 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 How to use Redis cache elimination strategy and transactions to implement optimistic locking
How to use Redis cache elimination strategy and transactions to implement optimistic locking
How to use Redis cache elimination strategy and transactions to implement optimistic locking
Cache elimination strategy
Title LRU principle
LRU (Least recently used, least recently used) algorithm is based on the historical access records of the data To eliminate data, the core idea is "if the data has been accessed recently, the probability of being accessed in the future is also higher."
The most common implementation is to use a linked list to save cached data. The detailed algorithm is implemented as follows:
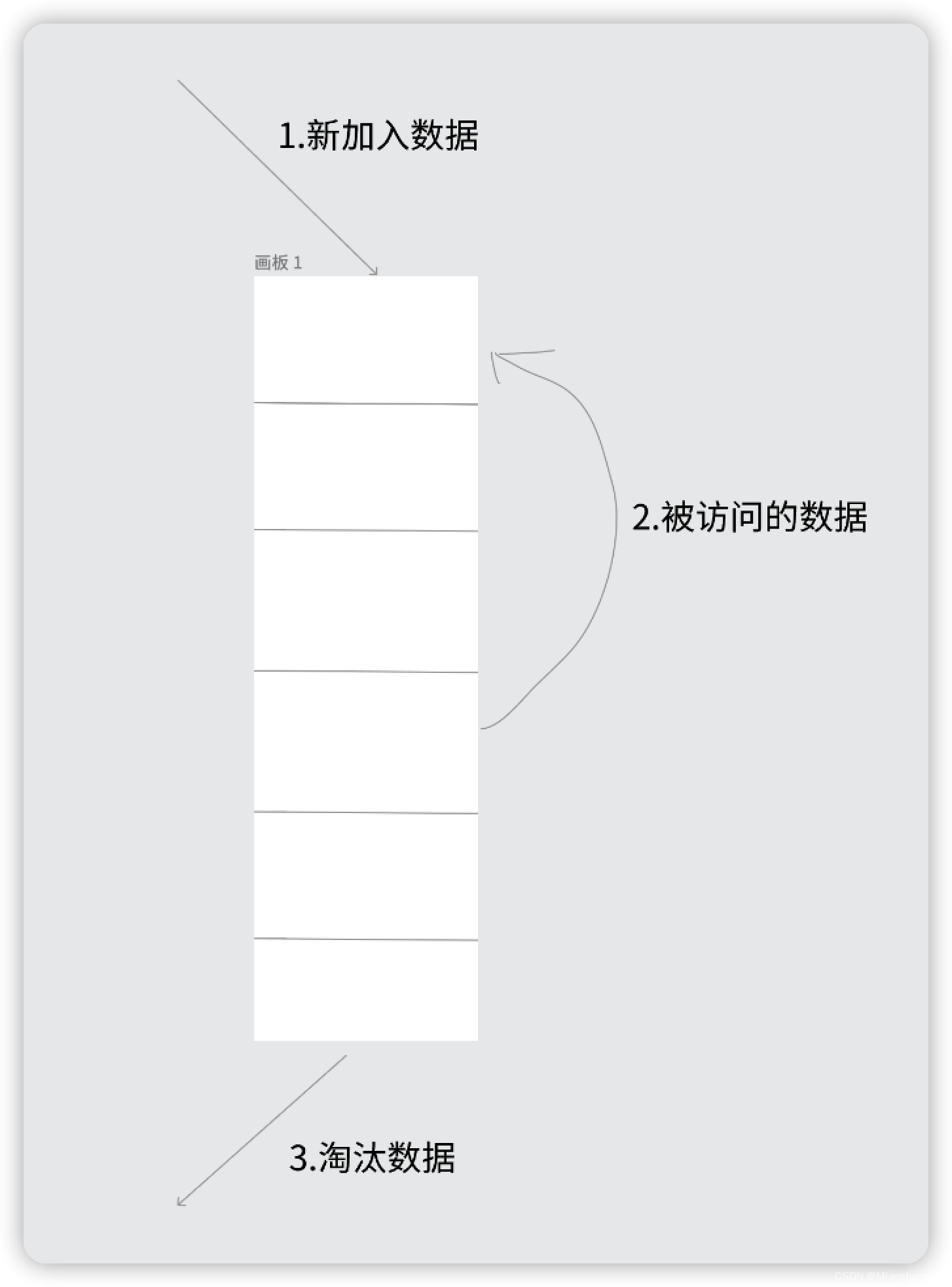
- ## New data is inserted into the head of the linked list;
- Whenever the cache hits (that is, the cached data is accessed), the data is moved to the head of the linked list;
- When the linked list is full, discard the data at the end of the linked list.
