 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Tips | Python automatically extracts and organizes PDF invoices in batches
Tips | Python automatically extracts and organizes PDF invoices in batches
Tips | Python automatically extracts and organizes PDF invoices in batches
This article shares a PDF-based Python office automation case solution, which was also proposed by a financial lady. Let’s first look at the real needs.
Description of requirements
There are multiple PDF type invoices in a certain folder
Each one Invoice PDF is a pure picture type, and the text information inside cannot be copied manually (in fact, most invoices can copy part of the text, but we will explain it in the form of pictures), as shown below: 
The requirements that need to be met are: obtain the total amount of , taxpayer identification number, and issuer , that is, the following three box positions: 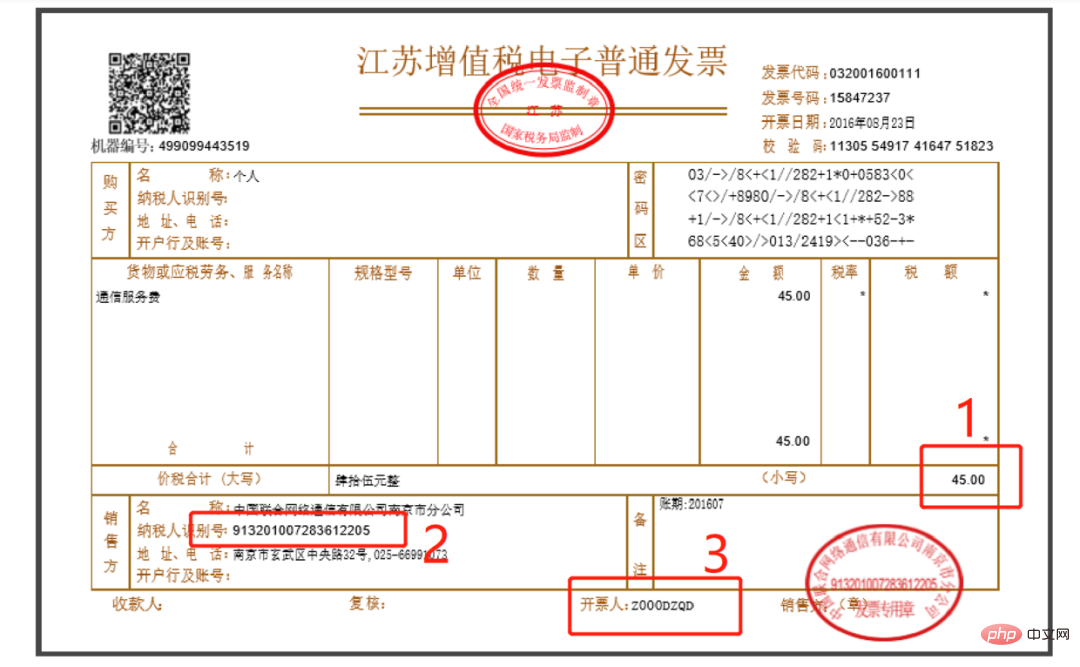
Finally combined with the batch Operation, after obtaining the above information, store it in Excel! 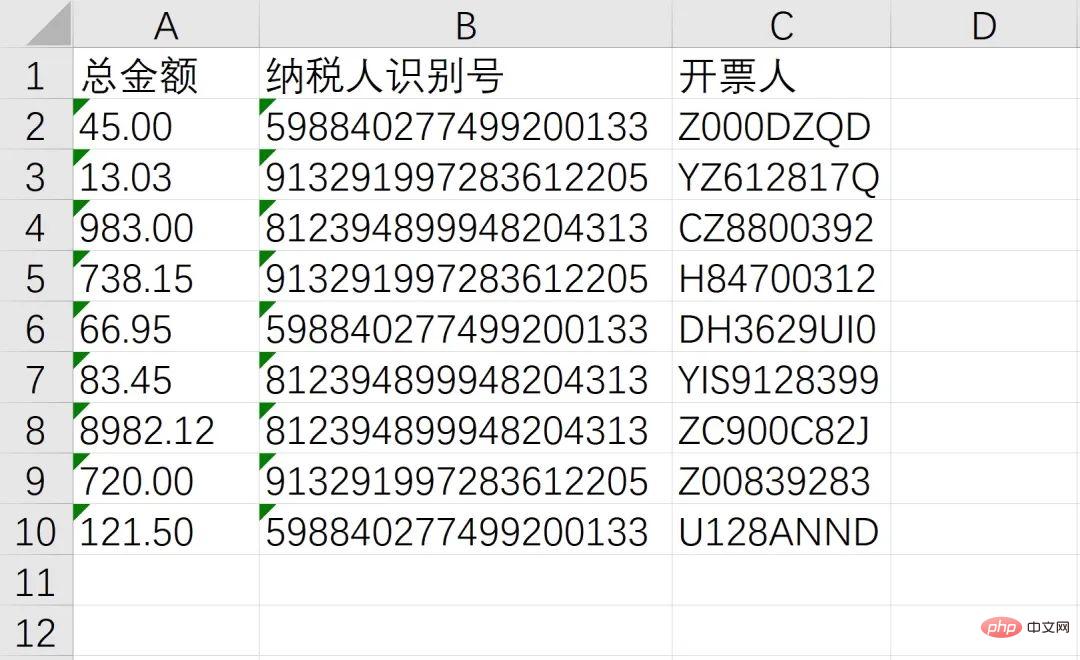
Ideas and code implementation
