 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Tsinghua's new research decrypts information cocoon room! New information dynamics theory published in Nature sub-journal
Tsinghua's new research decrypts information cocoon room! New information dynamics theory published in Nature sub-journal
Tsinghua's new research decrypts information cocoon room! New information dynamics theory published in Nature sub-journal
The rapid development of the new generation of information and intelligent technology is pushing mankind to gradually move into an intelligent society. With the support of digital technology and intelligent recommendation algorithms, media and platforms are becoming more and more considerate, and can always meet people's personalized preferences and needs as quickly and accurately as possible.
However, at the same time, intelligent and accurate recommendations have led to the continuous fermentation of the "information cocoon room" phenomenon. People with similar views form groups in cyberspace, and specific value preferences are gathered and amplified in the group. Gradually develop extreme views.
Every extreme view on celebrities or social events can be used as a tool for ideological participation and influence, adding fuel to the flames in cyberspace and the real world, setting off "turbulent public opinion." .
However, even so, we still know very little about information cocoons: How serious are information cocoons in real online systems? There is a lack of large-scale empirical research; what is the formation mechanism of information cocoons? Lack of basic theoretical support; how to solve the problem of information cocoon room? There is a lack of effective means.
Recently, the Urban Science and Computing Research Center of the Department of Electronics of Tsinghua University and the School of Public Policy and Management collaborated across disciplines to conduct the first large-scale data empirical research through large-scale empirical research and information dynamics theoretical modeling. And theory reveals the internal mechanism and phase transition boundaries of the emergence of information cocoon rooms in information media, providing a new way of understanding the complex social system of human-intelligence interaction in the current intelligent society.
The result was published in "Nature·Machine Intelligence" under the title "Human-AI adaptive dynamics drives the emergence of information cocoons" "(Nature Machine Intelligence) published online.

Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-023-00731-4
Code and data link: https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/Adaptive-Information-Dynamic-Model
This achievement focuses on news and video In two typical scenarios, by analyzing 570 million user behavior data and using information entropy to measure the severity of information cocooning, it was found that after one year of interaction, more than 57% of active users experienced varying degrees of information entropy decline, marking a real-world system The seriousness of the information cocoon.
Based on empirical findings, this result proposes a human-intelligence adaptive information dynamics model to model the key feedback loop between humans and recommendation algorithms, and through the system The evolution law of information entropy is used to describe the phase transition process of information cocoon.
This model reveals the phase change process and phase change boundary of the "diversity-partial information cocoon room-depth information cocoon room" complex system from the perspective of non-equilibrium statistical mechanics, and is used for control The problem of information cocoons in human-intelligence interactive complex social systems provides a theoretical basis and inspires subsequent designs to break the information cocoon by balancing the positive and negative feedback of the system, as well as precise algorithm push and user free exploration, thereby achieving responsible recommendations. algorithm.
Overview of the paper
As an emerging disruptive technology, artificial intelligence is profoundly changing human production, lifestyle and way of thinking, and has a profound impact on economic development and social progress. It has a significant and far-reaching impact. Among them, recommendation algorithms, as the most widely used artificial intelligence technology, can effectively alleviate the problem of information overload and greatly affect what people see, hear and think.
However, the recommendation algorithm is also a double-edged sword. The personalized recommendations it provides will make the information people are exposed to become more and more homogeneous, and they will gradually become trapped in information. In the cocoon room. This homogeneous information will not only limit people's horizons and alienate them from the collective and society, but will also encourage social conflicts and divisions.
Therefore, in order to curb the occurrence of information cocoons, understanding the mechanism behind them is the first step.
There have been studies on the problem of information homogeneity [1-5], most of which focus on human behavior or intelligent algorithms. Through empirical research methods, the study pointed out the potential factors of homogeneous crowd gathering on social media or the filtering effect of algorithms. However, due to limitations of data and methodology, only correlation conclusions can be provided.
Recently, some empirical studies [25,26] have conducted causal analysis. However, these studies still do not provide analysis and explanation of the underlying mechanism. Furthermore, most of the current recommendation algorithms are based on black-box artificial intelligence deep learning methods, and the hundreds of millions of parameters behind them make it more difficult for us to gain insight into the root causes of information cocoons.
In response to the problem of unknown sources of information cocooning, the research team focused on two typical scenarios: news and video. Through large-scale empirical research, they found that during one year of interaction, more than 57% of active users experienced Different degrees of information diversity decline, and it is pointed out that similarity-based matching and positive and negative feedback are key elements that affect the information homogenization process.