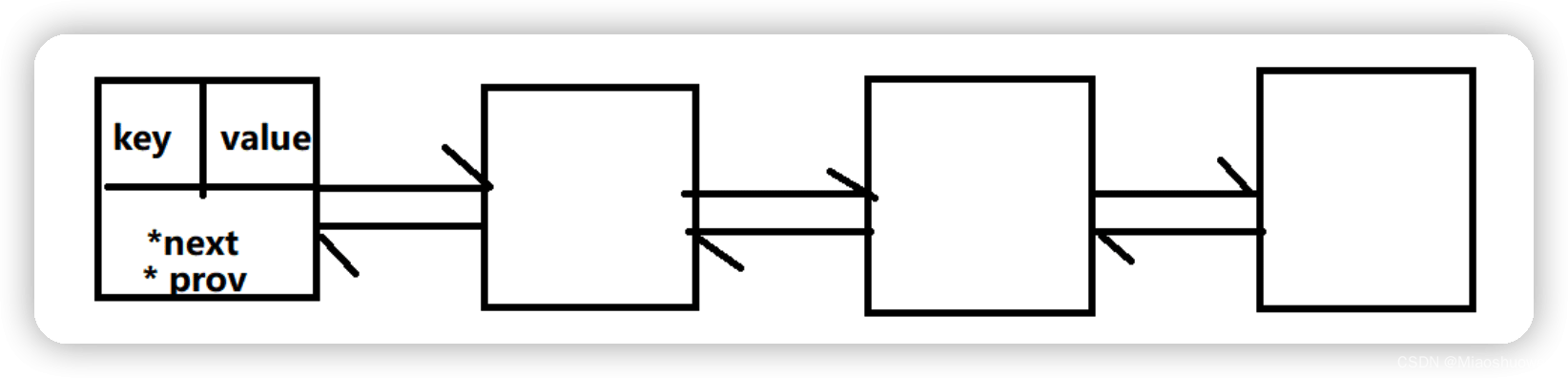
In Java, you can use LinkHashMap to implement LRU using hash linked list implementation:
In redis, users are allowed to set the maximum memory size maxmemory. The default is 0. The maximum cache is not specified. If new data is added, Exceeding the maximum memory will cause redis to crash, so it must be set.redis When the size of the memory data set increases to a certain size, the data elimination strategy will be implemented. Elimination strategy
redis elimination strategy configuration: maxmemory-policy voltile-lru, supports hot configuration
redis provides 6 types of data elimination Strategy:
volatile-lru: Select the least recently used data set (server.db[i].expires) with an expiration time set Data elimination
volatile-ttl:Select the data that will expire from the data set (server.db[i].expires) that has set the expiration time.
volatile-random: Randomly select data to eliminate from the data set (server.db[i].expires) that has set expiration time
allkeys-lru: Select the least recently used data from the data set (server.db[i].dict) to eliminate
-
allkeys-random: Randomly select data from the data set (server.db[i].dict) to eliminate
no-enviction (eviction): Prohibit eviction of data
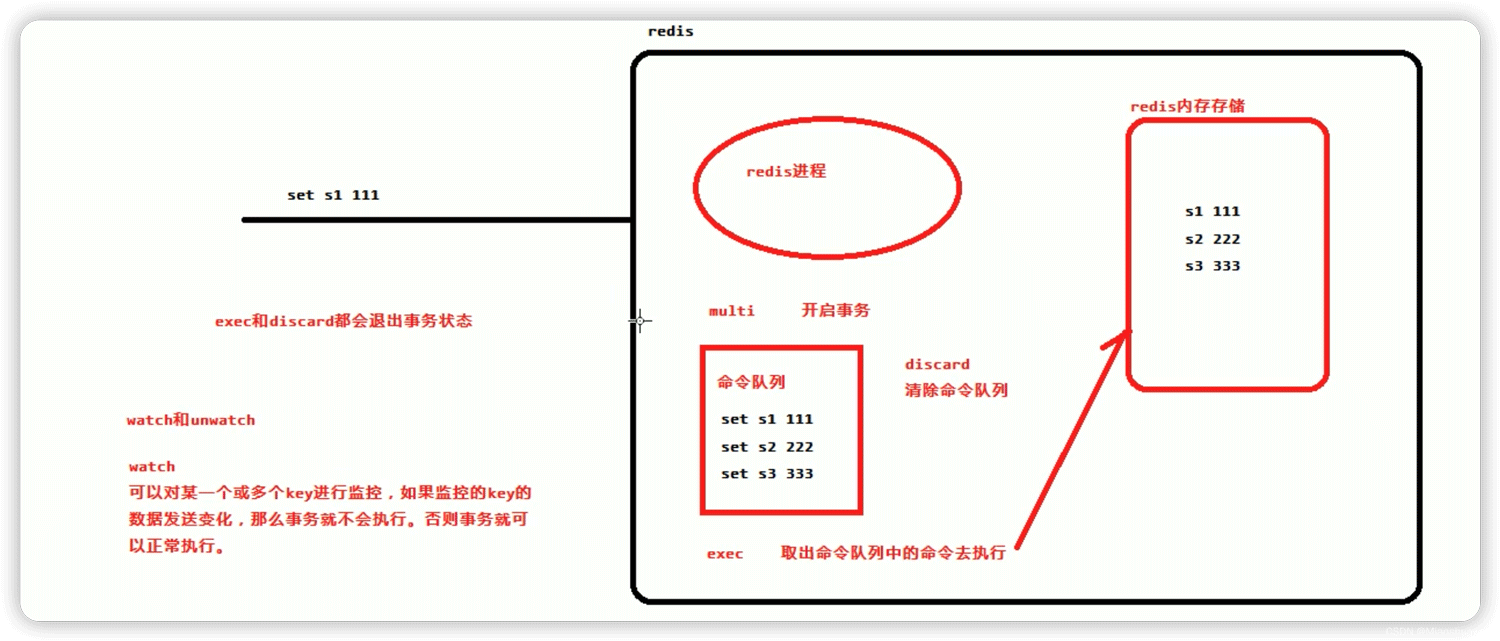
- Redis transaction is through MULTI, EXEC, DISCARD and WATCH, UNWATCH these five commands to complete.
- Redis’ individual commands are atomic, so you need to ensure that the transactional object is a command set.
- Redis serializes the command set and ensures the continuous and uninterrupted execution of the command set in the same transaction
- Redis does not support return Roll operation. The transaction command
Syntax:
multi
Syntax:
exec
Syntax:
discard
Syntax:
watch key [key…]
Notes: Use this command to implement Redis’s optimistic locking.
UNWATCHClear all keys previously monitored for a transactionSyntax:
unwatch
Command illustration:
Transaction demonstration:
127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set s1 111 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> hset set1 name zhangsan QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> exec 1) OK 2) (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set s2 222 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> hset set2 age 20 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> discard OK 127.0.0.1:6379> exec (error) ERR EXEC without MULTI 127.0.0.1:6379> watch s1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set s1 555 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379> exec # 此时在没有exec之前,通过另一个命令窗口对监控的s1字段进行修改 (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379> get s1 111
