 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Getters and Modifiers in PHP: Exploring New Dimensions of Data Access
Getters and Modifiers in PHP: Exploring New Dimensions of Data Access
Getters and Modifiers in PHP: Exploring New Dimensions of Data Access

Getters and Modifiers in PHP: Exploring New Dimensions of Data Access
Introduction:
In PHP development, manipulating data is the most common thing for developers One of the tasks. In order to make data access and modification more convenient and safe, PHP provides two powerful features: getters and modifiers. This article will explore the role and usage of getters and modifiers, and use specific code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two features.
1. The function and usage of the getter
1.1 The function of the getter
The getter is a special method that is used to perform a series of operations when reading the value of a private attribute. Filter or process. The acquirer can modify, verify or process the attributes before reading them to ensure that the acquired data has a certain degree of rationality and completeness.
1.2 Usage of getter
In terms of implementation, the method name of the getter starts with "get", followed by the attribute name that needs to be obtained, for example:
class MyData {
private $name;
public function getName() {
// 过滤或处理$name的逻辑代码
return $this->name;
}
}above In the code, the getName() method is a getter, used to obtain the value of the private property $name. We can add arbitrary processing logic to this method to ensure that when the value of the $name attribute is obtained externally, we can get verified or processed results.
1.3 Advantages of Getters
By using getters, we can effectively control and filter the access behavior of properties. Getters not only make obtaining properties more flexible, but also avoid direct access to private properties and increase code security. In addition, getters can also provide data consistency and stability, making objects more reliable and controllable when used externally.
2. The role and usage of modifiers
2.1 The role of modifiers
Modifiers are a special method used to perform a series of filters when setting the value of a private property. or processing. The modifier can modify, verify or process the attribute value before setting it to ensure that the set value has a certain degree of rationality and completeness.
2.2 Usage of modifier
In terms of implementation, the method name of the modifier starts with "set", followed by the attribute name that needs to be set, for example:
class MyData {
private $name;
public function setName($value) {
// 过滤或处理$value的逻辑代码
$this->name = $value;
}
}above In the code, the setName($value) method is a modifier, used to set the value of the private property $name. We can add arbitrary processing logic to this method to ensure that we get verified or processed results when setting the value of the $name attribute.
2.3 Advantages of Modifiers
By using modifiers, we can effectively control and filter the property setting behavior. Modifiers not only make setting properties more flexible, but also avoid setting private properties directly, increasing code security. In addition, modifiers can also provide data consistency and stability, making objects more reliable and controllable when used externally.
3. Comprehensive application of getters and modifiers
The following is a simple code example to show the comprehensive application of getters and modifiers:
class User {
private $name;
private $age;
public function getName() {
return $this->name;
}
public function setName($value) {
if (strlen($value) < 3) {
throw new Exception("用户名长度不能少于3个字符");
}
$this->name = $value;
}
public function getAge() {
return $this->age;
}
public function setAge($value) {
if ($value < 18 || $value > 60) {
throw new Exception("年龄必须在18到60之间");
}
$this->age = $value;
}
}
$user = new User();
$user->setName('Tom'); // 设置用户名
$user->setAge(25); // 设置年龄
echo $user->getName(); // 获取用户名
echo $user->getAge(); // 获取年龄In the above code, the User class Two private properties $name and $age are defined and equipped with corresponding getters and modifiers respectively. The $name and $age attribute values obtained through the getter have been verified and filtered accordingly, ensuring the rationality and integrity of the data. When setting the $name and $age attribute values through modifiers, corresponding verification and filtering can also be performed to ensure the accuracy and security of the data.
Summary:
Through the explanation and sample code of this article, we have a deeper understanding of the functions and usage of getters and modifiers. By applying getters and modifiers, we can better protect and manage data, increasing the flexibility and reliability of our code. I hope that readers can have a deeper understanding and application of these two important features in PHP through the introduction of this article.