Further, based on empirical discovery and practice in the field of recommendation algorithms, the research team was inspired by the idea of stochastic thermodynamics and creatively proposed a human-intelligence adaptive information dynamics model.
This model mechanically models the key feedback loop between humans and recommendation algorithms by describing two basic mechanisms based on similarity matching and feedback utilization, and through system information entropy The evolution of the system is used to describe the phase transition process of the system.
Through simulation experiments and theoretical analysis, the phase change process and phase change boundaries of the complex system of "diversity-partial information cocoon room-deep information cocoon room" are revealed, providing a basis for the controller- The information cocoon problem in intelligent interactive complex social systems provides a theoretical foundation and practical methods.
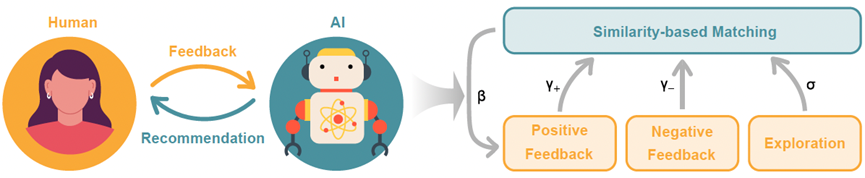
Human-Intelligence Adaptive Information Dynamics Model
Technical Points
The research team focused on two typical content recommendation scenarios: news and video. Through empirical analysis of large-scale real data, the research team characterized the severity of the real-world information cocoon and its influencing factors.
Specifically, the research team used information entropy to characterize the diversity of information received by users and found that more than 57% of active users experienced varying degrees of decline in information diversity. Its vision is gradually limited by recommendation algorithms to a narrow information cocoon.
Through further analysis, the research team found that the strength of the recommendation algorithm based on similarity matching and positive and negative feedback are key factors that affect the generation of information cocoons. This empirical study not only quantifies the severity of information cocoons in real large-scale online information systems for the first time, but also lays the foundation for the subsequent theoretical model.
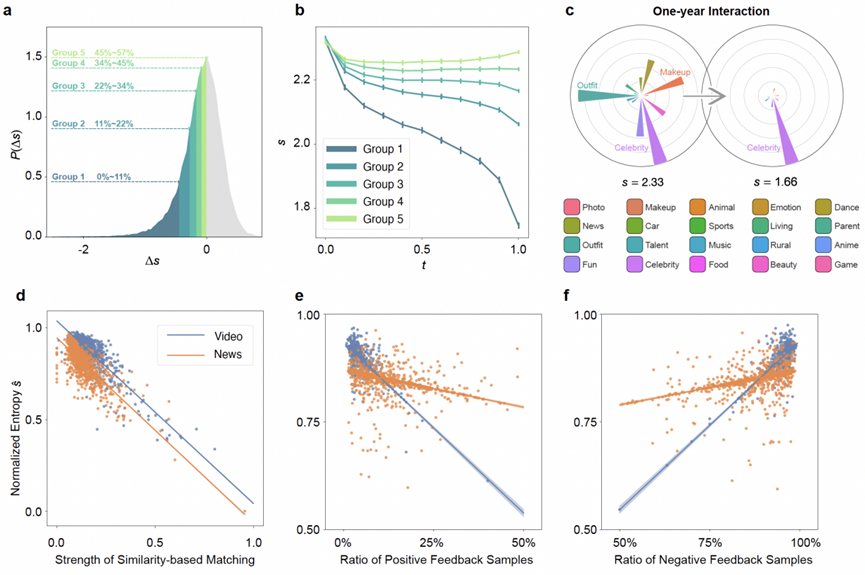
(a-c) Focus on two typical scenes of news and video to quantify real-world information Severity of cocoon room; (d-f) Similarity matching strength, positive and negative feedback are important factors affecting the formation of information cocoon room.
Based on empirical conclusions and practice in the field of recommendation algorithms, combined with the theory of stochastic thermodynamics, the research team creatively proposed a human-intelligence adaptive information dynamics model.
This model uses information entropy to represent the diversity of information that users are exposed to, and uses system information entropy distribution to represent the state of the system.
Different from deep learning models that rely on hundreds of millions of parameters, the proposed model only relies on two basic mechanisms based on similarity matching and user feedback to model humans mechanically. The key feedback loop between recommendation algorithm and human-intelligence complex dynamic interaction process using stochastic dynamic equations.
