Deep understanding of JavaScript deep copy performance
This article mainly shares with you the analysis of JavaScript deep copy performance. How to copy an object in JavaScript? This is a very simple question, but the answer is not simple.
If you don't know what it means, take a look at the following example:
function mutate(obj) {
obj.a = true;
}
const obj = {a: false};
mutate(obj)
console.log(obj.a); // 输出 trueFunction mutate changes its parameters. In the value-passing scenario, the formal parameter of the function is just a copy of the actual parameter - a copy - and the actual parameter is not changed when the function call is completed. But in JavaScript's pass-by-reference scenario, the formal parameters and actual parameters of the function point to the same object. When the formal parameters are changed inside the parameters, the actual parameters outside the function are also changed.
So in some cases, you need to retain the original object. In this case, you need to pass a copy of the original object into the function to prevent the function from changing the original object.
Shallow copy: Object.assign()
A simple way to obtain a copy of an object is to use Object.assign(target, sources...) . It accepts any number of source objects, enumerates all their properties and assigns them to target. If we use a new empty object target, then we can copy the object.
const obj = /* ... */;
const copy = Object.assign({}, obj);However this is just a shallow copy. If our objects contain other objects as their properties, they will maintain shared references, which is not what we want:
function mutateDeepObject(obj) {
obj.a.thing = true;
}
const obj = {a: {thing: false}};
const copy = Object.assign({}, obj);
mutateDeepObject(copy)
console.log(obj.a.thing); // prints trueObject.assignMethod will only copy the source object Own and enumerable properties to the target object. This method uses the[[Get]]of the source object and the[[Set]]of the target object, so it calls the relevantgetterandsetter. Therefore, it assigns properties rather than just copying or defining new properties. If the merge source containsgetter, this may make it unsuitable for merging new properties into the prototype. In order to copy a property definition (including its enumerability) to the prototype,Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()andObject.defineProperty()should be used.
So what to do now? There are several ways to create a deep copy of an object.
Note: Maybe someone mentioned the object destructuring operation, which is also a shallow copy.
JSON.parse
One of the oldest ways to create a copy of an object is to convert that object to its JSON string representation, Then parse it back into an object. This feels a bit oppressive, but it works:
const obj = /* ... */; const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
The disadvantage here is that you create a temporary, potentially large string just to put it back into the parser. Another disadvantage is that this method cannot handle cyclic objects. And looping objects happens often. For example, when you build a tree-like data structure, a node refers to its parent, which in turn refers to its children.
const x = {};
const y = {x};
x.y = y; // Cycle: x.y.x.y.x.y.x.y.x...
const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(x)); // throws! In addition, such as Map, Set, RegExp, Date, ArrayBuffer and Other built-in types are lost when serialized.
Structured Clone Structured Cloning Algorithm
Structured cloning is an existing algorithm for transferring values from one place to another. For example, it is used whenever you call postMessage to send a message to another window or WebWorker. The nice thing about structured cloning is that it handles cyclic objects and supports a large number of built-in types. The problem is, at the time of writing this article, the algorithm is not available directly, only as part of other APIs. I guess we should know what's included, shouldn't we. . .
MessageChannel
As I said, the structured cloning algorithm works as long as you call postMessage. We can create a MessageChannel and send messages. On the receiving end, the message contains a structured clone of our original data object.
function structuralClone(obj) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
const {port1, port2} = new MessageChannel();
port2.onmessage = ev => resolve(ev.data);
port1.postMessage(obj);
});
}
const obj = /* ... */;
const clone = await structuralClone(obj);The disadvantage of this method is that it is asynchronous. Although this is not a big deal, sometimes you need to use a synchronous method to deep copy an object.
History API
If you have ever written a SPA using history.pushState(), you know that you can provide a state object to save the URL. It turns out that this state object uses structured cloning - and it's synchronous. We must be careful not to mess up the state objects used by the program logic, so we need to restore the original state after completing the cloning. To prevent any surprises, use history.replaceState() instead of history.pushState().
function structuralClone(obj) {
const oldState = history.state;
history.replaceState(obj, document.title);
const copy = history.state;
history.replaceState(oldState, document.title);
return copy;
}
const obj = /* ... */;
const clone = structuralClone(obj);However, using the browser's engine just to copy an object feels a bit excessive. Additionally, Safari browser limits the number of replaceState calls to 100 times in 30 seconds.