The above is the detailed content of Getters and Modifiers in PHP: Exploring New Dimensions of Data Access. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
DAO (Data Access Object) in Java is used to separate application code and persistence layer, its advantages include: Separation: Independent from application logic, making it easier to modify it. Encapsulation: Hide database access details and simplify interaction with the database. Scalability: Easily expandable to support new databases or persistence technologies. With DAOs, applications can call methods to perform database operations such as create, read, update, and delete entities without directly dealing with database details.
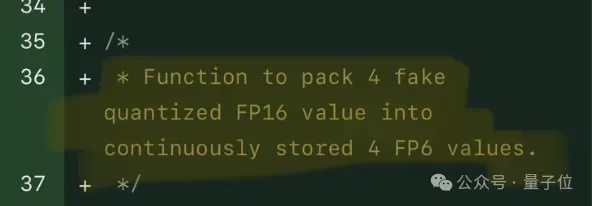 Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
FP8 and lower floating point quantification precision are no longer the "patent" of H100! Lao Huang wanted everyone to use INT8/INT4, and the Microsoft DeepSpeed team started running FP6 on A100 without official support from NVIDIA. Test results show that the new method TC-FPx's FP6 quantization on A100 is close to or occasionally faster than INT4, and has higher accuracy than the latter. On top of this, there is also end-to-end large model support, which has been open sourced and integrated into deep learning inference frameworks such as DeepSpeed. This result also has an immediate effect on accelerating large models - under this framework, using a single card to run Llama, the throughput is 2.65 times higher than that of dual cards. one
 How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
U disk is one of the commonly used storage devices in our daily work and life, but sometimes we encounter situations where the U disk is write-protected and cannot write data. This article will introduce several simple and effective methods to help you quickly remove the write protection of the USB flash drive and restore the normal use of the USB flash drive. Tool materials: System version: Windows1020H2, macOS BigSur11.2.3 Brand model: SanDisk UltraFlair USB3.0 flash drive, Kingston DataTraveler100G3USB3.0 flash drive Software version: DiskGenius5.4.2.1239, ChipGenius4.19.1225 1. Check the physical write protection switch of the USB flash drive on some USB flash drives Designed with
 What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
An API interface is a specification for interaction between software components and is used to implement communication and data exchange between different applications or systems. The API interface acts as a "translator", converting the developer's instructions into computer language so that the applications can work together. Its advantages include convenient data sharing, simplified development, improved performance, enhanced security, improved productivity and interoperability.
 Usage of service layer in java
May 07, 2024 am 04:24 AM
Usage of service layer in java
May 07, 2024 am 04:24 AM
The Service layer in Java is responsible for business logic and business rules for executing applications, including processing business rules, data encapsulation, centralizing business logic and improving testability. In Java, the Service layer is usually designed as an independent module, interacts with the Controller and Repository layers, and is implemented through dependency injection, following steps such as creating an interface, injecting dependencies, and calling Service methods. Best practices include keeping it simple, using interfaces, avoiding direct manipulation of data, handling exceptions, and using dependency injection.
 What does mysql database do?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
What does mysql database do?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
MySQL is a relational database management system that provides the following main functions: Data storage and management: Create and organize data, supporting various data types, primary keys, foreign keys, and indexes. Data query and retrieval: Use SQL language to query, filter and retrieve data, and optimize execution plans to improve efficiency. Data updates and modifications: Add, modify or delete data through INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE commands, supporting transactions to ensure consistency and rollback mechanisms to undo changes. Database management: Create and modify databases and tables, back up and restore data, and provide user management and permission control.
 What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
Schema in MySQL is a logical structure used to organize and manage database objects (such as tables, views) to ensure data consistency, data access control and simplify database design. The functions of Schema include: 1. Data organization; 2. Data consistency; 3. Data access control; 4. Database design.
 Redis cache implementation principle
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
Redis cache implementation principle
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
The Redis caching mechanism is implemented through key-value storage, memory storage, expiration policies, data structures, replication, and persistence. It follows the steps of obtaining data, cache hit, cache miss, writing to cache, and updating cache to provide fast data access and high-performance caching services.





