TCP协议灵魂 12 问,总会用得到
先亮出这篇文章的思维导图
001. 能不能说一说 TCP 和 UDP 的区别?
UDP 相比,TCP 有三大核心特性:面向连接。所谓的连接,指的是客户端和服务器的连接,在双方互相通信之前,TCP 需要三次握手建立连接,而 UDP 没有相应建立连接的过程。
可靠性。TCP 花了非常多的功夫保证连接的可靠,这个可靠性体现在哪些方面呢?一个是有状态,另一个是可控制。
无状态, 不可控的。面向字节流。UDP 的数据传输是基于数据报的,这是因为仅仅只是继承了 IP 层的特性,而 TCP 为了维护状态,将一个个 IP 包变成了字节流。
002: 说说 TCP 三次握手的过程?为什么是三次而不是两次、四次?
恋爱模拟
爱的能力。爱和被爱的能力。被爱的能力。爱和被爱的能力,两人开始一段甜蜜的爱情。真实握手
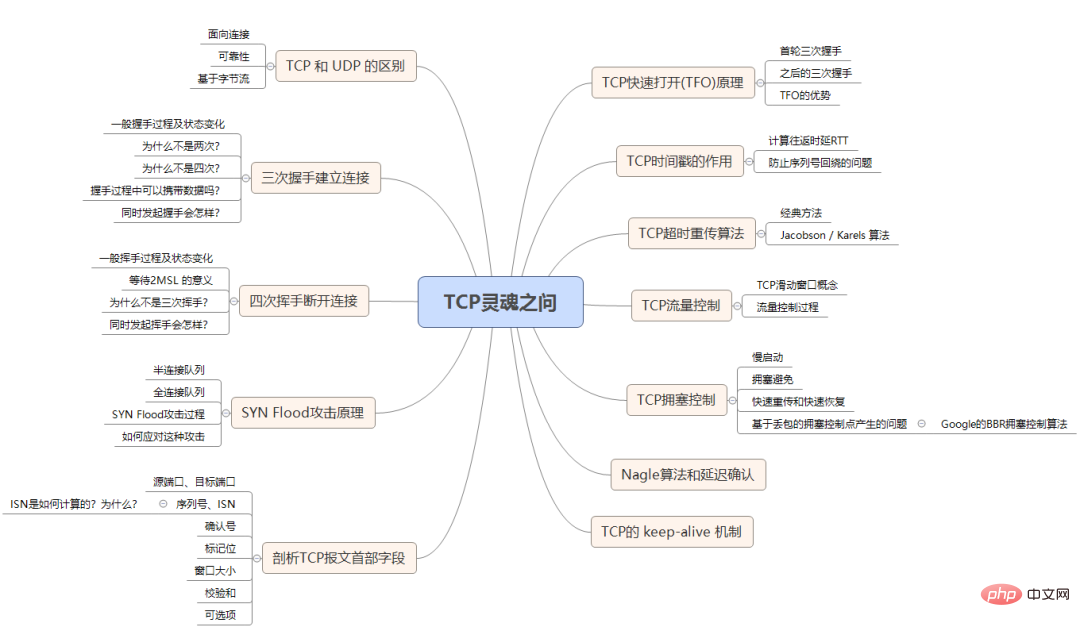
发送的能力和接收的能力。于是便会有下面的三次握手的过程: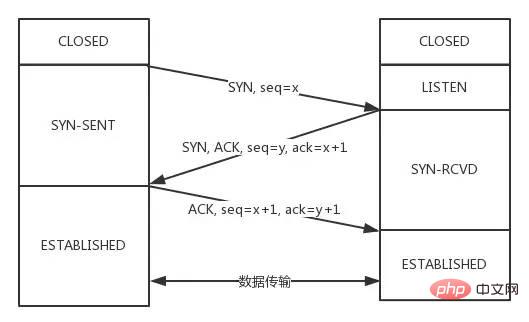
CLOSED状态。然后服务端开始监听某个端口,进入了LISTEN状态。SYN-SENT状态。SYN和ACK(对应客户端发来的SYN),自己变成了SYN-REVD。ACK给服务端,自己变成了ESTABLISHED状态;服务端收到ACK之后,也变成了ESTABLISHED状态。凡是需要对端确认的,一定消耗TCP报文的序列号。
为什么不是两次?
