Python Redis data processing methods
1. Preface
Redis: Remote Dictionary Server, that is: remote dictionary service. The bottom layer of Redis is written in C language. It is an open source, memory-based NoSql database
Because of Redis The performance far exceeds that of other databases, and it supports advantages such as clustering, distribution, and master-slave synchronization, so it is often used in scenarios such as caching data, high-speed reading and writing
2. Preparation
We will use the cloud Server Centos 7.8 Installing Redis-Server as an example
First, install the Redis database on the cloud server
# 下载epel仓库 yum install epel-release # 安装redis yum install redis
Then, modify the Redis configuration file through the vim command, open the remote connection, and set the connection password
Configuration file directory:/etc/redis.conf
bind is changed to 0.0.0.0, allowing external network access
- ##requirepass Set an access password
# vim /etc/redis.conf # 1、bing从127.0.0.1修改为:0.0.0.0,开放远程连接 bind 0.0.0.0 # 2、设置密码 requirepass 123456
# 启动Redis服务,默认redis端口号是6379 systemctl start redis # 打开防火墙 systemctl start firewalld.service # 开放6379端口 firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6379/tcp --permanent # 配置立即生效 firewall-cmd --reload
# 安装依赖,便于操作redis pip3 install redis
from redis import Redis
class RedisF(object):
def __init__(self):
# 实例化Redis对象
# decode_responses=True,如果不加则写入的为字节类型
# host:远程连接地址
# port:Redis端口号
# password:Redis授权密码
self.redis_obj = Redis(host='139.199.**.**',port=6379,password='123456',decode_responses=True,charset='UTF-8', encoding='UTF-8')- name: key, represents the key
- value: value, the value to be saved
- ex: expiration time, in seconds, if not set, then it will never expire; otherwise, it will be deleted if it expires
- px: expiration time, in milliseconds
- nx/xx: whether the set operation is The execution is related to whether the name key exists.
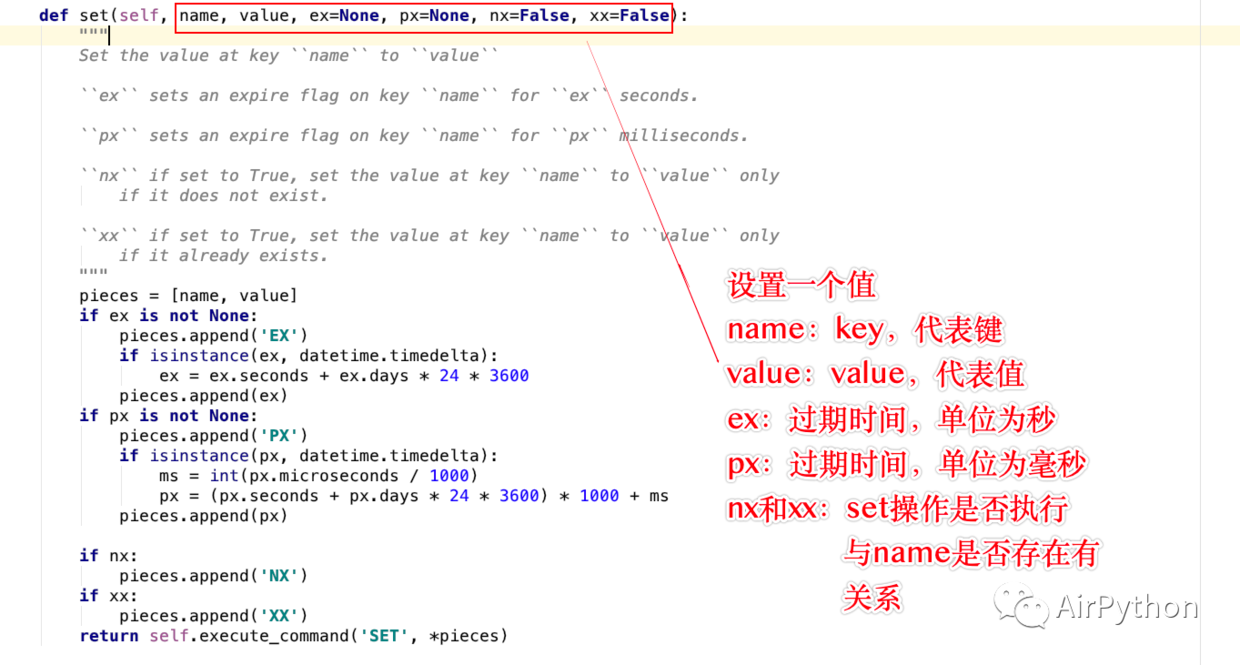
# set():单字符串操作 # 添加一个值,并设置超时时间为120s self.redis_obj.set('name', 'airpython', ex=120) # get():获取这个值 print(self.redis_obj.get('name')) # delete():删除一个值或多个值 self.redis_obj.delete('name') print(self.redis_obj.get('name'))
# mset():设置多个值
self.redis_obj.mset({"foo": "foo1", "zoo": "zoo1"})
# mget():获取多个值
result = self.redis_obj.mget("foo", "zoo")
print(result)- lpush/rpush: Insert one or more values into the head or tail of the list, where lpush represents the head insertion; rpush represents the tail insertion of data
- lset: Insert the value into the corresponding position in the list through the index
- linsert: Insert data before or after the list element ##lindex : Get an element in the list through index, where 0 represents the first element; -1 represents the last element
- #lrange: By specifying the starting position and ending position, from Get the value of the specified area in the list
- llen: Get the length of the list. If the list corresponding to the Key does not exist, return 0
- lpop: Remove and return the first element in the list
- rpop: Remove and return the last element in the list
- The example code is as follows :