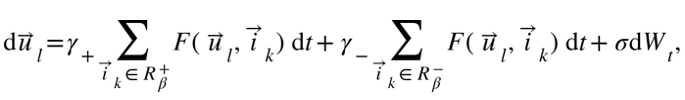
Among them, 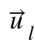 represents the observed interest distribution of user l,
represents the observed interest distribution of user l, 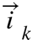 represents the characteristic distribution of item k, and
represents the characteristic distribution of item k, and 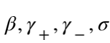 represents similarity-based matching strength, positive feedback utilization, negative feedback utilization, and free exploration intensity respectively.
represents similarity-based matching strength, positive feedback utilization, negative feedback utilization, and free exploration intensity respectively.
Based on the above formula, we can derive the Focke-Planck equation describing the observed preferences of users on various topics. Further, through the mean field approximation method, we can finally The distribution of information entropy received by users over the population is derived.
The research team pointed out that under different parameter spaces, the human-intelligence interactive complex social system has three states: diversification, partial information cocoon room and deep information cocoon room, and these three system states are respectively divided into three states: Characterized by different information entropy distributions.
Large-scale simulation experiments and empirical analysis further verified the explanatory power and effectiveness of the proposed model.
With (a) similarity-based matching strength or (b) positive feedback utilization As the rate increases, the human-intelligence interactive complex social system has experienced a phase transition process from a diversified state to a partial information cocoon state, and then to a deep information cocoon state. The red dotted line is the theoretical line, and the histogram is the simulation line.
The research team found that as the strength of similarity-based matching or the utilization of positive feedback increases, the complex system presents a state from a diversified state to a partial information cocoon state, and then to The phase transition process of depth information cocoon state.
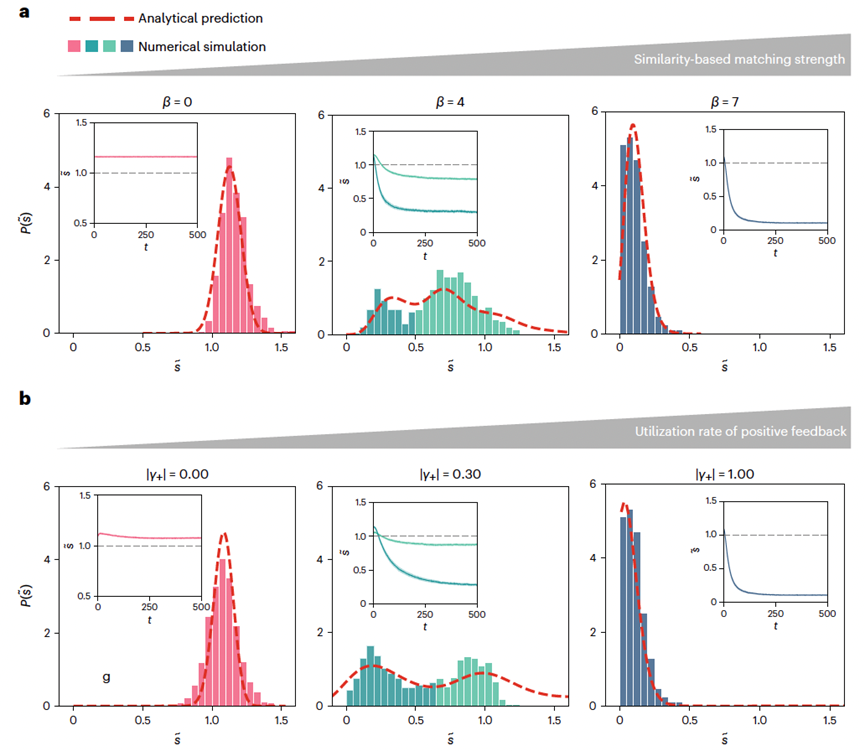
However, if the utilization rate of negative feedback or the intensity of free exploration is increased, the system will undergo a reverse phase change process, that is, from a deep information cocoon to a partial information cocoon, and finally to a diverse status. The above four phase transition processes have been consistently verified by theoretical analysis and large-scale simulation experiments.
As (a) the utilization of negative feedback increases or (b) the intensity of free exploration increases, human-intelligence interaction complex social systems experience It describes the reverse phase transition process from the deep information cocoon state to the partial information cocoon state, and then to the diversified state. The red dotted line is the theoretical line, and the histogram is the simulation line.
Through joint analysis, the research team demonstrated the phase change diagram of the overall system driven by the joint drive of four elements based on similarity recommendation, utilization of positive and negative feedback, and free exploration, and revealed The inner mechanism of emergence in information cocoon.