implement optimistic locking. The specific ideas are as follows:
- Use the watch function of redis to monitor the status value of this redisKey
- Get the value of redisKey
- Create redis transaction
- Give the value of this key 1
然后去执行这个事务,如果key的值被修改过则回滚,key不加1
public void watch() {
try {
String watchKeys = "watchKeys";
//初始值 value=1
jedis.set(watchKeys, 1);
//监听key为watchKeys的值
jedis.watch(watchkeys);
//开启事务
Transaction tx = jedis.multi();
//watchKeys自增加一
tx.incr(watchKeys);
//执行事务,如果其他线程对watchKeys中的value进行修改,则该事务将不会执行
//通过redis事务以及watch命令实现乐观锁
List<Object> exec = tx.exec();
if (exec == null) {
System.out.println("事务未执行");
} else {
System.out.println("事务成功执行,watchKeys的value成功修改");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jedis.close();
}
}Redis乐观锁实现秒杀
public class RedisLock {
public static void main(String[] arg) {
//库存key
String redisKey = "stock";
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
try {
Jedis jedis = new RedisProperties.Jedis("127.0.0.1", 6378);
// 可以被秒杀的库存的初始值,库存总共20个
jedis.set(redisKey, "0");
jedis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
Jedis jedis1 = new Jedis("127.0.0.1", 6378);
try {
jedis1.watch(redisKey);
String redisValue = jedis1.get(redisKey);
int valInteger = Integer.valueOf(redisValue);
String userInfo = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 没有秒完
if (valInteger < 20) {
Transaction tx = jedis1.multi();
tx.incr(redisKey);
List list = tx.exec();
// 秒成功 失败返回空list而不是空
if (list != null && list.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("用户:" + userInfo + ",秒杀成 功!当前成功人数:" + (valInteger + 1));
}
// 版本变化,被别人抢了。
else {
System.out.println("用户:" + userInfo + ",秒杀失 败");
}
}
// 秒完了
else {
System.out.println("已经有20人秒杀成功,秒杀结束");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jedis1.close();
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to use Redis cache elimination strategy and transactions to implement optimistic locking. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.





