How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
1. Customized RedisTemplate
1.1. Redis API default serialization mechanism
The API-based Redis cache implementation uses the RedisTemplate template for data caching operations. Open the RedisTemplate class here to view Source code information of this class
public class RedisTemplate<K, V> extends RedisAccessor implements RedisOperations<K, V>, BeanClassLoaderAware {
// 声明了key、value的各种序列化方式,初始值为空
@Nullable
private RedisSerializer keySerializer = null;
@Nullable
private RedisSerializer valueSerializer = null;
@Nullable
private RedisSerializer hashKeySerializer = null;
@Nullable
private RedisSerializer hashValueSerializer = null;
...
// 进行默认序列化方式设置,设置为JDK序列化方式
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
super.afterPropertiesSet();
boolean defaultUsed = false;
if (this.defaultSerializer == null) {
this.defaultSerializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(
this.classLoader != null ?
this.classLoader : this.getClass().getClassLoader());
}
...
}
...
}As can be seen from the above RedisTemplate core source code, various serialization methods for cached data key and value are declared inside RedisTemplate, and the initial values are empty; in the afterPropertiesSet() method , determine if the default serialization parameter defaultSerializer is empty, set the default serialization method of data to JdkSerializationRedisSerializer
According to the analysis of the above source code information, the following two important conclusions can be drawn:
(1) When using RedisTemplate for Redis data caching operations, the internal default serialization method is JdkSerializationRedisSerializer, so the entity class for data caching must implement the JDK's own serialization interface (such as Serializable);
( 2) When using RedisTemplate to perform Redis data caching operations, if the cache serialization method defaultSerializer is customized, the customized serialization method will be used.
In addition, in the RedisTemplate class source code, the various serialization types of cached data keys and values seen are RedisSerializer. Enter the RedisSerializer source code to view the serialization methods supported by RedisSerializer (after entering the class, use Ctrl Alt and left-click the class name to view)
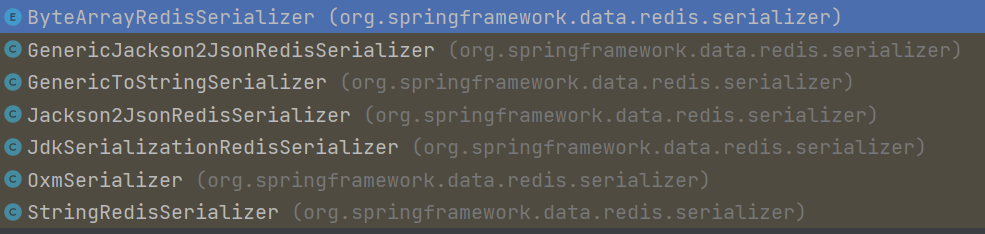
It can be seen that RedisSerializer is a Redis The serialization interface has 6 implementation classes by default. These 6 implementation classes represent 6 different data serialization methods. Among them, JdkSerializationRedisSerializer comes with JDK and is also the default data serialization method used within RedisTemplate. Developers can choose other supported serialization methods (such as JSON method) as needed.
1.2. Customized RedisTemplate serialization Mechanism
After introducing Redis dependency into the project, the RedisAutoConfiguration automatic configuration provided by Spring Boot will take effect. Open the RedisAutoConfiguration class and view the definition of RedisTemplate in the internal source code
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"redisTemplate"}
)
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
...
}As can be seen from the above RedisAutoConfiguration core source code, in the Redis automatic configuration class, a RedisTemplate is initialized through the Redis connection factory RedisConnectionFactory; above the class The @ConditionalOnMissingBean annotation (as the name suggests, takes effect when a Bean does not exist) is added to indicate that if the developer customizes a Bean named redisTemplate, the default initialized RedisTemplate will not take effect.
If you want to use RedisTemplate with a custom serialization method for data caching operations, you can refer to the above core code to create a Bean component named redisTemplate and set the corresponding serialization method in the component
Next, create a package named com.lagou.config in the project, create a Redis custom configuration class RedisConfig under the package, and customize the Bean component named redisTemplate according to the above ideas
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
// 自定义RedisTemplate
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 创建一个JSON格式序列化对象,对缓存数据的key和value进行转换
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 设置RedisTemplate模板api序列化方式为json
template.setDefaultSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
}defines a RedisConfig configuration class through the @Configuration annotation, and uses the @Bean annotation to inject a redisTemplate component with the default name of the method name (note that the Bean component name must be redisTemplate). In the defined Bean component, a RedisTemplate is customized, using the customized Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer data serialization method; in the customized serialization method, an ObjectMapper is defined for data conversion settings
1.3, effect testing
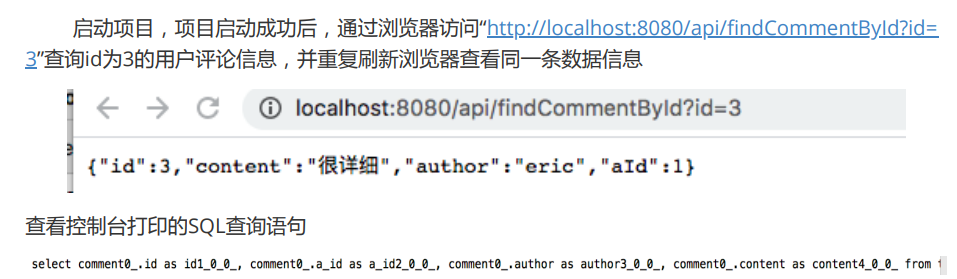
It can be seen that executing the findById() method correctly queries the user comment information Comment, and repeats the same query operation. The database only executes the SQL statement once, which shows that the customization The Redis cache takes effect.
