Mysql源码学习――源码目录结构_MySQL
bitsCN.com
Mysql源码结构
目录清单
目录名 注释
Bdb 伯克利DB表引擎
BUILD 构建工程的脚本
Client 客户端
Cmd-line-utils 命令行工具
Config 构建工程所需的一些文件
Dbug Fred Fish的调试库
Docs 文档文件夹
Extra 一些相对独立的次要的工具
Heap HEAP表引擎
Include 头文件
Innobase INNODB表引擎
Libmysql 动态库
Libmysql_r 为了构建线程安全的libmysql库
Libmysqld 服务器作为一个嵌入式的库
Man 用户手册
Myisam MyISAM表引擎
Myisammrg MyISAM Merge表引擎
Mysql-test mysqld的测试单元
Mysys MySQL的系统库
Ndb Mysql集群
Netware Mysql网络版本相关文件
NEW-RPM 部署时存放RPM
Os2 针对OS/2操作系统的底层函数
Pstack 进行堆栈
Regex 正则表达式库(包括扩展的正则表达式函数)
SCCS 源码控制系统(不是源码的一部分)
Scripts 批量SQL脚本,如初始化库脚本
Server-tools 管理工具
Sql 处理SQL命令;Mysql的核心
Sql-bench Mysql的标准检查程序
Sql-common 一些sql文件夹相关的C文件
SSL 安全套接字层
Strings 字符串函数库
Support-files 用于在不同系统上构建Mysql的文件
Tests 包含Perl和C的测试
Tools
Vio 虚拟I/O库
Zlib 数据压缩库,用于WINDOWS
下面给出几个比较重要的目录清单:
文件清单
目录名 文件名 注释
Client
get_password.c 命令行输入密码
Mysql.cc MySQL命令行工具
Mysqladmin.cc 数据库weihu
Mysqldump.c 将表的内容以SQL语句输出,即逻辑备份
Mysqlimport.c 文本文件数据导入表中
Mysqlmanager-pwgen.c 密码生成
Mysqlshow.c 显示数据库,表和列
Mysqltest.c 被mysql测试单元使用的测试程序
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MYSYS
Array.c 动态数组
Charset.c 动态字符集,默认字符集
Charset-def.c 包含客户端使用的字符集
Checksum.c 为内存块计算校验和,用于pack_isam
Default.c 从*.cnf和*.ini文件中查找默认配置项
Default_modify.c 编辑可选项
Errors.c 英文错误文本
Hash.c hash查找、比较、释放函数
List.c 双向链表
Make-conf.c 创建*.conf文件
Md5.c MD5算法
Mf_brkhant.c
Mf_cache.c 打开临时文件,并使用io_cache进行缓存
Mf_driname.c 解析,转换路径名
Mf_fn_ext.c 获取文件名的后缀
Mf_format.c 格式化文件名
Mf_getdate 获取日期:
yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss format
mf_iocache.c 缓存I/O
mf_iocaches.c 多键值缓存
mf_loadpath.c 获取全路径名
mf_pack.c 创建需要的压缩/非压缩文件名
mf_path.c 决定是否程序可以找到文件
mf_qsort.c 快速排序
mf_qsort2.c 快速排序2
mf_radix.c 基数排序
mf_soundex.c 探测算法(EDN NOV 14, 1985)
mf_strip.c 去字符串结尾空格
mf_tempdir.c 临时文件夹的创建、查找、删除
mf_tempfile.c 临时文件的创建
mf_unixpath.c 转化文件名为UNIX风格
mf_util.c 常用函数
mf_wcomp.c 使用通配符比较
mf_wfile.c 通配符查找文件
mulalloc.c 同时分配多个指针
my_access.c 检查文件或路径是否合法
my_aes.c AES加密算法
my_alarm.c 警报相关
my_alloc.c 同时分配临时结果集缓存
my_append.c 一个文件到另一个
my_bit.c 除法使用,位运算
my_bitmap.c 位图
my_chsize.c 填充或截断一个文件
my_clock.c 时钟函数
my_compress.c 压缩
my_copy.c 拷贝文件
my_crc32.c
my_create.c 创建文件
my_delete.c 删除文件
my_p.c 获取文件名
my_dup.c 打开复制文件
my_error.c 错误码
my_file.c
my_fopen.c 打开文件
my_fstream.c 文件流读/写
my_gethostbyname.c 获取主机名
my_gethwaddr.c 获取硬件地址
my_getopt.c 查找生效的选项
my_getsystime.c time of day
my_getwd.c 获取工作目录
my_handler.c
my_init.c 初始化变量和函数
my_largepage.c 获取OS的分页大小
my_lib.c 比较/转化目录名和文件名
my_lock.c 锁住文件
my_lockmem.c 分配一块被锁住的内存
my_lread.c 读取文件到内存
my_lwrite.c 内存写入文件
my_malloc.c 分配内存
my_messnc.c 标准输出上输出消息
my_mkdir.c 创建目录
my_mmap.c 内存映射
my_net.c net函数
my_netware.c Mysql网络版
my_once.c 一次分配,永不free
my_open.c 打开一个文件
my_os2cond.c 操作系统cond的简单实现
my_os2dirsrch.c 模拟Win32目录查询
my_os2dlfcn.c 模拟UNIX动态装载
my_os2file64.c 文件64位设置
my_os2mutex.c 互斥量
my_os2thread.c 线程
my_os2tls.c 线程本地存储
my_port.c
my_pthread.c 线程的封装
my_quick.c 读/写
my_read.c 从文件读bytes
my_realloc.c 重新分配内存
my_redel.c 重命名和删除文件
my_seek.c 查找
my_semaphore.c 信号量
my_sleep.c 睡眠等待
my_static.c 静态变量
my_symlink.c 读取符号链接
my_symlink2.c 2
my_sync.c 同步内存和文件
my_thr_init.c 初始化/分配线程变量
my_wincond.c
