Taking stock of the basics of strings in Python
Why do we need strings?
When calling a browser to log in to some websites, you need to enter a password. After the browser sends the password to the server, the server will verify the password. The verification process is to compare the previous The saved password is compared with the password passed this time. If they are equal, the password is considered correct, otherwise it is considered incorrect; since the server wants to store these passwords, it can use a database (such as MySQL) to achieve this.
Of course, for the sake of simplicity, we can first find a variable to store the password; so how to store passwords with letters? This is where strings are used.
1. The format of strings in Python
is defined as follows Variable a stores a value of numeric type.
a = 100
The variable b defined below stores a string type value.
b = "hello itcast.cn"
或者
b = 'hello itcast.cn'Small summary:
in double quotes or single quotes Data is the string
二、字符串输出
例:
name = 'ming'
position = '讲师'
address = '中山市平区建材城西路金燕龙办公楼1层'
print('--------------------------------------------------')
print("姓名:%s"%name)
print("职位:%s"%position)
print("公司地址:%s"%address)
print('--------------------------------------------------')结果:
--------------------------------------------------
姓名:ming
职位:讲师
公司地址:中山市昌平区建材城西路金燕龙办公楼1层
--------------------------------------------------三、字符串输入
input通过它能够完成从键盘获取数据,然后保存到指定的变量中;
注意:input获取的数据,都以字符串的方式进行保存,即使输入的是数字,那么也是以字符串方式保存。
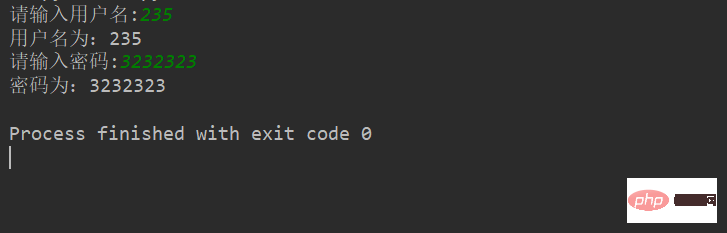
例:
userName = input('请输入用户名:')
print("用户名为:%s"%userName)
password = input('请输入密码:')
print("密码为:%s"%password)结果:(根据输入的不同结果也不同)
4. Subscripts and slicing
1. Subscript index
So-called"Subscript" is the number, just like the number of the storage cabinet in the supermarket. You can find the corresponding storage space through this number.
"Subscript" in life
Supermarket locker

The use of "subscript" in strings
#Lists and tuples support subscript indexing for easy understanding. Strings are actually arrays of characters. So subscript indexing is also supported.