为什么不是四次?
发送和接收的能力,那四次握手可以嘛?三次握手过程中可以携带数据么?
ESTABLISHED状态,并且已经能够确认服务器的接收、发送能力正常,这个时候相对安全了,可以携带数据。同时打开会怎样?
SYN报文,状态变化会是怎样的呢?
SYN报文的同时,接收方也给发送方发SYN报文,两个人刚上了!SYN,两者的状态都变为SYN-SENT。SYN后,两者状态都变为SYN-REVD。ACK + SYN,这个报文在对方接收之后,两者状态一起变为ESTABLISHED。003: 说说 TCP 四次挥手的过程
过程拆解
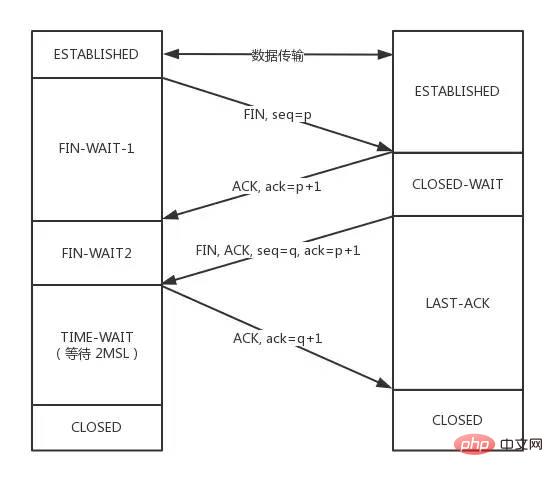
ESTABLISHED状态。FIN 报文,在 TCP 报文中的位置如下图: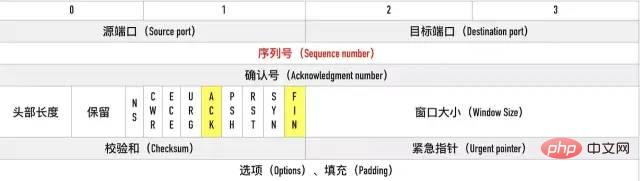
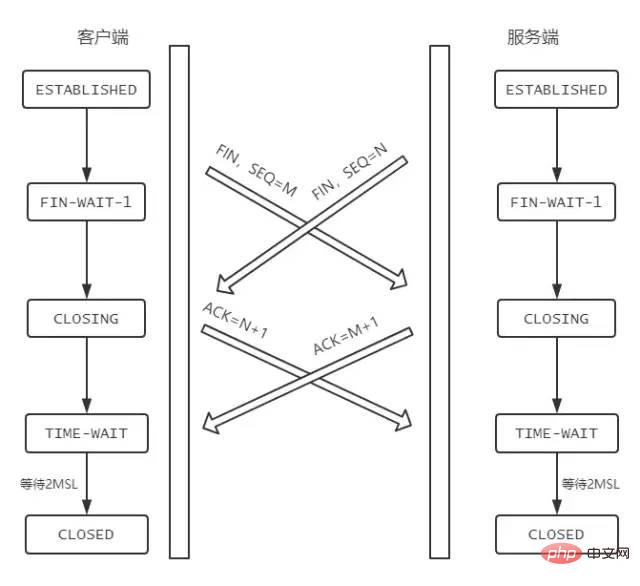
FIN-WAIT-1状态。注意, 这时候客户端同时也变成了half-close(半关闭)状态,即无法向服务端发送报文,只能接收。CLOSED-WAIT状态。FIN-WAIT2状态。FIN,自己进入LAST-ACK状态,FIN后,自己变成了TIME-WAIT状态,然后发送 ACK 给服务端。MSL(Maximum Segment Lifetime,报文最大生存时间), 在这段时间内如果客户端没有收到服务端的重发请求,那么表示 ACK 成功到达,挥手结束,否则客户端重发 ACK。等待2MSL的意义
1 个 MSL 确保四次挥手中主动关闭方最后的 ACK 报文最终能达到对端 1 个 MSL 确保对端没有收到 ACK 重传的 FIN 报文可以到达
为什么是四次挥手而不是三次?
