How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?
Tips for optimizing Hibernate query performance include: using lazy loading to defer loading collections and associated objects; using batch processing to combine update, delete, or insert operations; using second-level cache to store frequently queried objects in memory; using HQL outer join to retrieve entities and related entities; optimize query parameters to avoid SELECT N 1 query mode; use cursors to retrieve massive data in blocks; use indexes to improve the performance of specific queries.

Hibernate Tips for optimizing database query performance
Hibernate is a powerful ORM framework that simplifies interaction with the database. Optimizing Hibernate query performance is critical to improving overall application performance. This article will discuss some effective techniques for optimizing Hibernate queries and illustrate them through practical cases.
1. Use lazy loading
Lazy loading can postpone the loading of collections and associated objects until they are needed. This helps reduce the query's return result size and memory footprint.
Code case:
// 配置延迟加载 @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) private User author;
2. Using batch processing
Hibernate batch processing can combine multiple update, delete or INSERT operations into one batch deal with. This reduces the number of round trips to the database, thereby improving performance when operating in batches.
Code example:
// 批处理更新
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
session.beginTransaction();
for (User user : users) {
session.saveOrUpdate(user);
}
session.flush();
session.getTransaction().commit();3. Using the second-level cache
The second-level cache stores objects that are frequently queried from the database in memory. Avoid subsequent queries to the database. For frequently accessed data, this can significantly improve performance.
Code example:
<!-- 配置二级缓存 --> <property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache" value="true" /> <property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class" value="org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory" />
4. Using HQL outer join
HQL outer join allows retrieving an entity and all its related entities, even if some The related entity does not exist. This reduces the need to issue multiple database queries.
Code example:
String query = "SELECT u FROM User u LEFT JOIN FETCH u.orders"; List<User> users = session.createQuery(query).getResultList();
5. Optimizing query parameters
Hibernate query parameters allow dynamically generated queries by replacing values in the query at runtime . Optimizing query parameters includes avoiding the SELECT N 1 query mode and using batch parameters.
Code example:
// 使用批处理参数
Query query = session.createQuery("FROM User u WHERE u.id IN (:ids)");
query.setParameterList("ids", ids);6. Using cursors
For processing massive data, cursors allow data to be retrieved in blocks, thereby reducing memory usage and improve performance.
Code example:
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
ScrollableResults results = session.createQuery("FROM User").scroll(ScrollMode.FORWARD_ONLY);
while (results.next()) {
User user = (User) results.get(0);
// 处理用户
}7. Using appropriate indexes can significantly improve the performance of specific queries. Further optimization can be done by creating a covering index or a compound index.
Code Example:The above is the detailed content of How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!CREATE INDEX idx_user_name ON User(name);

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What to do if your Huawei phone has insufficient memory (Practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory)
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
What to do if your Huawei phone has insufficient memory (Practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory)
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:34 PM
Insufficient memory on Huawei mobile phones has become a common problem faced by many users, with the increase in mobile applications and media files. To help users make full use of the storage space of their mobile phones, this article will introduce some practical methods to solve the problem of insufficient memory on Huawei mobile phones. 1. Clean cache: history records and invalid data to free up memory space and clear temporary files generated by applications. Find "Storage" in the settings of your Huawei phone, click "Clear Cache" and select the "Clear Cache" button to delete the application's cache files. 2. Uninstall infrequently used applications: To free up memory space, delete some infrequently used applications. Drag it to the top of the phone screen, long press the "Uninstall" icon of the application you want to delete, and then click the confirmation button to complete the uninstallation. 3.Mobile application to
 How to fine-tune deepseek locally
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
How to fine-tune deepseek locally
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
Local fine-tuning of DeepSeek class models faces the challenge of insufficient computing resources and expertise. To address these challenges, the following strategies can be adopted: Model quantization: convert model parameters into low-precision integers, reducing memory footprint. Use smaller models: Select a pretrained model with smaller parameters for easier local fine-tuning. Data selection and preprocessing: Select high-quality data and perform appropriate preprocessing to avoid poor data quality affecting model effectiveness. Batch training: For large data sets, load data in batches for training to avoid memory overflow. Acceleration with GPU: Use independent graphics cards to accelerate the training process and shorten the training time.
 What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
1. First, enter the Edge browser and click the three dots in the upper right corner. 2. Then, select [Extensions] in the taskbar. 3. Next, close or uninstall the plug-ins you do not need.
 For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
The familiar open source large language models such as Llama3 launched by Meta, Mistral and Mixtral models launched by MistralAI, and Jamba launched by AI21 Lab have become competitors of OpenAI. In most cases, users need to fine-tune these open source models based on their own data to fully unleash the model's potential. It is not difficult to fine-tune a large language model (such as Mistral) compared to a small one using Q-Learning on a single GPU, but efficient fine-tuning of a large model like Llama370b or Mixtral has remained a challenge until now. Therefore, Philipp Sch, technical director of HuggingFace
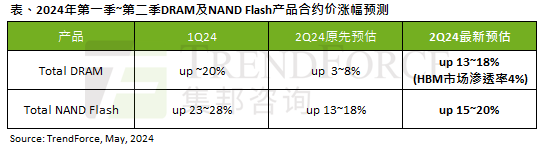 The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
According to a TrendForce survey report, the AI wave has a significant impact on the DRAM memory and NAND flash memory markets. In this site’s news on May 7, TrendForce said in its latest research report today that the agency has increased the contract price increases for two types of storage products this quarter. Specifically, TrendForce originally estimated that the DRAM memory contract price in the second quarter of 2024 will increase by 3~8%, and now estimates it at 13~18%; in terms of NAND flash memory, the original estimate will increase by 13~18%, and the new estimate is 15%. ~20%, only eMMC/UFS has a lower increase of 10%. ▲Image source TrendForce TrendForce stated that the agency originally expected to continue to
 What warnings or caveats should be included in Golang function documentation?
May 04, 2024 am 11:39 AM
What warnings or caveats should be included in Golang function documentation?
May 04, 2024 am 11:39 AM
Go function documentation contains warnings and caveats that are essential for understanding potential problems and avoiding errors. These include: Parameter validation warning: Check parameter validity. Concurrency safety considerations: Indicate the thread safety of a function. Performance considerations: Highlight the high computational cost or memory footprint of a function. Return type annotation: Describes the error type returned by the function. Dependency Note: Lists external libraries or packages required by the function. Deprecation warning: Indicates that a function is deprecated and suggests an alternative.
 What does sizeof mean in c language
Apr 29, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
What does sizeof mean in c language
Apr 29, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
sizeof is an operator in C that returns the number of bytes of memory occupied by a given data type or variable. It serves the following purposes: Determines data type sizes Dynamic memory allocation Obtains structure and union sizes Ensures cross-platform compatibility
 What pitfalls should we pay attention to when designing distributed systems with Golang technology?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
What pitfalls should we pay attention to when designing distributed systems with Golang technology?
May 07, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Pitfalls in Go Language When Designing Distributed Systems Go is a popular language used for developing distributed systems. However, there are some pitfalls to be aware of when using Go, which can undermine the robustness, performance, and correctness of your system. This article will explore some common pitfalls and provide practical examples on how to avoid them. 1. Overuse of concurrency Go is a concurrency language that encourages developers to use goroutines to increase parallelism. However, excessive use of concurrency can lead to system instability because too many goroutines compete for resources and cause context switching overhead. Practical case: Excessive use of concurrency leads to service response delays and resource competition, which manifests as high CPU utilization and high garbage collection overhead.






