Build scalable enterprise applications with Spring Boot
When developing enterprise-level applications, scalability is crucial. Enterprise-level applications need to be able to handle large amounts of business logic and data, and new functionality needs to be added continuously as needs change. Spring Boot is a popular Java framework that helps developers build scalable enterprise-level applications. This article will explore how to use Spring Boot to build scalable enterprise-level applications, including the following topics:
- Introduction to Spring Boot
- Best Practices for Building Scalable Enterprise-level Applications
- How to design and implement a scalable architecture
- How to manage and extend applications
- Introduction to Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a framework based on Spring Tools for rapid application development. It allows developers to use the core functionality of the Spring framework while simplifying application configuration and deployment. Spring Boot also provides many features, such as built-in web server, automatic configuration, Swagger UI support, etc., which can help developers build enterprise-level applications more efficiently.
- Best practices for building scalable enterprise applications
When building scalable enterprise applications, there are some best practices that need to be followed to ensure that the application can meet future needs. Here are some key best practices:
2.1 Layered Architecture
Layered architecture is a design pattern that splits an application into different layers. Each layer has specific responsibilities so that the application logic can be organized more clearly. Typically, enterprise-level applications include the following hierarchy:
- Presentation layer: Handles user interface-related operations, such as displaying web pages and responding to user requests.
- Business logic layer: handles business logic, such as verifying user identity, calculating the total order price, etc.
- Data access layer: Interact with the database or other data storage methods and perform various database operations.
The layered architecture helps to enhance the scalability of the application, because each layer can handle its tasks independently. When you need to expand a certain function, you only need to modify the corresponding layer. That’s it.
2.2 Use design patterns
Design patterns can help developers better organize code and improve code readability, maintainability and scalability. For example, the singleton pattern allows the use of unique instances to share resources, and the factory pattern can hide the registration code inside, making the application easier to maintain. Understanding and using various design patterns is key to developing scalable, enterprise-grade applications.
2.3 Using Dependency Injection
Using dependency injection can help developers manage dependencies between classes more flexibly. Spring Boot uses this pattern to manage dependencies and provide appropriate inversion of control. This means that an application can obtain the required dependencies from different services rather than instantiating those dependencies specifically. This makes it easier for developers to replace dependencies, making applications more flexible and scalable.
- How to design and implement a scalable architecture
Designing and implementing a scalable architecture requires considering the following factors:
3.1 Asynchronous programming
Asynchronous programming can improve application performance by allowing multiple requests to be processed simultaneously. For enterprise applications, it is common to use asynchronous event processing such as Java Message Service (JMS). JMS can handle requests without blocking threads, so it can handle large numbers of requests more efficiently.
3.2 Vertical expansion and horizontal expansion
Vertical expansion refers to increasing system resources, such as increasing the RAM, CPU, etc. of the server. As opposed to vertical scaling, horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to balance the load. Enterprise-grade applications need to be able to scale both vertically and horizontally to meet growing demand.
3.3 Database design
Properly designing the database structure is another key factor to ensure the scalability of the application. The data model must be able to handle all types of queries gracefully, including large numbers of records and high concurrent loads. Application availability and scalability can also be improved using techniques such as horizontal partitioning, redundancy, and backup.
- How to manage and scale the application
Once the application is built, it is also important to manage and scale it. Spring Boot provides a variety of methods to manage and extend applications, including:
4.1 Monitoring
Spring Boot provides a number of monitors and loggers that can assist in monitoring applications and provide Real-time feedback on performance and errors. Monitors can identify which parts need fixing or optimizing and issue alerts.
4.2 Deployment
Spring Boot can easily deploy applications to multiple environments, including local development, testing and production environments. Using the CI/CD process to automate build and deployment can improve deployment quality and stability.
4.3 Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures that the application is always in top condition and can adapt to new technologies and needs. During maintenance, various bugs and problems need to be fixed, and new functions and extensibility need to be added to adapt to changing needs.
Summarize
Building scalable enterprise-level applications using Spring Boot is a complex task that requires following best practices and good design habits. Developers need to use good architecture and design, adopt appropriate technology, and implement maintenance plans to ensure that applications can adapt to growing demands. At the same time, developers need to constantly learn new technologies and methods to stay competitive and continuously improve the scalability and usability of applications.