FIN, 往往不会立即返回FIN, 必须等到服务端所有的报文都发送完毕了,才能发FIN。因此先发一个ACK表示已经收到客户端的FIN,延迟一段时间才发FIN。这就造成了四次挥手。ACK和FIN的发送合并为一次挥手,这个时候长时间的延迟可能会导致客户端误以为FIN没有到达客户端,从而让客户端不断的重发FIN。同时关闭会怎样?
004: 说说半连接队列和 SYN Flood 攻击的关系
CLOSED变为LISTEN, 同时在内部创建了两个队列:半连接队列和全连接队列,即SYN队列和ACCEPT队列。半连接队列
SYN到服务端,服务端收到以后回复ACK和SYN,状态由LISTEN变为SYN_RCVD,此时这个连接就被推入了SYN队列,也就是半连接队列。全连接队列
ACK, 服务端接收后,三次握手完成。这个时候连接等待被具体的应用取走,在被取走之前,它会被推入另外一个 TCP 维护的队列,也就是全连接队列(Accept Queue)。SYN Flood 攻击原理
SYN。对于服务端而言,会产生两个危险的后果:处理大量的
SYN包并返回对应ACK, 势必有大量连接处于SYN_RCVD状态,从而占满整个半连接队列,无法处理正常的请求。由于是不存在的 IP,服务端长时间收不到客户端的
ACK,会导致服务端不断重发数据,直到耗尽服务端的资源。
如何应对 SYN Flood 攻击?
增加 SYN 连接,也就是增加半连接队列的容量。 减少 SYN + ACK 重试次数,避免大量的超时重发。 利用 SYN Cookie 技术,在服务端接收到 SYN后不立即分配连接资源,而是根据这个SYN计算出一个Cookie,连同第二次握手回复给客户端,在客户端回复ACK的时候带上这个Cookie值,服务端验证 Cookie 合法之后才分配连接资源。
005: 介绍一下 TCP 报文头部的字段
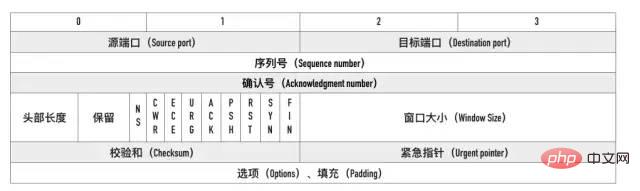
源端口、目标端口
四元组——源 IP、源端口、目标 IP 和目标端口。序列号
Sequence number, 指的是本报文段第一个字节的序列号。在 SYN 报文中交换彼此的初始序列号。 保证数据包按正确的顺序组装。
ISN
Initial Sequence Number(初始序列号),在三次握手的过程当中,双方会用过SYN报文来交换彼此的 ISN。确认号
ACK(Acknowledgment number)。用来告知对方下一个期望接收的序列号,小于ACK的所有字节已经全部收到。标记位
SYN,ACK,FIN,RST,PSH。FIN:即 Finish,表示发送方准备断开连接。RST:即 Reset,用来强制断开连接。PSH:即 Push, 告知对方这些数据包收到后应该马上交给上层的应用,不能缓存。窗口大小
校验和
可选项

TimeStamp: TCP 时间戳,后面详细介绍。 MSS: 指的是 TCP 允许的从对方接收的最大报文段。 SACK: 选择确认选项。 Window Scale:窗口缩放选项。