The essence of the requirement is an image recognition problem, because the content in the PDF is of image type and cannot be pressed Conventional methods extract the text directly. The solution is to use optical character recognition (OCR) to recognize the text in the picture. But at the same time, it should be noted that PDF is not a picture after all. In order to complete OCR, in addition to OCR itself, Ghostscript and ImageMagick must be downloaded to complete type conversion. Taking the Windows system as an example, you need to install the following three software on your computer:
Ghostscript32-bitImageMagick32-bittesseract-OCR32-bit
There is no special place in downloading and installing the three software (tesseract configuration is slightly complicated, but there are many tutorials on the Internet, so I won’t go into details here. ), readers can search for download and configuration by themselves. The code is explained below. First import the required modules:
from wand.image import Image from PIL import Image as PI import pyocr import pyocr.builders import io import re import os import shutil
For specific module uses, please refer to the specific code below. Among them, wand and pyocr need to be installed separately because they are non-standard libraries. Open the command line and enter:
pip install wand pip install pyocr
This requirement also involves docking Excel. You can consider using the Workbook of the openpyxl library to create a new Excel file:
from openpyxl import Workbook
Put the invoice.pdf in the requirement on the desktop. The desktop path can be obtained through the following code based on the os module:
# 获取桌面路径包装成一个函数
def GetDesktopPath():
return os.path.join(os.path.expanduser("~"), 'Desktop')
path = GetDesktopPath() + r'\发票.pdf'Get the configured tesseract for later calling:
tool = pyocr.get_available_tools()[0]
通过 wand 模块将 PDF 文件转化为分辨率为 300 的 jpeg 图片形式:
image_pdf = Image(filename=path, resolution=300) image_jpeg = image_pdf.convert('jpeg')
将图片解析为二进制矩阵:
image_lst = []
for img in image_jpeg.sequence:
img_page = Image(image=img)
image_lst.append(img_page.make_blob('jpeg'))用 io 模块的 BytesIO 方法读取二进制内容为图片形式:
new_img = PI.open(io.BytesIO(image_lst[0])) new_img.show()
接下来分别截取需要提取部位字符串的图片了,尽量让图片中只有需要识别的部分,获取识别出来容易简单处理获得需要的内容。
首先以总金额为例,截取图片用 image.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) 四个参数需要反复调试才能确定。经确定四个参数分别是 1600 760 1830 900,尝试截取和预览图片:
### 解析1Z开头码 left = 350 top = 600 right = 1300 bottom = 730 image_obj1 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) image_obj1.show()
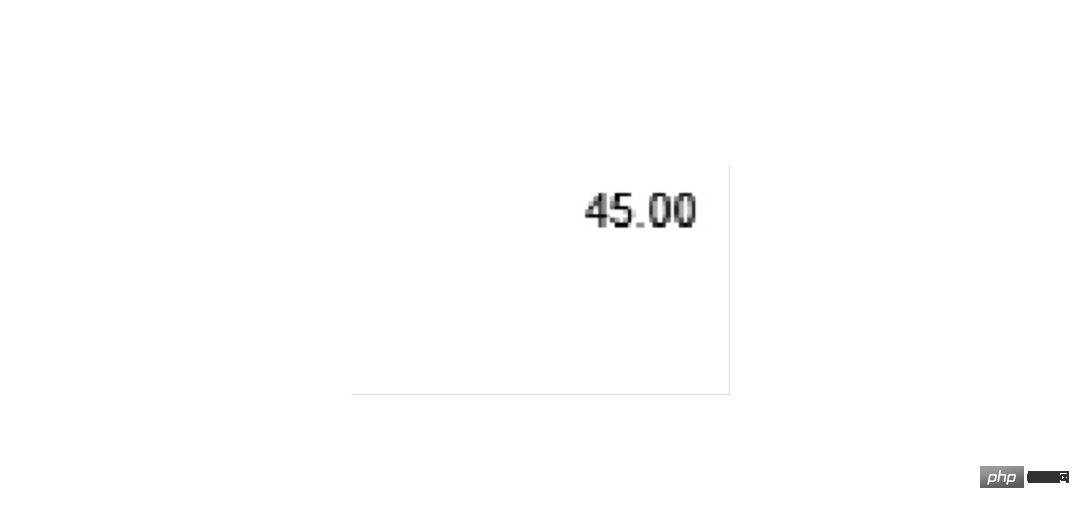