If there is a string: name = 'abcdef', the actual storage in memory is as follows:
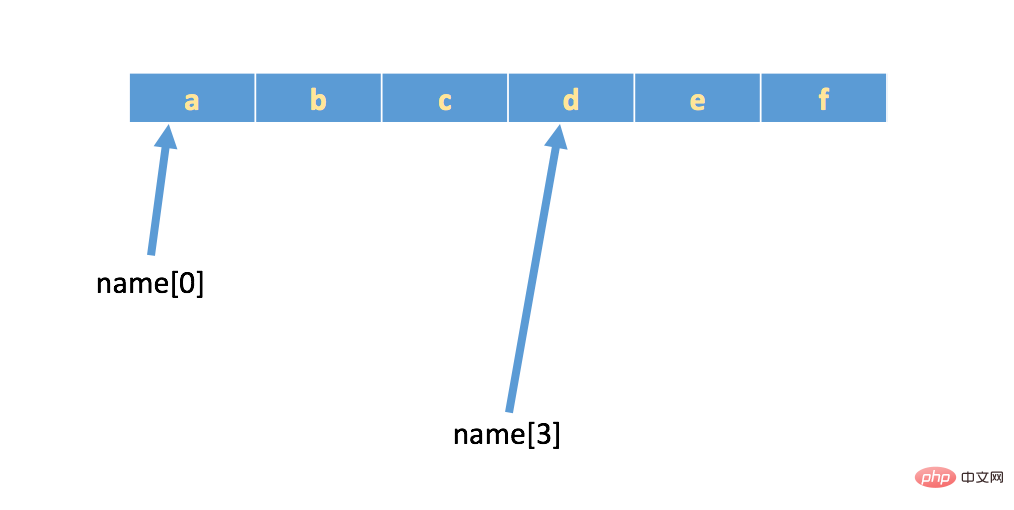
If you want to remove some characters, you can use to subscript Method, (note that subscripts in Python start from 0)
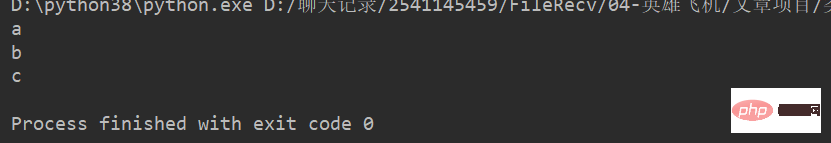
name = 'abcdef' print(name[0]) print(name[1]) print(name[2])
运行结果:
2. 切片的概念:
切片是指对操作的对象截取其中一部分的操作。字符串、列表、元组都支持切片操作。
3. 切片的语法:[起始:结束:步长]
注意:选取的区间属于左闭右开型,即从"起始"位开始,到"结束"位的前一位结束(不包含结束位本身)。
我们以字符串为例讲解。
如果取出一部分,则可以在中括号[]中,使用 :
例:
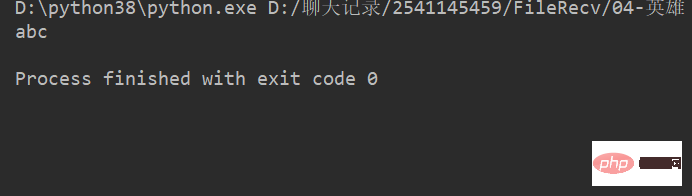
name = 'abcdef'
print(name[0:3]) # 取 下标0~2 的字符运行结果 :
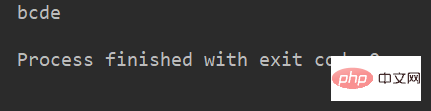
例:
name = 'abcdef'
print(name[0:5]) # 取 下标为0~4 的字符运行结果:
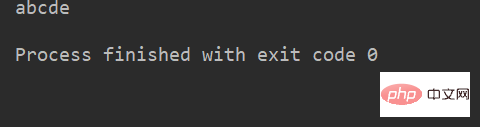
例:
name = 'abcdef'
print(name[3:5]) # 取 下标为3、4 的字符运行结果:
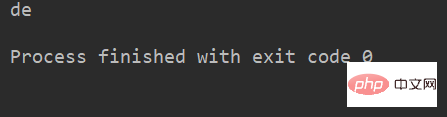
例:
name = 'abcdef'
print(name[2:]) # 取 下标为2开始到最后的字符运行结果:
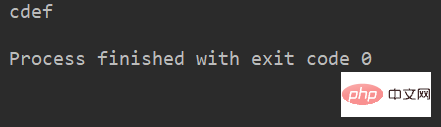
例:
name = 'abcdef'
print(name[1:-1]) # 取 下标为1开始 到 最后第2个 之间的字符运行结果:
>>> a = "abcdef" >>> a[:3] #运行结果 'abc' >>> a[::2] #运行结果 'ace' >>> a[5:1:2] '' #运行结果 >>> a[1:5:2] 'bd' #运行结果 >>> a[::-2] 'fdb' #运行结果 >>> a[5:1:-2] 'fd' #运行结果
五、字符串常见16种操作
以字符串'lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs',为例。
介绍字符常见的操作。
<1> find
检测 str 是否包含在 lstr中,如果是返回开始的索引值,否则返回-1。
语法:
lstr.find(str, start=0, end=len(lstr))
例:
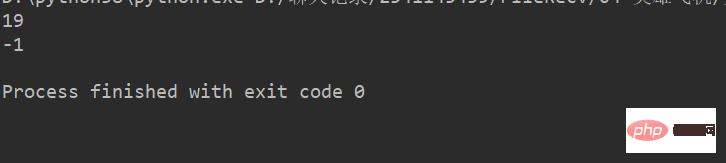
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs'
print(lstr.find("Museum"))
print(lstr.find("dada"))运行结果:
<2> index
跟find()方法一样,只不过如果str不在 lstr中会报一个异常。
语法:
lstr.index(str, start=0, end=len(lstr))
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs'
print(lstr.index("dada"))运行结果:

<3> count
返回 str在start和end之间 在 lstr里面出现的次数
语法:
lstr.count(str, start=0, end=len(lstr))
例:
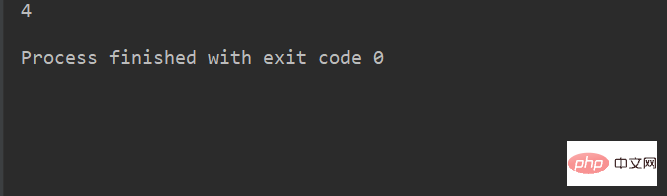
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs'
print(lstr.count("s"))运行结果:
<4> replace
把 lstr 中的 str1 替换成 str2,如果 count 指定,则替换不超过 count 次.