006: 说说 TCP 快速打开的原理(TFO)
Cookie, 用它同样可以实现 TFO。TFO 流程
首轮三次握手
SYN给服务端,服务端接收到。SYN Cookie, 将这个Cookie放到 TCP 报文的 Fast Open选项中,然后才给客户端返回。后面的三次握手
Cookie、SYN 和HTTP请求(是的,你没看错)发送给服务端,服务端验证了 Cookie 的合法性,如果不合法直接丢弃;如果是合法的,那么就正常返回SYN + ACK。ACK还得正常传过来,不然怎么叫三次握手嘛。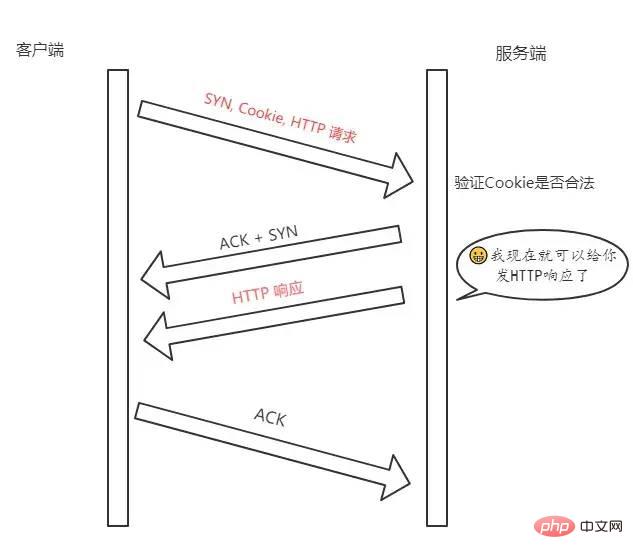
TFO 的优势
007: 能不能说说TCP报文中时间戳的作用?
timestamp是 TCP 报文首部的一个可选项,一共占 10 个字节,格式如下:kind(1 字节) + length(1 字节) + info(8 个字节)
计算往返时延 RTT(Round-Trip Time) 防止序列号的回绕问题
计算往返时延 RTT
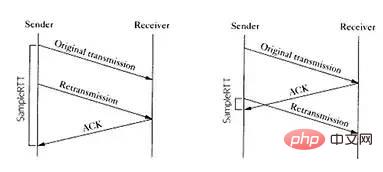
step 1: a 向 b 发送的时候, timestamp中存放的内容就是 a 主机发送时的内核时刻ta1。step 2: b 向 a 回复 s2 报文的时候, timestamp中存放的是 b 主机的时刻tb,timestamp echo字段为从 s1 报文中解析出来的 ta1。step 3: a 收到 b 的 s2 报文之后,此时 a 主机的内核时刻是 ta2, 而在 s2 报文中的 timestamp echo 选项中可以得到 ta1, 也就是 s2 对应的报文最初的发送时刻。然后直接采用 ta2 - ta1 就得到了 RTT 的值。
防止序列号回绕问题
1 ~ 2的数据包了,怎么区分谁是谁呢?这个时候就产生了序列号回绕的问题。008: TCP 的超时重传时间是如何计算的?
经典方法
SRTT = (α * SRTT) + ((1 - α) * RTT)
0.8,范围是0.8 ~ 0.9。RTO = min(ubound, max(lbound, β * SRTT))
1.3 ~ 2.0, lbound 是下界,ubound 是上界。0.8 ~ 0.9, RTT 对于 RTO 的影响太小。标准方法
Jacobson / Karels 算法。SRTT,公式如下:SRTT = (1 - α) * SRTT + α * RTT
α跟经典方法中的α取值不一样了,建议值是1/8,也就是0.125。RTTVAR(round-trip time variation)这个中间变量。RTTVAR = (1 - β) * RTTVAR + β * (|RTT - SRTT|)
RTO:RTO = µ * SRTT + ∂ * RTTVAR
µ建议值取1, ∂建议值取4。009: 能不能说一说 TCP 的流量控制?