def manage_list(self):
"""
操作列表
:return:
"""
# 1、新增一个列表,并左边插入一个数据
# 注意:可以一次加入多个元素,也可以一个个元素的加入
self.redis_obj.lpush('company', '阿里', '腾讯', '百度')
# 2、移除第一个元素
self.redis_obj.lpop("company")
# 3、右边插入数据
self.redis_obj.rpush('company', '字节跳动', '小米')
# 4、移除最后一个元素
self.redis_obj.rpop("company")
# 5、获取列表的长度
self.redis_obj.llen("company")
# 6、通过索引,获取列表中的某一个元素(第二个元素)
print('列表中第二个元素是:', self.redis_obj.lindex("company", 1))
# 7、根据范围,查看列表中所有的值
print(self.redis_obj.lrange('company', 0, -1))3. Operating Set collection
Set is an unordered collection of elements. The elements in the collection cannot be repeated. Redis also provides many methods to facilitate the operation of Set collection
Among them, the more commonly used methods are as follows:
- sadd: Add elements to the collection. Elements that already exist in the collection will be ignored. If the collection does not exist, create a new collection
- scard: Returns the number of elements in the collection
- smembers: Returns all elements in the collection
- ##srem : Remove one or more elements from the set, ignore if the element does not exist
- sinter: Return the intersection of two sets, the result is still a set
- sunion: Returns the union of two sets
- sdiff: Using the first set parameter as the standard, returns the difference of the two sets
- sunionstore: Calculate the union of two sets and save it to a new set
- sismember: Determine whether an element exists in the set
- spop: Randomly delete an element in the set and return
- The specific example code is as follows:
def manage_set(self):
"""
操作set集合
:return:
"""
self.redis_obj.delete("fruit")
# 1、sadd:新增元素到集合中
# 添加一个元素:香蕉
self.redis_obj.sadd('fruit', '香蕉')
# 再添加两个元素
self.redis_obj.sadd('fruit', '苹果', '桔子')
# 2、集合元素的数量
print('集合元素数量:', self.redis_obj.scard('fruit'))
# 3、移除一个元素
self.redis_obj.srem("fruit", "桔子")
# 再定义一个集合
self.redis_obj.sadd("fruit_other", "香蕉", "葡萄", "柚子")
# 4、获取两个集合的交集
result = self.redis_obj.sinter("fruit", "fruit_other")
print(type(result))
print('交集为:', result)
# 5、获取两个集合的并集
result = self.redis_obj.sunion("fruit", "fruit_other")
print(type(result))
print('并集为:', result)
# 6、差集,以第一个集合为标准
result = self.redis_obj.sdiff("fruit", "fruit_other")
print(type(result))
print('差集为:', result)
# 7、合并保存到新的集合中
self.redis_obj.sunionstore("fruit_new", "fruit", "fruit_other")
print('新的集合为:', self.redis_obj.smembers('fruit_new'))
# 8、判断元素是否存在集合中
result = self.redis_obj.sismember("fruit", "苹果")
print('苹果是否存在于集合中', result)
# 9、随机从集合中删除一个元素,然后返回
result = self.redis_obj.spop("fruit")
print('删除的元素是:', result)
# 3、集合中所有元素
result = self.redis_obj.smembers('fruit')
print("最后fruit集合包含的元素是:", result)其中,比较常用的方法如下:
zadd:往集合中新增元素,如果集合不存在,则新建一个集合,然后再插入数据
zrange:通过起始点和结束点,返回集合中的元素值(不包含分数);如果设置withscores=True,则返回结果会带上分数
zscore:获取某一个元素对应的分数
zcard:获取集合中元素个数
zrank:获取元素在集合中的索引
zrem:删除集合中的元素
zcount:通过最小值和最大值,判断分数在这个范围内的元素个数
实践代码如下:
def manage_zset(self):
"""
操作zset集合
:return:
"""
self.redis_obj.delete("fruit")
# 往集合中新增元素:zadd()
# 三个元素分别是:"banana", 1/"apple", 2/"pear", 3
self.redis_obj.zadd("fruit", "banana", 1, "apple", 2, "pear", 3)
