How to check disk space in Linux system How to check computer disk space
php editor Youzi will introduce you how to check the disk space in Linux system. Understanding computer disk space query methods is critical to system management and optimization. Through simple commands and tools, you can easily understand disk usage, free up space in time, and ensure the normal operation of the system. Follow our guide to master the skills of checking disk space and make your Linux system more efficient and stable.
How to operate:
View via df and du commands
df
df View the file system in units of disk partitions, and you can obtain information such as how much space is occupied by the hard disk and how much space is currently left.
For example, we use the df -h command to view disk information. The -h option displays it appropriately according to the size:
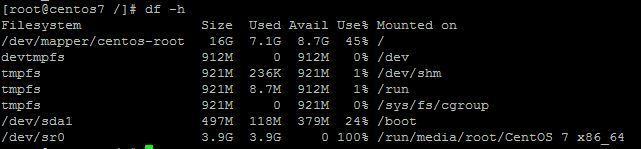
Display content parameter description:
- Filesystem:File system
- Size:Partition size
- Used:Used capacity
- Avail:The capacity that can still be used
- Use%: Used percentage
- Mounted on: Mount point
Related commands:
- df -hl: Check the remaining disk space
- df -h: Check the partition size of each root path
- du -sh [Directory name]: Return the directory size Size
- du -sm [folder]: Return the total number of M in the folder
- du -h [directory name]: View the size of all files in the specified folder (including subfolders )
du
The original English meaning ofdu is disk usage, which means to display the usage of disk space and is used to view the total size of the current directory.
For example, check the size of the current directory:
# du -sh
605M.
Display the space occupied by the specified file:
# du log2012.log
300 log2012.log
Display the space occupied by the test directory in an easy-to-read format:
# du -h test
608K test/test6
308K test/test4
4.0K test/scf/lib
4.0K test/scf/service/deploy/product
4.0K test/scf/service/deploy/info
12K test/scf/service/deploy
16K test/scf/service
4.0K test/scf/doc
4.0K test/scf/bin
32K test/scf
8.0K test/test3
1.3M test
du command is used to view the total size of the current directory:
- -s: Only the total number of occupied data blocks is given for each Names parameter.
- -a: Recursively display the number of data blocks occupied by each file in the specified directory and each file in the subdirectory. If neither -s nor -a is specified, only the number of disk blocks occupied by each directory in Names and its subdirectories is displayed.
- -b: List the disk space usage in bytes (the system defaults to k bytes).
- -k: List disk space usage in units of 1024 bytes.
- -c: Add a total at the end (system default setting).
- -l: Calculate the size of all files. For hard link files, calculate multiple times.
- -x: Skip directories on different file systems and do not count them.
- -h: Use K, M, G as units to improve the readability of information.
View hard disk space through graphical interface
For users who are accustomed to using graphical interfaces, there is a more intuitive and convenient method. Simply open a file manager (such as Nautilus or Thunar), select the directory or partition you are interested in, and right-click the mouse to select the "Properties" option in the pop-up menu. In the properties window, you will be able to see details such as the total capacity, used space, and remaining free space of the directory or partition.
Check hard disk space through third-party tools
If you want to get more detailed information about hard disk space, you can also use some third-party tools. For example, GParted is a powerful disk partitioning tool that can not only view the usage of hard disk partitions, but also manage and adjust partitions. In addition to the principles of the Linux operating system, Baobab is an intuitive and easy-to-use disk space analysis tool. It can graphically display the space occupied by each directory in your system, helping you quickly find files or directories that take up too much space.
Precautions:
When checking the hard disk space, please pay attention to the following points:
- 1. Make sure you have sufficient permissions to perform the corresponding operations;
- 2. Pay attention to choosing the appropriate viewing method, and choose the command line or graphical interface according to your own needs;
- 3. Regularly clean up useless files and temporary files to free up more hard disk space;
- 4. Operate carefully to avoid deleting important files or directories.
Through the introduction of this article, I believe that everyone has mastered the method of checking hard disk space under the Linux operating system. Whether you are a command line master or a graphical interface enthusiast, you can easily get the information you need. Remember, rational use of hard disk space will help improve system performance and work efficiency.
The above is the detailed content of How to check disk space in Linux system How to check computer disk space. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
How to switch Chinese mode with vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:39 PM
VS Code To switch Chinese mode: Open the settings interface (Windows/Linux: Ctrl, macOS: Cmd,) Search for "Editor: Language" settings Select "Chinese" in the drop-down menu Save settings and restart VS Code