Notification API
After a tweet, Jeremy Banks showed me a third way to leverage structured cloning: the Notification API.
function structuralClone(obj) {
return new Notification('', {data: obj, silent: true}).data;
}
const obj = /* ... */;
const clone = structuralClone(obj);Short and concise. I like it!
However, it requires the permission mechanism inside the browser, so I suspect it is very slow. For some reason, Safari always returns undefined.
Performance extravaganza
I want to measure which method is the most performant. In my first (naive) attempt, I took a small JSON object and cloned the object a thousand times in different ways. Fortunately, Mathias Bynens told me that V8 has a cache when you add properties to an object. So I'm benchmarking the cache. To make sure I never hit the cache, I wrote a function that generates an object of a given depth and width with a random key name and reran the test.
chart!
Here are the performance of different technologies in Chrome, Firefox and Edge. The lower the better.
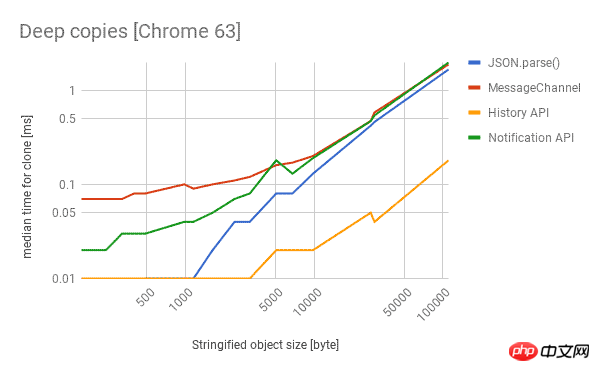
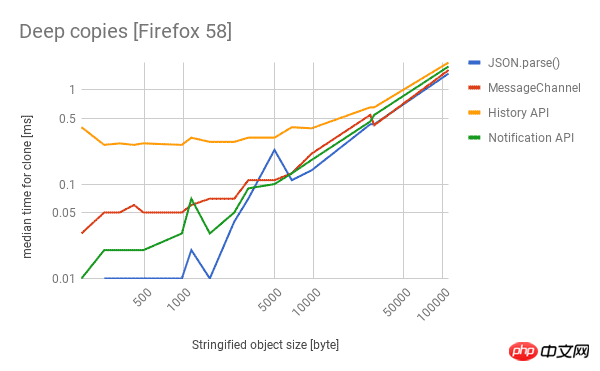
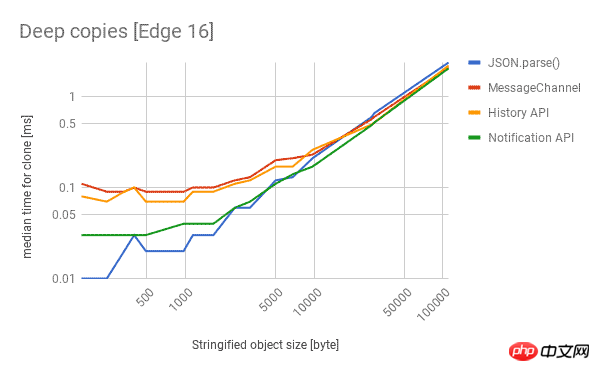
- If you are not looping over objects and do not need to preserve built-in types, you can use the cross-browser
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
to get the most Fast cloning performance, which really surprised me. - If you want a properly structured clone,
MessageChannel
is your only reliable cross-browser choice.
structuredClone() function? I certainly think so, the latest HTML specification is discussing this Synchronous clone = global.structuredClone(value, transfer = []) API · Issue #793 · whatwg/html.