# 查看集合中所有元素(不带分数)
result = self.redis_obj.zrange("fruit", 0, -1)
# ['banana', 'apple', 'pear']
print('集合中的元素(不带分数)有:', result)
# 查看集合中所有元素(带分数)
result = self.redis_obj.zrange("fruit", 0, -1, withscores=True)
# [('banana', 1.0), ('apple', 2.0), ('pear', 3.0)]
print('集合中的元素(带分数)有:', result)
# 获取集合中某一个元素的分数
result = self.redis_obj.zscore("fruit", "apple")
print("apple对应的分数为:", result)
# 通过最小值和最大值,判断分数在这个范围内的元素个数
result = self.redis_obj.zcount("fruit", 1, 2)
print("集合中分数大于1,小于2的元素个数有:", result)
# 获取集合中元素个数
count = self.redis_obj.zcard("fruit")
print('集合元素格式:', count)
# 获取元素的值获取索引号
index = self.redis_obj.zrank("fruit", "apple")
print('apple元素的索引为:', index)
# 删除集合中的元素:zrem
self.redis_obj.zrem("fruit", "apple")
print('删除apple元素后,剩余元素为:', self.redis_obj.zrange("fruit", 0, -1))4、操作哈希
哈希表中包含很多键值对,并且每一个键都是唯一的
Redis 操作哈希表,下面这些方法比较常用:
hset:往哈希表中添加一个键值对值
hmset:往哈希表中添加多个键值对值
hget:获取哈希表中单个键的值
hmget:获取哈希表中多个键的值列表
hgetall:获取哈希表中种所有的键值对
hkeys:获取哈希表中所有的键列表
hvals:获取哈表表中所有的值列表
hexists:判断哈希表中,某个键是否存在
hdel:删除哈希表中某一个键值对
hlen:返回哈希表中键值对个数
对应的操作代码如下:
def manage_hash(self):
"""
操作哈希表
哈希:一个键对应一个值,并且键不容许重复
:return:
"""
self.redis_obj.delete("website")
# 1、新建一个key为website的哈希表
# 往里面加入数据:baidu(field),www.baidu.com(value)
self.redis_obj.hset('website', 'baidu', 'www.alibababaidu.com')
self.redis_obj.hset('website', 'google', 'www.google.com')
# 2、往哈希表中添加多个键值对
self.redis_obj.hmset("website", {"tencent": "www.qq.com", "alibaba": "www.taobao.com"})
# 3、获取某一个键的值
result = self.redis_obj.hget("website", 'baidu')
print("键为baidu的值为:", result)
# 4、获取多个键的值
result = self.redis_obj.hmget("website", "baidu", "alibaba")
print("多个键的值为:", result)
# 5、查看hash表中的所有值
result = self.redis_obj.hgetall('website')
print("哈希表中所有的键值对为:", result)
# 6、哈希表中所有键列表
# ['baidu', 'google', 'tencent', 'alibaba']
result = self.redis_obj.hkeys("website")
print("哈希表,所有的键(列表)为:", result)
# 7、哈希表中所有的值列表
# ['www.alibababaidu.com', 'www.google.com', 'www.qq.com', 'www.taobao.com']
result = self.redis_obj.hvals("website")
print("哈希表,所有的值(列表)为:", result)
# 8、判断某一个键是否存在
result = self.redis_obj.hexists("website", "alibaba")
print('alibaba这个键是否存在:', result)
# 9、删除某一个键值对
self.redis_obj.hdel("website", 'baidu')
print('删除baidu键值对后,哈希表的数据包含:', self.redis_obj.hgetall('website'))
# 10、哈希表中键值对个数
count = self.redis_obj.hlen("website")
print('哈希表键值对一共有:', count)5、操作事务管道
Redis 支持事务管道操作,能够将几个操作统一提交执行
操作步骤是:
首先,定义一个事务管道
然后通过事务对象去执行一系列操作
提交事务操作,结束事务操作
下面通过一个简单的例子来说明:
def manage_steps(self):
"""
执行事务操作
:return:
"""
# 1、定义一个事务管道
self.pip = self.redis_obj.pipeline()
# 定义一系列操作
self.pip.set('age', 18)
# 增加一岁
self.pip.incr('age')
# 减少一岁
self.pip.decr('age')
# 执行上面定义3个步骤的事务操作
self.pip.execute()
# 判断
print('通过上面一些列操作,年龄变成:', self.redis_obj.get('age'))The above is the detailed content of Python Redis data processing methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang and Python each have their own advantages: Golang is suitable for high performance and concurrent programming, while Python is suitable for data science and web development. Golang is known for its concurrency model and efficient performance, while Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.