my_windac.c WINDOWS NT/2000自主访问控制
my_winsem.c 模拟线程
my_winthread.c 模拟线程
my_write.c 写文件
ptr_cmp.c 字节流比较函数
queue,c 优先级队列
raid2.c 支持RAID
rijndael.c AES加密算法
safemalloc.c 安全的malloc
sha1.c sha1哈希加密算法
string.c 字符串函数
testhash.c 测试哈希函数(独立程序)
test_charset 测试字符集(独立)
thr_lock.c 读写锁
thr_mutex.c 互斥量
thr_rwlock.c 同步读写锁
tree.c 二叉树
typelib.c 字符串中匹配字串
SQL
derror.cc 读取独立于语言的信息文件
Des_key_file.cc 加载DES密钥
Discover.cc frm文件的查找
Field.cc 存储列信息
Filed_conv.cc 拷贝字段信息
Filesort.cc 结果集排序(内存或临时文件)
Frm_crypt.cc get_crypt_from_frm
Gen_lex_hash.cc 查找、排列SQL关键字
Gstream.c GIS
Handler.cc 函数句柄
Hash_filo.cc 静态大小HASH表,
以FIFO方式存储主机名、IP表
Ha_berkeley.cc BDB的句柄
Ha_innodb.cc INNODB句柄
Hostname.cc 根据IP获取hostname
Init.cc 初始化和unireg相关的函数
item.cc item函数
item_buff.cc item的保存和比较的缓存
item_cmpfunc.cc 比较函数的定义
item_create.cc 创建一个item
item_func.cc 数字函数
item_geofunc.cc 集合函数
item_row.cc 记录项比较
item_strfunc.cc 字符串函数
item_subselect.cc 子查询
item_sum.cc 集函数(SUM,AVG...)
item_timefunc.cc 时间日期函数
item_uniq.cc 空文件
Key.cc 创建KEY以及比较
Lock.cc 锁
Log.cc 日志
log_event.cc 日志事件
Matherr.c 处理溢出
mf_iocache.cc 顺序读写的缓存
Mysqld.cc main,处理信号和连接
mf_decimal.cc decimal类型
my_lock.c
net_serv.cc socket数据包的解析
nt_servc.cc NT服务
opt_range.cc KEY排序
opt_sum.cc 集函数优化
parse_file.cc frm解析
Password.c 密码检查
Procedure.cc
Protocol.cc 数据包打包发送给客户端
protocol_cursor.cc 存储返送数据
Records.cc 读取记录集
repl_failsafe.cc
set_var.cc 设置、读取用户变量
Slave.cc slave节点
Sp.cc 存储过程和存储函数
sp_cache.cc
sp_head.cc
sp_pcontext.cc
sp_rcontext.cc
Spatial.cc 集合函数,点线面
Sql_acl.cc ACL
sql_analyse.cc
sql_base.cc 基础函数
sql_cache.cc 查询缓存
sql_client.cc
sql_crypt.cc 加解密
sql_db.cc 创建、删除DB
sql_delete.cc DELETE语句
sql_derived.cc 派生表
sql_do.cc DO
sql_error.cc 错误和警告
sql_handler.cc
sql_help.cc HELP
sql_insert.cc INSERT
sql_lex.cc 词法分析
sql_list.cc
sql_load.cc LOAD DATA 语句
sql_manager.cc 维护工作
sql_map.cc 内存映射
sql_olap.cc
sql_parse.cc 解析语句
sql_prepare.cc
sql_rename.cc 重命名table名
sql_repl.cc 复制
sql_select.cc SELECT和JOIN优化
sql_show.cc SHOW
sql_state.c 错误号和状态的映射
sql_string.cc
sql_table.cc DROP TABLE、ALTER TABLE
sql_trigger.cc 触发器
sql_udf.cc 用户自定义函数
sql_union.cc UNION操作符
sql_update.cc UPDATE
sql_view.cc 视图
Stacktrace.c 显示堆栈(LINUX/INTEL ONLY)
Strfunc.cc
Table.cc 表元数据获取(FRM)
thr_malloc.cc
Time.cc
Uniques.cc 副本的快速删除
Unireg.cc 创建一个FRM
更多内容请参考:
http://forge.mysql.com/wiki/MySQL_Internals_Files_In_MySQL_Sources#The_sql_Directory
bitsCN.com
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
It is also a Tusheng video, but PaintsUndo has taken a different route. ControlNet author LvminZhang started to live again! This time I aim at the field of painting. The new project PaintsUndo has received 1.4kstar (still rising crazily) not long after it was launched. Project address: https://github.com/lllyasviel/Paints-UNDO Through this project, the user inputs a static image, and PaintsUndo can automatically help you generate a video of the entire painting process, from line draft to finished product. follow. During the drawing process, the line changes are amazing. The final video result is very similar to the original image: Let’s take a look at a complete drawing.
 Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com The authors of this paper are all from the team of teacher Zhang Lingming at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), including: Steven Code repair; Deng Yinlin, fourth-year doctoral student, researcher
 From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com In the development process of artificial intelligence, the control and guidance of large language models (LLM) has always been one of the core challenges, aiming to ensure that these models are both powerful and safe serve human society. Early efforts focused on reinforcement learning methods through human feedback (RL
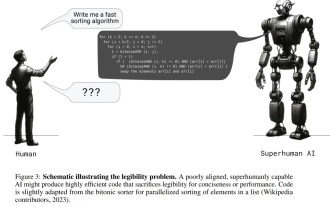 Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
If the answer given by the AI model is incomprehensible at all, would you dare to use it? As machine learning systems are used in more important areas, it becomes increasingly important to demonstrate why we can trust their output, and when not to trust them. One possible way to gain trust in the output of a complex system is to require the system to produce an interpretation of its output that is readable to a human or another trusted system, that is, fully understandable to the point that any possible errors can be found. For example, to build trust in the judicial system, we require courts to provide clear and readable written opinions that explain and support their decisions. For large language models, we can also adopt a similar approach. However, when taking this approach, ensure that the language model generates
 A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Recently, the Riemann Hypothesis, known as one of the seven major problems of the millennium, has achieved a new breakthrough. The Riemann Hypothesis is a very important unsolved problem in mathematics, related to the precise properties of the distribution of prime numbers (primes are those numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves, and they play a fundamental role in number theory). In today's mathematical literature, there are more than a thousand mathematical propositions based on the establishment of the Riemann Hypothesis (or its generalized form). In other words, once the Riemann Hypothesis and its generalized form are proven, these more than a thousand propositions will be established as theorems, which will have a profound impact on the field of mathematics; and if the Riemann Hypothesis is proven wrong, then among these propositions part of it will also lose its effectiveness. New breakthrough comes from MIT mathematics professor Larry Guth and Oxford University
 The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com. Introduction In recent years, the application of multimodal large language models (MLLM) in various fields has achieved remarkable success. However, as the basic model for many downstream tasks, current MLLM consists of the well-known Transformer network, which
 arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
cheers! What is it like when a paper discussion is down to words? Recently, students at Stanford University created alphaXiv, an open discussion forum for arXiv papers that allows questions and comments to be posted directly on any arXiv paper. Website link: https://alphaxiv.org/ In fact, there is no need to visit this website specifically. Just change arXiv in any URL to alphaXiv to directly open the corresponding paper on the alphaXiv forum: you can accurately locate the paragraphs in the paper, Sentence: In the discussion area on the right, users can post questions to ask the author about the ideas and details of the paper. For example, they can also comment on the content of the paper, such as: "Given to
 Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Show the causal chain to LLM and it learns the axioms. AI is already helping mathematicians and scientists conduct research. For example, the famous mathematician Terence Tao has repeatedly shared his research and exploration experience with the help of AI tools such as GPT. For AI to compete in these fields, strong and reliable causal reasoning capabilities are essential. The research to be introduced in this article found that a Transformer model trained on the demonstration of the causal transitivity axiom on small graphs can generalize to the transitive axiom on large graphs. In other words, if the Transformer learns to perform simple causal reasoning, it may be used for more complex causal reasoning. The axiomatic training framework proposed by the team is a new paradigm for learning causal reasoning based on passive data, with only demonstrations






