How to see what protocol m.2
Some friends don’t know what protocol their interface supports when buying M.2. They are afraid of buying the wrong one, or they don’t know what protocol the M.2 plugged into their computer supports. I will give you several methods below. The external distinction can be seen in the appearance and logo of the interface.
m.2 How to check the protocol
1. Look at the appearance of the interface. There is one NVME and two SATA. (It is not universal, just a method)


2. Check what protocols are supported on the M.2 hard disk.

3. The host checks what protocols the inserted SSD supports.
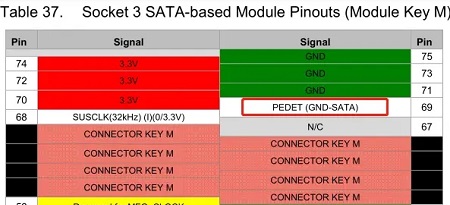
(1) When pin 69 is detected to be floating, it will be displayed that the SSD is of NVME protocol.

(2) When pin 69 is detected to be grounded, it will be displayed that the SSD is SATA protocol.
The above is the detailed content of How to see what protocol m.2. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Which protocol does vivo fast charging belong to?
Sep 06, 2022 pm 02:43 PM
Which protocol does vivo fast charging belong to?
Sep 06, 2022 pm 02:43 PM
There are two main protocols for vivo fast charging: 1. "QC 2.0" fast charging protocol. "QC2.0" is "Quick Charge 2.0" technology. It is version 2.0 of fast charging technology released by Qualcomm. It can output 5V, 9V, and 12V. , 20V four voltage groups; 2. PD fast charging protocol is a fast charging specification formulated by the "USB-IF" organization. It is one of the current mainstream fast charging protocols and can make the current default maximum power "5V/2A" The "type-c" interface is increased to 100W.
 What is the maximum watt of PD3.0 fast charging protocol?
Nov 08, 2022 pm 04:04 PM
What is the maximum watt of PD3.0 fast charging protocol?
Nov 08, 2022 pm 04:04 PM
The PD3.0 fast charging protocol supports up to “100W”. In November 2015, USB PD fast charging ushered in a major version update, entering the USB PD3.0 fast charging era; the PD3.0 protocol supports 5V3A, 9V3A, 12V3A, 15V3A, 20V5A output, and the maximum power can reach 100W. Not only can It can be used to charge mobile phones, and can also be used to power laptops or monitors.
 What are the 5 industrial communication protocols?
Sep 28, 2022 am 11:52 AM
What are the 5 industrial communication protocols?
Sep 28, 2022 am 11:52 AM
5 types of industrial communication protocols: 1. Modbus protocol, which is a universal language used in electronic controllers; 2. RS-232 protocol, which is a serial physical interface standard; 3. RS-485 protocol, which is based on RS232 Developed on the basis of; 4. HART protocol is a communication protocol used between on-site intelligent instruments and control room equipment; 5. MPI protocol is a cross-language communication protocol used to write parallel computers.
 SOAP Protocol Guide in PHP
May 20, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
SOAP Protocol Guide in PHP
May 20, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
With the continuous development of Internet technology, more and more enterprise-level applications need to provide interfaces to other applications to realize the interaction of data and business. In this case, we need a reliable protocol to transmit data and ensure data integrity and security. SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is an XML-based protocol that can be used to implement communication between applications in a Web environment. As a popular web programming language, PHP
 What is the difference between m.2 and sata solid state drives?
Feb 18, 2024 am 09:30 AM
What is the difference between m.2 and sata solid state drives?
Feb 18, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Is there a big gap between M.2 and SATA solid-state drives? Many novices may have questions when purchasing. In fact, the gap depends on whether M.2 supports NVME or SATA. If it is the former, the gap will be one day at a time. If it is the latter, there is basically no difference between the two. What is the difference between m.2 and sata solid state drives? Answer: There is a huge difference. The transfer speed between the two is almost the same. 1. The maximum transmission speed of SATA3.0 solid-state drive is 6Gbps, and the actual speed can reach up to 560MB/s. 2. Even M.2 solid-state drives that support the NVMe protocol can be increased to 3.5GB/s. However, M.2 also supports the SATA protocol. The reading speed of this hard disk is not the same as that of SATA.
 What is the difference between m.2 and SATA
Feb 18, 2024 am 09:09 AM
What is the difference between m.2 and SATA
Feb 18, 2024 am 09:09 AM
Distinguishing the difference between hard drives is the first lesson for beginners. Today we will talk about the difference between M.2 and SATA. There are always newcomers who can’t understand the difference between them. M.2 is new. The SATA interface is compatible with new motherboards and is supported by both old and new motherboards, with different prices and definitions. What is the difference between m.2 and SATA? 1. Compatibility difference: As an old interface, SATASSD has long become a mainstream interface standard and is compatible with all old motherboards. As a new interface, M.2SSD is not compatible with all motherboards due to the low motherboard support rate. However, all new motherboards now support the M.2 interface; it has even become standard, and some motherboards are equipped with more than one M.2 interface. , all support the NVME protocol. 2. Different protocols: M.2 is
 What is the qc4+ fast charging protocol?
Aug 18, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
What is the qc4+ fast charging protocol?
Aug 18, 2022 pm 03:49 PM
The QC4+ fast charging protocol is a combination of the USB PD PPS protocol and the QC3.0/2.0 fast charging protocol. It is a multi-functional, multi-protocol fast charging technology. The QC4+ charging protocol is compatible with USB PD3.0 (PPS) and is downwardly compatible with USB PD2.0, QC3.0, QC2.0, BC1.2 and other protocols. The first prerequisite for supporting USB PD and QC4+ is the support of USB-C interfaces at both ends and the power negotiation message based on the CC (configuration channel) in the USB-C interface.
 What technology does the x.25 protocol use?
Jul 18, 2022 pm 04:05 PM
What technology does the x.25 protocol use?
Jul 18, 2022 pm 04:05 PM
The "x.25" protocol uses packet switching technology; the "x.25" protocol is a computer-oriented data communication network, consisting of basic equipment such as transmission lines, packet switches, remote concentrators and packet terminals, and adopts a layered architecture , negotiation, control and information transmission of information exchange are carried out between the peer layers of the interface through the communication protocol between the peer layers.






