ajax has a small Disadvantages: Does not support browser "back" and "forward" keys.
However, now we can solve this small bug in ajax interactive requests through the history attribute of H5.
Event description:
H5 adds an event window.onpopstate. This event will be triggered when the user clicks those two buttons. But it is not enough to detect this event. You must also be able to pass some parameters. That is to say, when returning to the previous page, you must know the pageIndex of that page. This can be done through the pushState method of history. pushState(pageIndex) stores the pageIndex of the current page, and then obtains the pageIndex when returning to this page.
window.history.pushState Description:
window.history.pushState(state, title, url);
state object: is a JavaScript object, which is related to the new history entity created by the pushState() method. Used to store information about the entry you want to insert into the history. The State object can be any Jsonstring. Because Firefox will use the user's hard disk to access the state object, the maximum storage space of this object is 640k. If it is greater than this value, the pushState() method will throw an exception.
title: firefox now ignores this parameter, although it may be used in the future. The safest way to use it now is to pass an empty string to prevent future modifications.
url: Used to pass the URL of the new history entity. The browser will not load this URL after calling the pushState() method. Maybe try loading this URL after a while. For example, after the user restarts the browser, the new URL may not be an absolute path. If it is a relative path, it will be relative to the existing url. The new url must be in the same domain as the existing url, otherwise pushState() will throw an exception. This parameter is optional. If it is empty, it will be set to the current URL of the document.
Post the code directly:
/**
* Created: Aaron.
* address: http://www.cnblogs.com/aaron-pan/
*/
//var pageIndex=window.history.state===null?0:window.history.state.page;
(function($,window,undefined){
var loadData={
pageIndex:window.history.state===null?1:window.history.state.page,
//pageIndex:0,
init:function(){
this.getData(this.pageIndex);
this.nextPage();
},
getData:function(pageIndex){
var that=this;
$.ajax({
type:'post',
url:'./data/getMovices'+pageIndex+'.json',
dataType:'json',
async:false,
success:function(data){
that.renderDom(data);
}
})
},
renderDom:function(movies){
var bookHtml=
"<table>"+
"<tr>"+
"<th>电影</th>>"+
"<th>导演</th>"+
"<th>上映时间</th>"+
"</tr>";
for(var i=0;i<movies.length;i++){
bookHtml +=
"<tr>" +
" <td>" + movies[i].moviesName + "</td>" +
" <td><a>" + movies[i].moviesEditor + "</a></td>" +
" <td>" + movies[i].times + "</td>" +
"</tr>";
}
bookHtml+="</table>";
bookHtml +=
"<button>上一页</button>" +
"<button class='nextPage'>下一页</button>";
$('body').html(bookHtml);
},
nextPage:function(){
var that=this;
$(document).on("click",".nextPage",function(){
that.pageIndex++;
that.getData(that.pageIndex);
window.history.pushState({page:that.pageIndex},null,window.location.href);
//后退and刷新回到首页 window.history.replaceState({page:that.pageIndex},null,window.location.href);
})
},
};
loadData.init();
window.addEventListener("popstate",function(event){
var page=0;
if(event.state!==null){
page=event.state.page;
console.log('page:'+page);
}
console.log('page:'+page);
loadData.getData(page);
loadData.pageIndex=page;
})
})(jQuery,window,undefined);You can see the running results by directly calling the js file on the html page.
Running result:
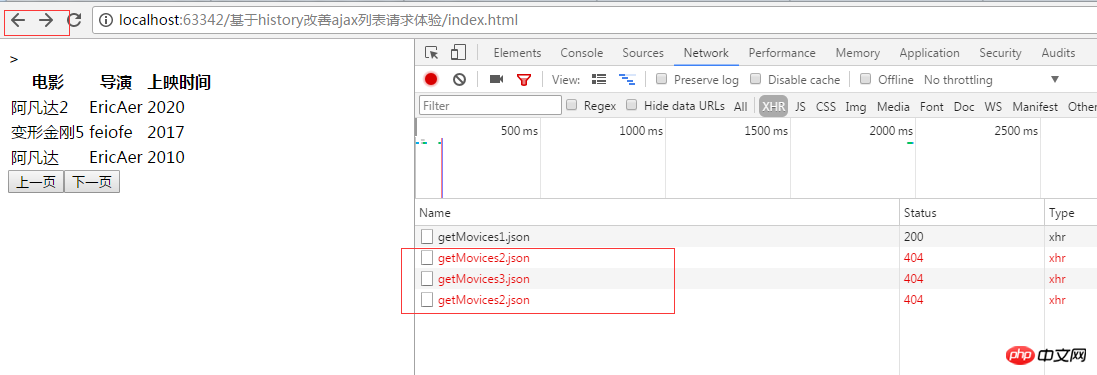
#In this way, you can interact through ajax and also realize the function of monitoring forward/background/refresh .
Attached browser compatibility:

I believe you have mastered the method after reading the case in this article. For more exciting things, please pay attention to php Other related articles on the Chinese website!
Recommended reading:
How Ajax+php performs data interaction and refreshes partial pages
Garbled characters appear when using Ajax How to deal with it
The above is the detailed content of Use history to enable ajax to support forward/back/refresh. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to resolve 403 errors in jQuery AJAX requests. The 403 error refers to a request that the server prohibits access to a resource. This error usually occurs because the request lacks permissions or is rejected by the server. When making jQueryAJAX requests, you sometimes encounter this situation. This article will introduce how to solve this problem and provide code examples. Solution: Check permissions: First ensure that the requested URL address is correct and verify that you have sufficient permissions to access the resource.
 How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library used to simplify client-side development. AJAX is a technology that sends asynchronous requests and interacts with the server without reloading the entire web page. However, when using jQuery to make AJAX requests, you sometimes encounter 403 errors. 403 errors are usually server-denied access errors, possibly due to security policy or permission issues. In this article, we will discuss how to resolve jQueryAJAX request encountering 403 error
 PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
Build an autocomplete suggestion engine using PHP and Ajax: Server-side script: handles Ajax requests and returns suggestions (autocomplete.php). Client script: Send Ajax request and display suggestions (autocomplete.js). Practical case: Include script in HTML page and specify search-input element identifier.
 How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403? When developing web applications, jQuery is often used to send asynchronous requests. However, sometimes you may encounter error code 403 when using jQueryAJAX, indicating that access is forbidden by the server. This is usually caused by server-side security settings, but there are ways to work around it. This article will introduce how to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403 and provide specific code examples. 1. to make
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows adding dynamic content without reloading the page. Using PHP and Ajax, you can dynamically load a product list: HTML creates a page with a container element, and the Ajax request adds the data to that element after loading it. JavaScript uses Ajax to send a request to the server through XMLHttpRequest to obtain product data in JSON format from the server. PHP uses MySQL to query product data from the database and encode it into JSON format. JavaScript parses the JSON data and displays it in the page container. Clicking the button triggers an Ajax request to load the product list.
 PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
In order to improve Ajax security, there are several methods: CSRF protection: generate a token and send it to the client, add it to the server side in the request for verification. XSS protection: Use htmlspecialchars() to filter input to prevent malicious script injection. Content-Security-Policy header: Restrict the loading of malicious resources and specify the sources from which scripts and style sheets are allowed to be loaded. Validate server-side input: Validate input received from Ajax requests to prevent attackers from exploiting input vulnerabilities. Use secure Ajax libraries: Take advantage of automatic CSRF protection modules provided by libraries such as jQuery.
 What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Ajax is not a specific version, but a technology that uses a collection of technologies to asynchronously load and update web page content. Ajax does not have a specific version number, but there are some variations or extensions of ajax: 1. jQuery AJAX; 2. Axios; 3. Fetch API; 4. JSONP; 5. XMLHttpRequest Level 2; 6. WebSockets; 7. Server-Sent Events; 8, GraphQL, etc.