截取成功后可以交给 OCR 了,代码为 tool.image_to_string()
txt1= tool.image_to_string(image_obj1) print(txt1)

同样,通过方位的调试就可以准确切割到需要的部分进行识别:
left = 560 top = 1260 right = 900 bottom = 1320 image_obj2 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) # image_obj2.show() txt2 = tool.image_to_string(image_obj2) # print(txt2)
最后是开票人的识别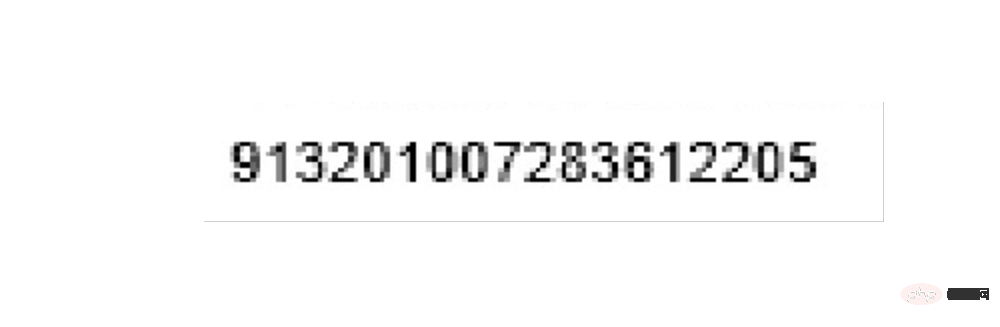
left = 1420 top = 1420 right = 1700 bottom = 1500 image_obj3 = new_img.crop((left, top, right, bottom)) # image_obj3.show() txt3 = tool.image_to_string(image_obj3) # print(txt3)
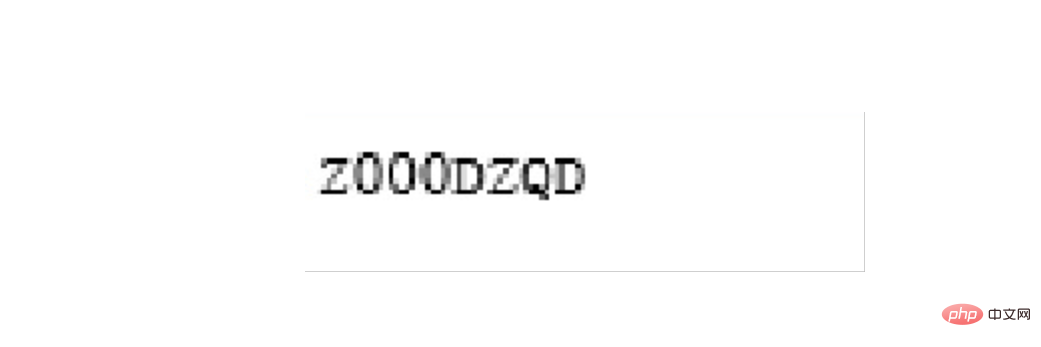
需要确认识别的内容是否正确,如果识别正确率欠佳可以考虑通过图片处理技术消除噪声,也可以去官网下载更高精度的训练包提高识别的正确性
至此,我们成功的识别了总金额、纳税人识别号、开票人三个消息,接下来就通过非常熟悉的 openpyxl 写入Excel,并使用 os 模块实现批量操作即可
workbook = Workbook() sheet = workbook.active header = ['总金额', '纳税人识别号', '开票人'] sheet.append(header) sheet.append([txt1, txt2, txt3]) workbook.save(GetDesktopPath() + r'\汇总.xlsx')
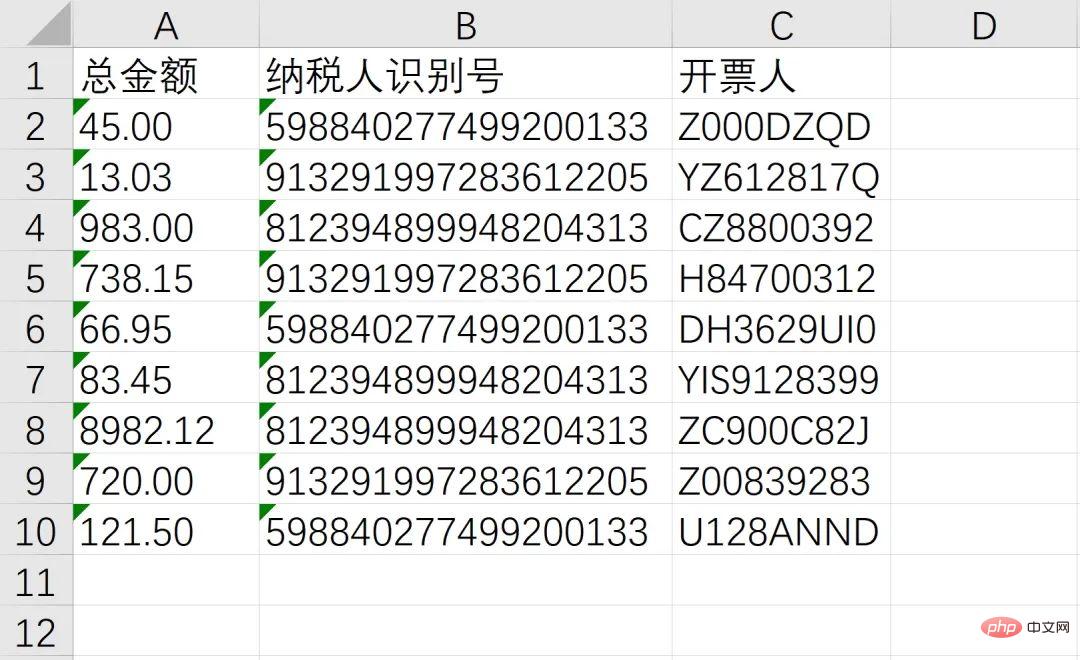
综上,整个需求就成功实现,从效果来看还是非常不错的!完整源码可由文中代码组合而成(已全部分享在文中),感兴趣的读者可以自己尝试!
最后想说的是,其实本文的案例可以衍生出很多实用的办公自动化脚本,例如
批量计算发票金额并重命名文件夹 根据发票类型批量分类 根据发票批量制作报销单 ··· ···
The above is the detailed content of Tips | Python automatically extracts and organizes PDF invoices in batches. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.