Use the Redis client visual management tool Redis Desktop Manager to view the cached data:
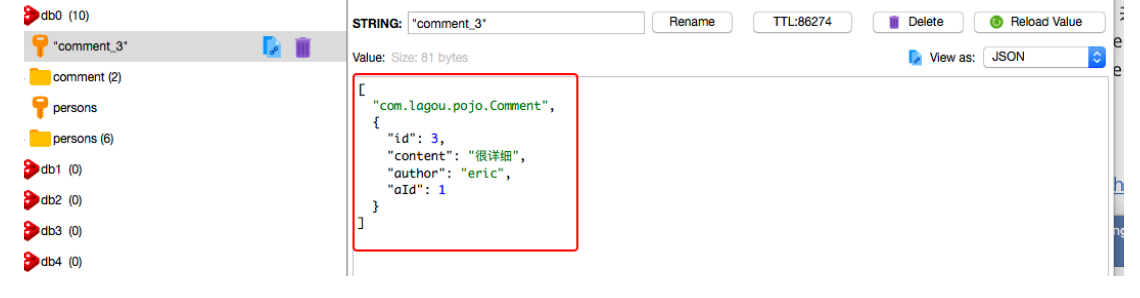
Execute the findById() method to query the user comment information and the Comment is correctly stored in Redis In the cache library, and the data cached to the Redis service has been stored and displayed in JSON format, it is also very convenient to view and manage, indicating that the customized Redis API template tool RedisTemplate takes effect
2. Customized RedisCacheManager
We have just improved the custom serialization method for the API-based RedisTemplate, thus realizing the JSON serialization method to cache data. However, this custom RedisTemplate has no effect on the annotation-based Redis cache. .
Next, we will explain the annotation-based Redis caching mechanism and custom serialization method
2.1. Redis annotation default serialization mechanism
Open Spring Boot to integrate Redis components The provided cache automatic configuration class RedisCacheConfiguration (under the org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache package), view the source code information of this class, its core code is as follows
@Configuration
class RedisCacheConfiguration {
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager
.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(this.determineConfiguration(resourceLoader.getClassLoader()));
List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
builder.initialCacheNames(new LinkedHashSet(cacheNames));
}
return (RedisCacheManager) this.customizerInvoker.customize(builder.build());
}
private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
determineConfiguration(ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (this.redisCacheConfiguration != null) {
return this.redisCacheConfiguration;
} else {
Redis redisProperties = this.cacheProperties.getRedis();
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
config = config.serializeValuesWith(SerializationPair.fromSerializer(
new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader)));
...
return config;
}
}
}从上述核心源码中可以看出,同RedisTemplate核心源码类似,RedisCacheConfiguration内部同样通过Redis连接工厂RedisConnectionFactory定义了一个缓存管理器RedisCacheManager;同时定制RedisCacheManager时,也默认使用了JdkSerializationRedisSerializer序列化方式。
如果想要使用自定义序列化方式的RedisCacheManager进行数据缓存操作,可以参考上述核心代码创建一个名为cacheManager的Bean组件,并在该组件中设置对应的序列化方式即可
在Spring Boot 2.X版本中,RedisCacheManager是独立构建的。因此,在SpringBoot 2.X版本中,对RedisTemplate进行自定义序列化机制构建后,仍然无法对RedisCacheManager内部默认序列化机制进行覆盖(这也就解释了基 于注解的Redis缓存实现仍然会使用JDK默认序列化机制的原因),想要基于注解的Redis缓存实现也使用自定义序列化机制,需要自定义RedisCacheManager
2.2、自定义RedisCacheManager
在项目的Redis配置类RedisConfig中,按照上一步分析的定制方法自定义名为cacheManager的Bean组件
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 分别创建String和JSON格式序列化对象,对缓存数据key和value进行转换
RedisSerializer<String> strSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jacksonSerial = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
// om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY); // 上面注释过时代码的替代方法
jacksonSerial.setObjectMapper(om);
// 定制缓存数据序列化方式及时效
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1)) // 设置缓存数据的时效(设置为了1天)
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(strSerializer)) // 对当前对象的key使用strSerializer这个序列化对象,进行转换
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(jacksonSerial)) // 对value使用jacksonSerial这个序列化对象,进行转换
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager
.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(config).build();
return cacheManager;
}上述代码中,在RedisConfig配置类中使用@Bean注解注入了一个默认名称为方法名的cacheManager组件。在定义的Bean组件中,通过RedisCacheConfiguration对缓存数据的key和value分别进行了序列化方式的定制,其中缓存数据的key定制为StringRedisSerializer(即String格式),而value定制为了Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(即JSON格式),同时还使用entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1))方法将缓存数据有效期设置为1天
完成基于注解的Redis缓存管理器RedisCacheManager定制后,可以对该缓存管理器的效果进行测试(使用自定义序列化机制的RedisCacheManager测试时,实体类可以不用实现序列化接口)
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.