1str.replace(str1, str2, 1str.count(str1))
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs'
print(lstr.replace("s", "ttennd"))运行结果:

<5> split
以 str 为分隔符切片 lstr,如果 maxsplit有指定值,则仅分隔 maxsplit 个子字符串
1str.split(str=" ", 2)
例:
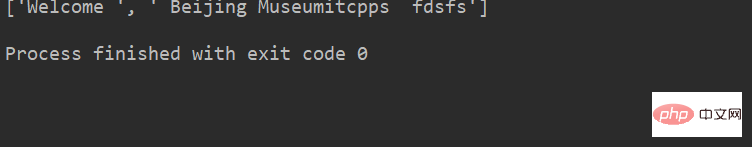
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs'
print(lstr.split("to", 5))运行结果:
<6> capitalize
把字符串的第一个字符大写。
1str.capitalize()
例:
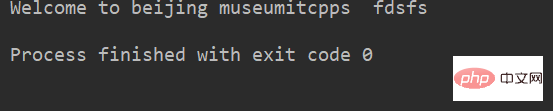
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.capitalize())
运行结果:
<7> title
把字符串的每个单词首字母大写。
>>> a = "hello itcast" >>> a.title() 'Hello Itcast' #运行结果
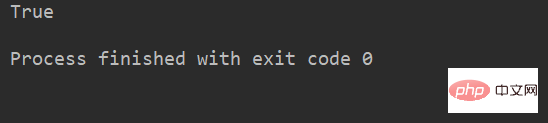
<8> startswith
检查字符串是否是以 obj 开头, 是则返回 True,否则返回 False
1str.startswith(obj)
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.startswith('we'))
运行结果:
<9> endswith
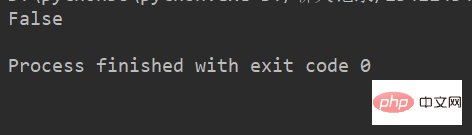
检查字符串是否以obj结束,如果是返回True,否则返回 False.
1str.endswith(obj)
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.endswith('hfs'))
运行结果:
<10> lower
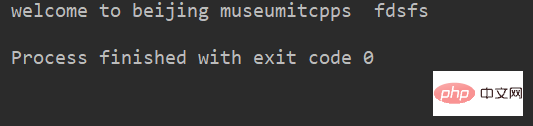
转换 lstr 中所有大写字符为小写
1str.lower()
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.lower())
运行结果:
<11> upper
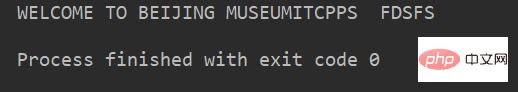
转换 lstr 中的小写字母为大写
1str.upper()
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.upper())
运行结果:
<12> strip
删除lstr字符串两端的空白字符。
>>> a = "\n\t itcast \t\n" >>> a.strip() 'itcast' #运行结果
<13> rfind
类似于 find()函数,不过是从右边开始查找。
1str.rfind(str, start=0,end=len(1str) )
例:
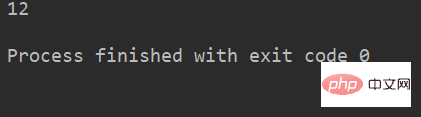
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.rfind('eijing'))
运行结果:
<14> rindex
类似于 index(),不过是从右边开始。
1str.rindex( str, start=0,end=len(1str))
例:
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.rindex('eijing'))
运行结果:

<15> partition
把lstr以str分割成三部分,str前,str和str后。
1str.partition(str)
例:
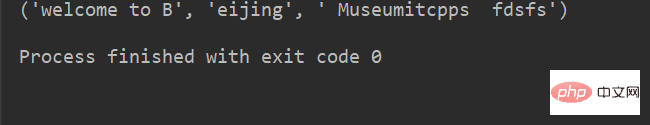
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' print(lstr.partition('eijing'))
运行结果:
<16> join
mystr 中每个字符后面插入str,构造出一个新的字符串。
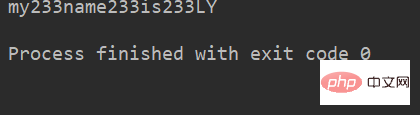
lstr = 'welcome to Beijing Museumitcpps fdsfs' str='233' lstr.join(str) li=["my","name","is","LY"] print(str.join(li))
运行结果:
六、总结
本文详细的讲解了Python基础 ( 字符串 )。介绍了有关字符串,切片的操作。下标索引。以及在实际操作中会遇到的问题,提供了解决方案。希望可以帮助你更好的学习Python。
The above is the detailed content of Taking stock of the basics of strings in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.