滑动窗口的概念。TCP 滑动窗口
发送窗口
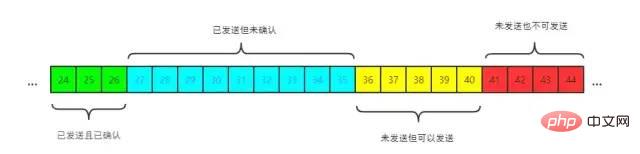
已发送且已确认 已发送但未确认 未发送但可以发送 未发送也不可以发送
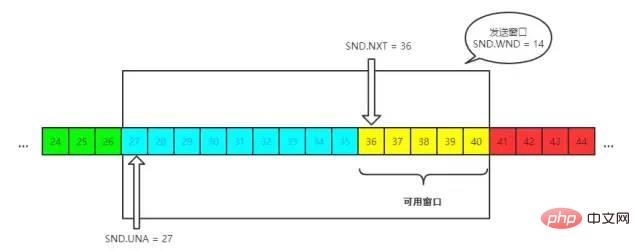
send, WND 即window, UNA 即unacknowledged, 表示未被确认,NXT 即next, 表示下一个发送的位置。接收窗口
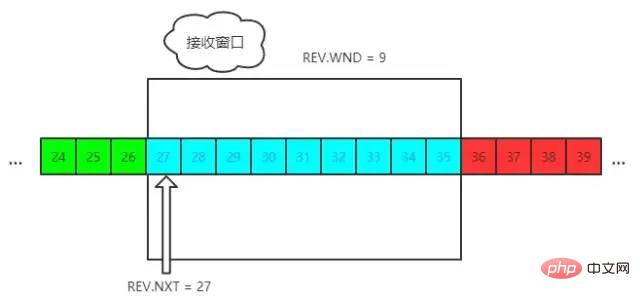
receive,NXT 表示下一个接收的位置,WND 表示接收窗口大小。流量控制过程
可用窗口减少了 100 个字节,这很好理解。60 个字节被留在了缓冲队列中。010: 能不能说说 TCP 的拥塞控制?
拥塞控制需要处理的问题。拥塞窗口(Congestion Window,cwnd) 慢启动阈值(Slow Start Threshold,ssthresh)
慢启动 拥塞避免 快速重传和快速恢复
拥塞窗口
接收窗口(rwnd)是 接收端给的限制拥塞窗口(cwnd)是 发送端的限制
发送窗口的大小。发送窗口?发送窗口大小 = min(rwnd, cwnd)
cwnd的变化。慢启动
慢启动。运作过程如下:首先,三次握手,双方宣告自己的接收窗口大小 双方初始化自己的拥塞窗口(cwnd)大小 在开始传输的一段时间,发送端每收到一个 ACK,拥塞窗口大小加 1,也就是说,每经过一个 RTT,cwnd 翻倍。如果说初始窗口为 10,那么第一轮 10 个报文传完且发送端收到 ACK 后,cwnd 变为 20,第二轮变为 40,第三轮变为 80,依次类推。
拥塞避免
cwnd翻倍,现在cwnd只是增加 1 而已。快速重传和快速恢复
快速重传
选择性重传
SACK这个属性,通过left edge和right edge告知发送端已经收到了哪些区间的数据报。因此,即使第 5 个包丢包了,当收到第 6、7 个包之后,接收端依然会告诉发送端,这两个包到了。剩下第 5 个包没到,就重传这个包。这个过程也叫做选择性重传(SACK,Selective Acknowledgment),它解决的是如何重传的问题。快速恢复
拥塞阈值降低为 cwnd 的一半 cwnd 的大小变为拥塞阈值 cwnd 线性增加
011: 能不能说说 Nagle 算法和延迟确认?
Nagle 算法
当第一次发送数据时不用等待,就算是 1byte 的小包也立即发送 后面发送满足下面条件之一就可以发了: 数据包大小达到最大段大小(Max Segment Size, 即 MSS) 之前所有包的 ACK 都已接收到
延迟确认
接收到了大于一个 frame 的报文,且需要调整窗口大小 TCP 处于 quickack 模式(通过 tcp_in_quickack_mode设置)发现了乱序包
两者一起使用会怎样?
012. 如何理解 TCP 的 keep-alive?
keep-alive, 不过 TCP 层面也是有keep-alive机制,而且跟应用层不太一样。sudo sysctl -a | grep keepalive // 每隔 7200 s 检测一次 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 7200 // 一次最多重传 9 个包 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 9 // 每个包的间隔重传间隔 75 s net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 75
keep-alive选项,为什么?7200s 也就是两个小时检测一次,时间太长 时间再短一些,也难以体现其设计的初衷, 即检测长时间的死连接
The above is the detailed content of TCP协议灵魂 12 问,总会用得到. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? In fact, the method is very simple. Users can directly enter the command prompt, and then press the ctrl shift enter key combination to perform the operation, or directly execute the reset command to set it up. Let this site do the following. Let us carefully introduce to users how to reset the TCP/IP protocol stack in Windows 10. Method 1 to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in Windows 10. Administrator permissions 1. We use the shortcut key win R to directly open the run window, then enter cmd and hold down the ctrl shift enter key combination. 2. Or we can directly search for command prompt in the start menu and right-click
 How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
TCP client A client sample code that uses the TCP protocol to achieve continuous dialogue: importsocket#Client configuration HOST='localhost'PORT=12345#Create a TCP socket and connect to the server client_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket .SOCK_STREAM)client_socket.connect((HOST,PORT))whileTrue:#Get user input message=input("Please enter the message to be sent:&
 See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
The "connection-oriented" mentioned here means that you need to establish a connection, use the connection, and release the connection. Establishing a connection refers to the well-known TCP three-way handshake. When using a connection, data is transmitted in the form of one send and one confirmation. There is also the release of the connection, which is our common TCP four wave waves.
 How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
Why is there this blog about using one TCP connection to send multiple files? I have been reading some related things recently. There is no problem in simply using Socket for programming, but this only establishes some basic concepts. Still nothing can be done about the real problem. When I need to transfer files, I find that I seem to have just sent the data (binary data), but some information about the file is lost (the file extension). And each time I can only use one Socket to send one file, there is no way to send files continuously (because I rely on closing the stream to complete sending files, which means that I actually don’t know the length of the file, so I can only send files as one Socket connection represents a file).
 Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
TCP is a type of computer network communication protocol and a connection-oriented transmission protocol. In Java application development, TCP communication is widely used in various scenarios, such as data transmission between client and server, real-time transmission of audio and video, etc. Netty4 is a high-performance, highly scalable, and high-performance network programming framework that can optimize the data exchange process between the server and the client to make it more efficient and reliable. The specific implementation steps of using Netty4 for TCP communication are as follows: Introduction
 Linux SIGPIPE signal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Linux SIGPIPE signal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Among the TCP communication parties, for the convenience of description, the communication parties are replaced by A and B in the following. According to the TCP protocol, if B continues to send data after A closes the connection, B will receive A's RST response. If B continues to send data, the system will send a SIGPIPE signal to inform that the connection has been disconnected and stop sending. The system's default processing behavior for the SIGPIPE signal is to let process B exit. The default processing behavior of the operating system for the SIGPIPE signal is very unfriendly. Let us analyze it. TCP communication is a full-duplex channel, which is equivalent to two simplex channels, and each end of the connection is responsible for one. When the opposite end "closes", although the intention is to close the entire two channels, the local end only receives the FIN packet. According to the provisions of the TCP protocol, when a
 How to configure TCP load balancing in Nginx
May 19, 2023 am 08:29 AM
How to configure TCP load balancing in Nginx
May 19, 2023 am 08:29 AM
Assuming that the Kubernetes cluster has been configured, we will create a virtual machine for Nginx based on CentOS. The following are the details of the settings in the experiment: Nginx (CenOS8Minimal)–192.168.1.50KubeMaster–192.168.1.40KubeWorker1–192.168.1.41KubeWorker2–192.168.1.42 Step 1) Install the epel repository because the nginx software package is not in the CentOS system default repository. So you need to install e
 What is the difference between tcp and ip
Sep 04, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
What is the difference between tcp and ip
Sep 04, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
TCP and IP are two different protocols in the Internet: 1. TCP is a transport layer protocol, while IP is a network layer protocol; 2. TCP provides functions such as segmentation, sorting, confirmation and retransmission of data packets. , and the IP protocol is responsible for providing source and destination addresses for data packets; 3. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, while the IP protocol is connectionless; 4. TCP also provides flow control and congestion control.