JQuery’s $.extend shallow copy and deep copy example analysis
Achieve deep copy in jquery Copy and shallow copy
What are shallow and deep copies in Js
The above is the detailed content of Deep understanding of JavaScript deep copy performance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Windows 10 vs. Windows 11 performance comparison: Which one is better? With the continuous development and advancement of technology, operating systems are constantly updated and upgraded. As one of the world's largest operating system developers, Microsoft's Windows series of operating systems have always attracted much attention from users. In 2021, Microsoft released the Windows 11 operating system, which triggered widespread discussion and attention. So, what is the difference in performance between Windows 10 and Windows 11? Which
 Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Recommended: Excellent JS open source face detection and recognition project
Apr 03, 2024 am 11:55 AM
Face detection and recognition technology is already a relatively mature and widely used technology. Currently, the most widely used Internet application language is JS. Implementing face detection and recognition on the Web front-end has advantages and disadvantages compared to back-end face recognition. Advantages include reducing network interaction and real-time recognition, which greatly shortens user waiting time and improves user experience; disadvantages include: being limited by model size, the accuracy is also limited. How to use js to implement face detection on the web? In order to implement face recognition on the Web, you need to be familiar with related programming languages and technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, WebRTC, etc. At the same time, you also need to master relevant computer vision and artificial intelligence technologies. It is worth noting that due to the design of the Web side
 Comparison of PHP and Go languages: big performance difference
Mar 26, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Comparison of PHP and Go languages: big performance difference
Mar 26, 2024 am 10:48 AM
PHP and Go are two commonly used programming languages, and they have different characteristics and advantages. Among them, performance difference is an issue that everyone is generally concerned about. This article will compare PHP and Go languages from a performance perspective, and demonstrate their performance differences through specific code examples. First, let us briefly introduce the basic features of PHP and Go language. PHP is a scripting language originally designed for web development. It is easy to learn and use and is widely used in the field of web development. The Go language is a compiled language developed by Google.
 Comparing the performance of Win11 and Win10 systems, which one is better?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Comparing the performance of Win11 and Win10 systems, which one is better?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
The Windows operating system has always been one of the most widely used operating systems on personal computers, and Windows 10 has long been Microsoft's flagship operating system until recently when Microsoft launched the new Windows 11 system. With the launch of Windows 11 system, people have become interested in the performance differences between Windows 10 and Windows 11 systems. Which one is better between the two? First, let’s take a look at W
 The local running performance of the Embedding service exceeds that of OpenAI Text-Embedding-Ada-002, which is so convenient!
Apr 15, 2024 am 09:01 AM
The local running performance of the Embedding service exceeds that of OpenAI Text-Embedding-Ada-002, which is so convenient!
Apr 15, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Ollama is a super practical tool that allows you to easily run open source models such as Llama2, Mistral, and Gemma locally. In this article, I will introduce how to use Ollama to vectorize text. If you have not installed Ollama locally, you can read this article. In this article we will use the nomic-embed-text[2] model. It is a text encoder that outperforms OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 and text-embedding-3-small on short context and long context tasks. Start the nomic-embed-text service when you have successfully installed o
 Performance comparison of different Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:14 PM
Performance comparison of different Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 07:14 PM
Performance comparison of different Java frameworks: REST API request processing: Vert.x is the best, with a request rate of 2 times SpringBoot and 3 times Dropwizard. Database query: SpringBoot's HibernateORM is better than Vert.x and Dropwizard's ORM. Caching operations: Vert.x's Hazelcast client is superior to SpringBoot and Dropwizard's caching mechanisms. Suitable framework: Choose according to application requirements. Vert.x is suitable for high-performance web services, SpringBoot is suitable for data-intensive applications, and Dropwizard is suitable for microservice architecture.
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values takes a relatively long time.
 What impact do C++ functions have on program performance?
Apr 12, 2024 am 09:39 AM
What impact do C++ functions have on program performance?
Apr 12, 2024 am 09:39 AM
The impact of functions on C++ program performance includes function call overhead, local variable and object allocation overhead: Function call overhead: including stack frame allocation, parameter transfer and control transfer, which has a significant impact on small functions. Local variable and object allocation overhead: A large number of local variable or object creation and destruction can cause stack overflow and performance degradation.