Specifically, similarity-based matching serves as an effective force field to promote complex interactive systems from diversification to homogeneity. Positive feedback further amplifies this force field, resulting in reduced information diversity.
Negative feedback and free exploration introduce disturbance into the system by resisting the effect of the effective force field, thus promoting information diversity.
Regarding the phase transition boundary, the theoretical prediction results and the simulation experimental results show a high degree of consistency. At the same time, through a large number of simulation experiments and empirical analysis, such as replacement functions, measured information entropy distribution, etc., The robustness and effectiveness of the proposed model are further verified.
System phase change diagram, (a-b) Three-dimensional system phase change diagram based on video and news scene data, (c-e) Two-dimensional system phase change diagram based on video scene data, (f-h ) Phase change diagram of a two-dimensional system based on news scene data.
With the widespread application of artificial intelligence technology, the complex interactions between humans and intelligent systems constitute a complex human-intelligence interaction system involving multiple entities and multiple feedbacks.
Current artificial intelligence is mostly based on deep learning technology, and its black-box nature further hinders a deep understanding of the dynamic characteristics and emergent behaviors in such complex interactive systems.
The adaptive information dynamics model proposed by the research team provides a mechanism for the in-depth study of various types of complex human-intelligence interaction systems by providing a mechanistic modeling of the emergent behavior of information cocoons. A powerful theoretical tool. Furthermore, the proposed theoretical model has practical guiding significance for responsible recommendation algorithm design.
This study points out two effective methods for information cocooning, namely promoting the effective use of negative feedback and modeling user preferences from a new perspective of learning users’ negative feedback; and promoting Users can explore freely and broaden their information horizons by increasing their freedom and autonomy in consuming their own content.
In summary, this research result not only points out the practical improvement direction for recommendation algorithm design, but also provides theoretical tools for understanding human-intelligence interactive complex social systems to inspire subsequent Related research on Complex System for AI.
Introduction to the authors
Ph.D. student Pu Jinghua and postdoctoral fellow Liu Jiazhen from the Urban Science and Computing Research Center, Department of Electronics, Tsinghua University are the co-first authors of the paper. Li Associate Professor Yong is the corresponding author; Assistant Professor Zhang Fang and Professor Su Jun of Tsinghua School of Public Policy and Management are co-authors.
The research results are supported by the Science and Technology Innovation 2030-"New Generation Artificial Intelligence" major project and the Natural Science Foundation of China.
The above is the detailed content of Tsinghua's new research decrypts information cocoon room! New information dynamics theory published in Nature sub-journal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1253
1253
 24
24
 Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
0.What does this article do? We propose DepthFM: a versatile and fast state-of-the-art generative monocular depth estimation model. In addition to traditional depth estimation tasks, DepthFM also demonstrates state-of-the-art capabilities in downstream tasks such as depth inpainting. DepthFM is efficient and can synthesize depth maps within a few inference steps. Let’s read about this work together ~ 1. Paper information title: DepthFM: FastMonocularDepthEstimationwithFlowMatching Author: MingGui, JohannesS.Fischer, UlrichPrestel, PingchuanMa, Dmytr
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI is indeed changing mathematics. Recently, Tao Zhexuan, who has been paying close attention to this issue, forwarded the latest issue of "Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society" (Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society). Focusing on the topic "Will machines change mathematics?", many mathematicians expressed their opinions. The whole process was full of sparks, hardcore and exciting. The author has a strong lineup, including Fields Medal winner Akshay Venkatesh, Chinese mathematician Zheng Lejun, NYU computer scientist Ernest Davis and many other well-known scholars in the industry. The world of AI has changed dramatically. You know, many of these articles were submitted a year ago.
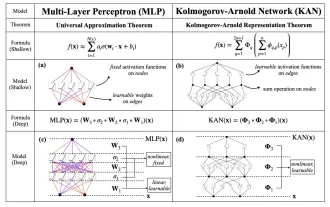 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
 Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Facing lag, slow mobile data connection on iPhone? Typically, the strength of cellular internet on your phone depends on several factors such as region, cellular network type, roaming type, etc. There are some things you can do to get a faster, more reliable cellular Internet connection. Fix 1 – Force Restart iPhone Sometimes, force restarting your device just resets a lot of things, including the cellular connection. Step 1 – Just press the volume up key once and release. Next, press the Volume Down key and release it again. Step 2 – The next part of the process is to hold the button on the right side. Let the iPhone finish restarting. Enable cellular data and check network speed. Check again Fix 2 – Change data mode While 5G offers better network speeds, it works better when the signal is weaker
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving



