File Management on Linux: 7 Tips and 4 Tools
Linux is an excellent operating system that provides a powerful command line and flexible file system. However, if you don't pay attention to file organization and cleanup, your computer may become cluttered, affecting your efficiency and experience. This article will share some tips and tools for organizing files and cleaning up your computer on Linux to help you maintain a clean and orderly work environment.
1. Give the file a meaningful name
Give your files and directories descriptive and meaningful names that reflect their contents or purpose. This makes it easier to guess the contents of future folders or files.
Keep in mind that Linux is case sensitive, so the directories linuxmi and Linuxmi are different, even if they have the same name.
Avoid using spaces and special characters. Using spaces in folder or file names can cause problems in scripts or when using the command line. You can use hyphens (-) or underscores (_) to separate words in the name.

The most important thing is to be consistent when naming your files. For example, I use snake_case for all filenames. It uses lowercase letters and words separated by underscores. For example, a job application letter would be named job_application_letter.doc.
For directories, I use Pascal_Snake_Case. Capitalize the first letter of each word and separate words with underscores. For example, my repository for all Python projects will be named Python_Projects.
Find or create a naming convention that suits your needs and use it consistently across your systems.
2. Always use file extension
Related to naming, use file extensions whenever possible and maintain consistency. For example, you can save all your Word documents with the Open Document Format extension, which means that all Word documents will have the ".odt" extension.

If you're consistent, it's easy to associate certain file types with default programs. This saves you time in the long run.
File extensions make searching for files easier. Additionally, you can easily run automated scripts or commands targeting specific file extensions.
3. Organize your directory structure
We all know those people who put all directories on their desktop or in a specific folder. What a mess! Be sure to avoid doing this and always keep your desktop clean.
Putting too many directories in one place can be confusing and make it difficult to locate files, thus affecting productivity.
By default, Linux has specific directories used to store specific types of files, such as the Pictures directory, Videos directory or Music directory. This demonstrates the importance of grouping related items, so follow the same principles when creating a table of contents.

Organize your directory structure so that it does not contain too many files and subdirectories. Place related items in specific directories and create more categories if necessary. Just make sure your directories aren't nested too deeply.
4. Location is crucial
In addition to organizing your directory structure correctly, it is also very important to place all files in the correct location.
Learn best practices from Linux itself. It follows a directory structure to organize files. Therefore, you should follow the same principles. For example, the /etc/ directory is for configuration files, while the /bin/ directory is for user binaries or programs.

File location is critical for quickly navigating and finding files. It also plays an important role when performing backups or synchronizing data. For example, if all your photos are in the Pictures directory, you can just back up the Pictures directory to make sure all your important memories are there.
5. Sort files
To further improve work efficiency, you should sort directories and files according to your needs. You can sort files by date, name, type or date modified, and file size. This will make it easier for you to find and locate the file later.
Sorting files by modification date can help you identify frequently used files. Conversely, files that have not been modified for a long time may need to be deleted.
Overall, sorting files by certain parameters will give you a lot of benefits. It will increase your productivity and simplify file management.
6. Custom directory preferences
Linux provides many file and directory customization options that can improve your workflow. For example, you can change the catalog icon so items can be found at a glance.
You can also create symbolic links for frequently accessed projects. But make sure all symbolic links are working properly. Regularly take the time to repair broken symbolic links.
Use the directory preference menu to customize how you interact with your files. For example, you can customize whether a file opens with a double-click or a single click. You can also customize whether certain context menus appear when you right-click a file or directory.
Additionally, you can customize your search preferences and specify the depth of your search.
Related:
- Find all symbolic links in Linux https://www.linuxmi.com/linux-find-soft-links.html
- How to create symbolic links in Linux [Complete Guide] https://www.linuxmi.com/creating-symbolic-links-in-linux.html
7. Clean up unnecessary files
Use the disk management tools that come with Linux to understand how much disk space you are using and find out which files are taking up a lot of disk space.
Disk Usage Analyzer is a graphical tool that interactively displays an overview of disk usage. The red area shows the directories taking up the most space.
You can also use the du command and the df command to find the directory size and disk usage. The df -h command displays disk usage in human-readable format.
To identify large files or directories, you can run the sudo du /-h | sort -h command. It will show all directories under the root (/) directory and the disk space used by them. The -h flag indicates that the output is displayed in human-readable format. Then, import the output into the sort command to sort the directories by disk usage size.

Browse the output to identify files taking up too much space and determine whether they are still relevant. Otherwise, you can clear them.
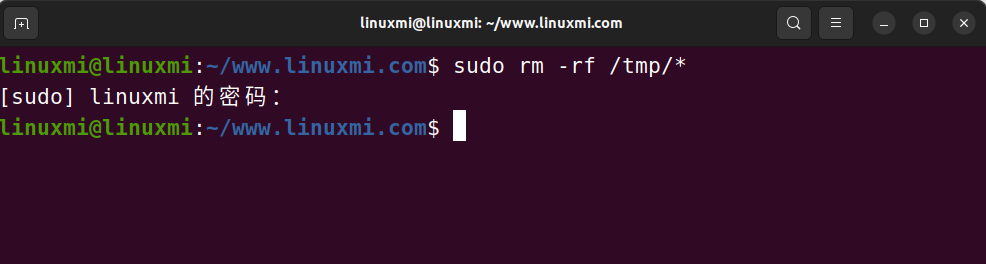
Clean your computer cache regularly and delete temporary files that are no longer needed using the following command:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ sudo rm -rf /tmp/*
View the log files and determine the log files that are no longer needed. Most log files are located in the /var/log directory.
All deleted files will be placed in the Recycle Bin by default. However, they still take up disk space. Consider emptying your Recycle Bin to get rid of cluttered files.
Be careful when using the rm command. It permanently deletes files and can cause chaos if used incorrectly.
Organize your files and be more productive on Linux
These tips will help you get the most out of your Linux system. Use meaningful names, structure your directories, purge old files, and be consistent throughout.
If you use the GNOME desktop environment, you can also increase your productivity by installing some of the best GNOME Shell extensions.
Through this article, we learned some tips and tools for organizing files and cleaning up the computer on Linux. These include giving files meaningful names, using file extensions, structuring directories appropriately, choosing appropriate storage locations, sorting files according to different criteria, customizing directory preferences, and regularly cleaning out unnecessary files. We've also covered some useful tools like BleachBit, FSlint, Stacer, and Baobab that can help you manage files and free up space more easily. Hopefully these tips and tools will help you work and play more efficiently on Linux.
The above is the detailed content of File Management on Linux: 7 Tips and 4 Tools. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.