The above is the detailed content of Build scalable enterprise applications with Spring Boot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1658
1658
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1231
1231
 24
24
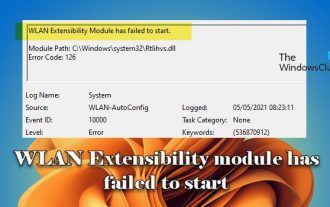 WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
WLAN extensibility module cannot start
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
This article details methods to resolve event ID10000, which indicates that the Wireless LAN expansion module cannot start. This error may appear in the event log of Windows 11/10 PC. The WLAN extensibility module is a component of Windows that allows independent hardware vendors (IHVs) and independent software vendors (ISVs) to provide users with customized wireless network features and functionality. It extends the capabilities of native Windows network components by adding Windows default functionality. The WLAN extensibility module is started as part of initialization when the operating system loads network components. If the Wireless LAN Expansion Module encounters a problem and cannot start, you may see an error message in the event viewer log.
 Optimizing PHP PDO queries: improving performance and scalability
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Optimizing PHP PDO queries: improving performance and scalability
Feb 20, 2024 am 09:30 AM
Using Prepared Statements Prepared statements in PDO allow the database to precompile queries and execute them multiple times without recompiling. This is essential to prevent SQL injection attacks, and it can also improve query performance by reducing compilation overhead on the database server. To use prepared statements, follow these steps: $stmt=$pdo->prepare("SELECT*FROMusersWHEREid=?");Bind ParametersBind parameters are a safe and efficient way to provide query parameters that can Prevent SQL injection attacks and improve performance. By binding parameters to placeholders, the database can optimize query execution plans and avoid performing string concatenation. To bind parameters, use the following syntax:
 Technical practice of Docker and Spring Boot: quickly build high-performance application services
Oct 21, 2023 am 08:18 AM
Technical practice of Docker and Spring Boot: quickly build high-performance application services
Oct 21, 2023 am 08:18 AM
Technical practice of Docker and SpringBoot: quickly build high-performance application services Introduction: In today's information age, the development and deployment of Internet applications have become increasingly important. With the rapid development of cloud computing and virtualization technology, Docker, as a lightweight container technology, has received widespread attention and application. SpringBoot has also been widely recognized as a framework for rapid development and deployment of Java applications. This article will explore how to combine Docker and SpringB
 Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
WebLogic and Tomcat are two commonly used Java application servers. They have some differences in scalability and functionality. This article will analyze the scalability of these two servers and compare the differences between them. First, let's take a look at WebLogic's scalability. WebLogic is a highly scalable Java application server developed by Oracle. It provides many advanced features, including transaction management, JDBC connection pooling, distributed caching, etc. WebLogic support
 How scalable and maintainable are Java functions in large applications?
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
How scalable and maintainable are Java functions in large applications?
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Java functions provide excellent scalability and maintainability in large applications due to the following features: Scalability: statelessness, elastic deployment and easy integration, allowing easy adjustment of capacity and scaling of deployment. Maintainability: Modularity, version control, and complete monitoring and logging simplify maintenance and updates. By using Java functions and serverless architecture, more efficient processing and simplified maintenance can be achieved in large applications.
 Build cloud-native applications from scratch using Docker and Spring Boot
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
Build cloud-native applications from scratch using Docker and Spring Boot
Oct 20, 2023 pm 02:16 PM
Build cloud-native applications from scratch using Docker and SpringBoot Summary: Cloud-native applications have become a trend in modern software development. By using container technology and microservice architecture, rapid deployment and scaling can be achieved, and the reliability and maintainability of applications can be improved. . This article will introduce how to use Docker and SpringBoot to build cloud native applications and provide specific code examples. 1. Background introduction Cloud native application (CloudNativeApplication) refers to
 How to evaluate the scalability of golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
How to evaluate the scalability of golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
The scalability of the Go framework allows it to be easily expanded as the application grows. Key features include a modular design that allows components to be easily added or replaced; concurrency support to maximize application throughput; and vertical and horizontal scalability to meet changing load demands. Using the Kratos framework as an example, developers can scale applications to meet high concurrency and performance needs by adding new modules, integrating new modules, and scaling to multiple servers.
 Integration practice of Docker and Spring Boot: optimizing development process and deployment efficiency
Oct 24, 2023 am 10:10 AM
Integration practice of Docker and Spring Boot: optimizing development process and deployment efficiency
Oct 24, 2023 am 10:10 AM
Integration practice of Docker and SpringBoot: optimizing development process and deployment efficiency With the rapid development of cloud computing technology, virtualization container technology Docker has become an important tool for development and deployment. In modern software development, building, packaging, and deploying applications quickly and efficiently is critical. Docker makes this process simple, reliable and repeatable. This article will introduce how to integrate Docker and SpringBoot to optimize the development process and deployment efficiency, and improve




