Redis data structure type example code analysis
intset
When the set collection stores integers, the encoding is intset type (small integer collection)
typedef struct intset {
int32 encoding;
int32 length;
int contents[];
}| Description | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Determines whether the integer bit width is 16 bits, 32 bits or 64 bits | Enumeration representation | |
| Number of elements | ||
| Integer array, storing element values |
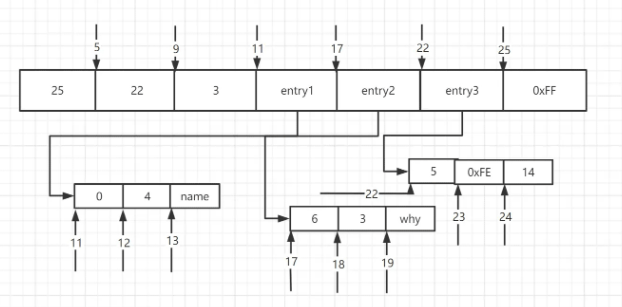
ziplist
If the following conditions are met in the configuration file, the encoding type of hash and zset will be ziplist (compressed list).
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 # 当hash元素个数小于512时 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 # 当hash键或值长度小于64时 zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 # 当zset元素个数小于128时 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 # 当zset值小于64时
typedef struct ziplist {
int32 zlbytes;
int32 zltail_offset;
int16 zllength;
T[] entries;
int8 zlend;
}
typedef struct entry {
int<var> prevlen;
int<var> encoding;
byte[] content;
}| Description | zlbytes | |
|---|---|---|
##zltail_offset | ||
| Used to quickly locate the last node, and then traverse in reverse order | zllength | |
entries | ||
| ##zlend | Marks the end of the compressed list ||
| prevlen | The byte length of the previous entry | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| encoding | Encoding type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| content | element content, optional | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 字段 | 描述 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
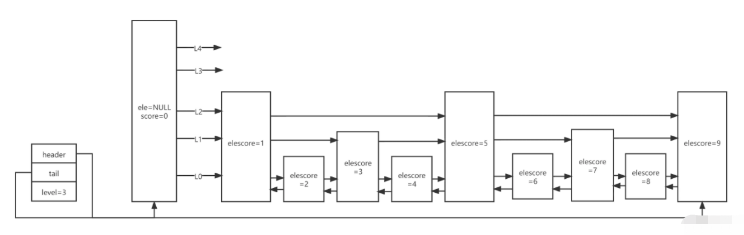
| header | 指向跳跃列表的头指针 | value固定为NULL,score固定为0,backward为null |
| tail | 指向跳跃列表的尾指针 | |
| maxLevel | 当前跳跃表最大层数 | 最大为64 |
| value | 用于存储字符串类型的数据 | |
| score | 用于存储分值 | |
| backward | 回退节点 | 图中的←箭头 |
| forwards | 前进节点 | 图中的→箭头,每一层对应一个 |
| span | 跨度,存储一个节点跳到下一个节点中间跳过了多少节点 | 如score1指向score5,则span值为4,这是排名的实现原理 |
最小分值的backward固定null,对于每一个新插入的节点,会调用一个随机算法,来给它分配一个合理的层数
level1的概率为1-0.25=0.75,实际为100%,因为跳跃列表的最小层数为1
level2的概率为0.75*0.25=0.1875level3的概率为0.1875*0.25=0.0468 ......
leveln的概率为(1-0.25)*Math.pow(0.25,n-1)
总结
Redis作为单线程内存服务,在响应、数据结构上作出了很多的优化,值得我们学习
| 对象类型 | 编码类型 |
|---|---|
| string | int、raw、embstr |
| list | quicklist |
| hash | dict、ziplist |
| set | intset、dict |
| zset | ziplist、skiplist+dict |
HyperLogLog
HyperLogLog的原理为伯努利试验,即丢硬币,根据连续出现反面的次数X,推算出一共丢了2的X次方次硬币,当X很大时,推算出来的总数与实际总数误差就很接近了。具体可查询其他文章。
pfadd
element经过hash算法之后是一个64位的固定值
低14位为桶
查找高50位第一个为1的位数,如果大于当前桶的位数,就将其设置为当前桶的位数
假设hash值是 :{此处省略45位}01100 00000000000101
低14位的二进制转为10进制,值为5(regnum),即我们把数据放在第5个桶
高50位第一个1的位置是3,即count值为3
registers[5]取出历史值oldcount
如果count > oldcount,则更新 registers[5] = count
如果count <= oldcount,则不做任何处理
HyperLogLog用了16384个桶,每个桶占用6bit,因此说一个HyperLogLog所占用内存是12K。
调和平均数:
假设我的工资为10_000,马云的工资为1_000_000,那我和马云的平均工资为505_000,我肯定是不认同的。。。
如果使用调和平均数,则为2/(1/10_000+1/1_000_000)=19_801
同理,桶位数的平均数为:n/(1/桶1位数+1/桶2位数+...+1/桶n位数)
桶的平均个数为:Math.pow(2,桶位数的平均数)
总数量:const*桶总数n*桶的平均个数,其中constant为不定值,与桶个数有关,假设m为桶个数,取对数
pfcount
p=log2m
switch (p) {
case 4:
constant = 0.673 * m * m;
case 5:
constant = 0.697 * m * m;
case 6:
constant = 0.709 * m * m;
default:
constant = (0.7213 / (1 + 1.079 / m)) * m * m;
}The above is the detailed content of Redis data structure type example code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.